Utma Accounts Are Opened Under The Tax Id Of The
Holbox
Mar 17, 2025 · 5 min read
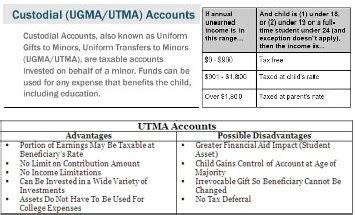
Table of Contents
UTMA Accounts: Opened Under the Tax ID of the Custodian
Understanding Uniform Transfers to Minors Act (UTMA) accounts is crucial for anyone looking to manage assets for a minor. One of the key aspects to grasp is the tax implications, specifically regarding which tax ID number is used to report income generated within the account. This article will delve deep into the intricacies of UTMA accounts and the tax ID associated with them.
What is a UTMA Account?
A UTMA account, previously known as a Uniform Gifts to Minors Act (UGMA) account, is a custodial account established for the benefit of a minor. It allows an adult, the custodian, to manage assets on behalf of a minor, the beneficiary. These assets can include a wide range of investments, from stocks and bonds to mutual funds and even real estate (though less common).
The key difference between a UTMA and a UGMA account lies in the types of assets that can be held. UTMA accounts can hold a broader range of assets compared to UGMA accounts. However, for tax purposes, the operational differences are minimal, and the same tax ID rules apply.
Key Features of a UTMA Account:
- Ownership: While the custodian manages the account, legal ownership rests with the minor.
- Control: The custodian has complete control over the assets until the minor reaches the age of majority (typically 18 or 21, depending on state laws).
- Flexibility: UTMA accounts offer flexibility in managing assets for the minor's future.
- Tax Implications: Income generated within the account is taxed at the minor's tax rate, which can be advantageous depending on the minor's income bracket.
The Tax ID: It's All About the Custodian
This is the crucial point: UTMA accounts are opened and reported under the custodian's Social Security number (SSN). The minor does not have a tax ID specifically associated with the account. All income generated by the assets within the UTMA account, including dividends, interest, and capital gains, is reported on the custodian's tax return using their SSN.
This means the custodian is responsible for filing the appropriate tax forms, paying any applicable taxes, and keeping accurate records of all transactions within the UTMA account. The custodian's tax liability is limited to the taxes owed on the income generated within the account; they are not responsible for the assets themselves.
Why the Custodian's SSN?
Using the custodian's SSN for tax reporting streamlines the process significantly. Minors, by definition, do not typically have their own income tax filing requirements or a separate tax ID. Attributing the income to the custodian simplifies reporting and ensures that taxes are accurately assessed and paid.
The IRS utilizes the custodian's tax ID to track and manage the tax implications associated with the assets held in the UTMA account. This simplifies tax administration and reduces potential errors or omissions.
Tax Implications for UTMA Accounts
The income generated within the UTMA account is taxed at the minor's tax rate, not the custodian's. This is a crucial distinction. While the custodian reports the income on their tax return using their SSN, the tax liability is that of the minor. This can be advantageous if the minor's tax bracket is lower than the custodian's.
However, it's important to note that Kiddie Tax rules may apply. These rules prevent high-income minors from benefiting from lower tax rates. The Kiddie Tax applies if the minor's unearned income exceeds a certain threshold. If this threshold is surpassed, a portion of the unearned income is taxed at the parent's or custodian's higher tax rate.
Common Income Sources in UTMA Accounts and their Tax Treatment:
- Dividends: Dividends received from stocks are considered unearned income and are taxed at the minor's rate (potentially subject to Kiddie Tax rules).
- Interest: Interest earned on savings accounts or bonds is also unearned income, taxable at the minor's rate (potentially subject to Kiddie Tax rules).
- Capital Gains: Profits from the sale of assets are considered capital gains. These are taxed at the minor's rate, subject to the applicable capital gains tax rates for their age and income bracket. Long-term capital gains rates generally are lower than ordinary income rates.
Record Keeping: Essential for Tax Compliance
Accurate record-keeping is paramount when it comes to UTMA accounts and tax compliance. The custodian is legally responsible for maintaining detailed records of all transactions, including:
- Date of transactions: Each deposit, withdrawal, and investment activity should be meticulously documented.
- Description of transactions: Clearly indicate the type of transaction (e.g., purchase of stock, sale of bond, dividend received).
- Amounts involved: Record the exact monetary values for all transactions.
- Supporting documentation: Keep copies of brokerage statements, tax documents (1099s, etc.), and any other relevant documentation to support the transactions.
These records not only aid in accurate tax filing but also provide essential information for future financial planning for the minor.
Choosing the Right Custodian: Considerations Beyond Tax Implications
While tax implications are crucial, selecting the right custodian involves broader considerations:
- Financial Expertise: Does the custodian possess the necessary knowledge and experience to manage the assets effectively?
- Trustworthiness: Is the custodian a trustworthy individual who will act in the best interests of the minor?
- Relationship with the Minor: Is the custodian someone who can build a positive relationship with the minor as they grow older and eventually assume control of the assets?
Transferring Ownership Upon Reaching the Age of Majority
Upon the minor reaching the age of majority, the assets are legally transferred to them. The custodian's role concludes, and the minor assumes full responsibility for managing their assets.
Conclusion: Understanding UTMA Accounts for Effective Financial Planning
Understanding the tax implications of UTMA accounts, specifically the use of the custodian's SSN for tax reporting, is critical for responsible financial planning for minors. Careful consideration of tax rates, potential Kiddie Tax implications, and diligent record-keeping are essential to ensure compliance and maximize the benefits of these accounts. Remember, choosing the right custodian is as important as understanding the tax ramifications. By diligently addressing these aspects, you can contribute effectively to a minor's financial future. This information serves as a general overview, and seeking professional financial and tax advice is always recommended to tailor strategies to individual circumstances.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Goal Displacement Satisficing And Groupthink Are
Mar 17, 2025
-
Where Should Glassware Be Stored After It Is Cleaned
Mar 17, 2025
-
A Favorable Labor Rate Variance Indicates That
Mar 17, 2025
-
Split The Worksheet Into Panes At Cell D16
Mar 17, 2025
-
A Winning Strategy Is One That
Mar 17, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Utma Accounts Are Opened Under The Tax Id Of The . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
