Use The Words To Fill-in The Sentences Describing Anatomical Position.
Holbox
Mar 18, 2025 · 6 min read
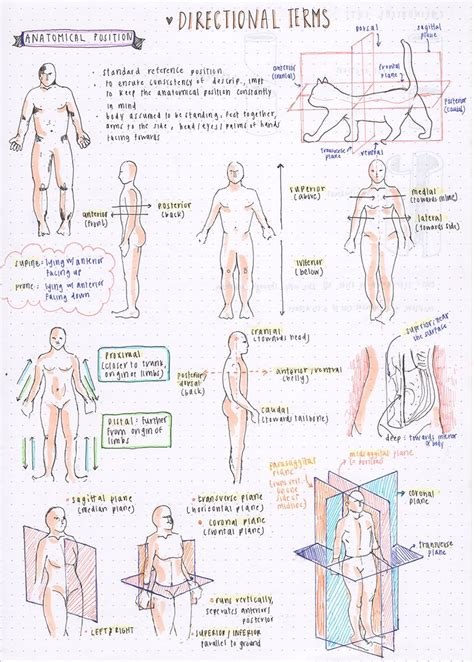
Table of Contents
Anatomical Position: A Comprehensive Guide with Interactive Exercises
Understanding anatomical position is fundamental to studying human anatomy and physiology. It provides a standardized reference point for describing the location of body structures and movements. This comprehensive guide will delve into the specifics of anatomical position, offering clear explanations and interactive exercises to solidify your understanding. We'll explore the key terms, directional terminology, and the importance of this foundational concept in medical fields and beyond.
Defining Anatomical Position: The Universal Standard
The anatomical position is a standardized reference posture used to describe the location of body parts and their relationships to each other. It is essential because it allows healthcare professionals and anatomists to communicate clearly and unambiguously about the human body, regardless of the patient's or cadaver's actual position.
Key Characteristics of Anatomical Position:
- Standing erect: The body is upright, facing directly forward.
- Feet slightly apart: The feet are positioned parallel to each other, with a slight distance between them.
- Arms at the sides: The arms hang naturally at the sides of the body.
- Palms facing forward: The palms of the hands are directed anteriorly (forward).
- Head facing forward: The head is held upright, with the eyes looking directly forward.
This seemingly simple posture is the cornerstone of precise anatomical description. Without a standardized position, describing a body part's location would be highly subjective and prone to misinterpretation.
Directional Terminology: Navigating the Body's Landscape
Understanding directional terminology is crucial for effectively utilizing and applying anatomical position. These terms precisely describe the location of structures relative to each other. Let's explore some common directional terms:
1. Superior (Cranial): Towards the head or upper part of the body. For example, the head is superior to the chest.
2. Inferior (Caudal): Towards the feet or lower part of the body. The knees are inferior to the hips.
3. Anterior (Ventral): Towards the front of the body. The sternum is anterior to the heart.
4. Posterior (Dorsal): Towards the back of the body. The spine is posterior to the heart.
5. Medial: Towards the midline of the body. The nose is medial to the ears.
6. Lateral: Away from the midline of the body. The ears are lateral to the nose.
7. Proximal: Closer to the point of attachment or origin. The elbow is proximal to the wrist. (Primarily used for limbs)
8. Distal: Farther from the point of attachment or origin. The fingers are distal to the elbow. (Primarily used for limbs)
9. Superficial: Closer to the surface of the body. The skin is superficial to the muscles.
10. Deep: Farther from the surface of the body. The bones are deep to the muscles.
Body Planes and Sections: Visualizing Internal Structures
To further understand the three-dimensional structure of the body, we utilize various planes and sections. These imaginary planes slice through the body, providing different perspectives of internal organs and structures.
1. Sagittal Plane: A vertical plane that divides the body into left and right portions. A midsagittal plane divides the body into equal left and right halves.
2. Frontal (Coronal) Plane: A vertical plane that divides the body into anterior (front) and posterior (back) portions.
3. Transverse (Horizontal) Plane: A horizontal plane that divides the body into superior (upper) and inferior (lower) portions.
Interactive Exercises: Putting Knowledge into Practice
Now, let's test your understanding with some interactive exercises. Imagine a person in anatomical position. Fill in the blanks with the appropriate directional terms:
Exercise 1:
- The _____ is superior to the abdomen. (Answer: thorax/chest)
- The _____ is inferior to the neck. (Answer: shoulders/clavicles)
- The heart is _____ to the sternum. (Answer: posterior)
- The ears are _____ to the eyes. (Answer: lateral)
- The nose is _____ to the ears. (Answer: medial)
- The skin is _____ to the muscles. (Answer: superficial)
- The bones are _____ to the skin. (Answer: deep)
- The elbow is _____ to the wrist. (Answer: proximal)
- The fingers are _____ to the elbow. (Answer: distal)
- The umbilicus (belly button) is _____ to the spine. (Answer: anterior)
Exercise 2: Plane Identification
- A plane that divides the body into equal left and right halves is a ______ plane. (Answer: midsagittal)
- A plane that divides the body into anterior and posterior sections is a ______ plane. (Answer: frontal/coronal)
- A plane that divides the body into superior and inferior sections is a ______ plane. (Answer: transverse/horizontal)
Exercise 3: Sentence Completion
Complete the following sentences using appropriate anatomical directional terms:
- The kidneys are located ______ to the liver. (Answer: posterior)
- The toes are ______ to the ankles. (Answer: distal)
- The lungs are ______ to the heart. (Answer: lateral)
- The ribs are ______ to the lungs. (Answer: superficial)
- The brain is ______ to the spinal cord. (Answer: superior)
The Importance of Anatomical Position in Various Fields
The understanding and application of anatomical position are not confined to the classroom or laboratory. It holds immense significance across various professional fields:
-
Medicine: Doctors, nurses, and other healthcare professionals rely heavily on anatomical position for accurate diagnosis, treatment planning, and communication. Describing the location of injuries, tumors, or other abnormalities requires precise and unambiguous language, which is rooted in anatomical position.
-
Surgery: Surgeons utilize anatomical position as a reference point during surgical procedures. Precise incisions and manipulations are guided by an understanding of the body's spatial organization.
-
Physical Therapy: Physical therapists use anatomical position to assess posture, identify movement limitations, and develop targeted rehabilitation programs.
-
Radiology: Radiological images (X-rays, CT scans, MRIs) are interpreted in relation to anatomical position. Understanding this reference point is vital for accurate diagnosis.
-
Sports Medicine: Sports medicine professionals use anatomical position to analyze athletic performance, identify potential injury risks, and design effective training regimens.
Beyond the Basics: Regional Anatomy and Beyond
While understanding basic anatomical position and directional terms is foundational, a comprehensive study of anatomy delves into regional anatomy, examining specific body regions in detail. This involves studying the relationships between different structures within those regions, building upon the fundamental knowledge provided by anatomical position.
For example, understanding the anatomical position allows one to precisely describe the location of the brachial plexus (a network of nerves in the arm) relative to the clavicle and scapula. Similarly, the location of abdominal organs can be described with precision relative to the umbilicus and other anatomical landmarks.
Conclusion: Mastering Anatomical Position for Success
Mastering anatomical position is paramount for anyone studying or working within the fields of healthcare, sports science, and related disciplines. It provides a universal language for describing the human body, ensuring clear and effective communication. This article has provided a comprehensive introduction, incorporating interactive exercises to reinforce understanding. Remember, consistent practice and application are key to developing a solid grasp of this fundamental concept. Through continuous learning and application, you can build a strong foundation for success in your chosen field.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Risk Management Is Important To Healthcare Facilities In Order To
Mar 18, 2025
-
The Idea Of Facility Layout Is To
Mar 18, 2025
-
Microbial Hyaluronidase Coagulase And Streptokinase Are Examples Of
Mar 18, 2025
-
What Is Unique About The Highlighted Veins
Mar 18, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Is Mismatched
Mar 18, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Use The Words To Fill-in The Sentences Describing Anatomical Position. . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
