The Idea Of Facility Layout Is To
Holbox
Mar 18, 2025 · 7 min read
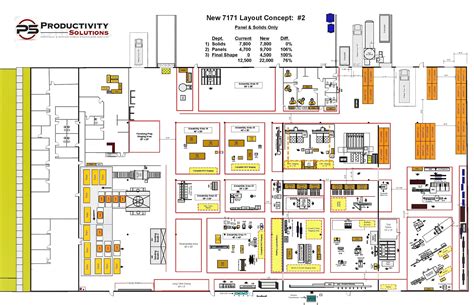
Table of Contents
- The Idea Of Facility Layout Is To
- Table of Contents
- The Idea of Facility Layout: Optimizing Space, Flow, and Efficiency
- Understanding the Core Principles of Facility Layout
- 1. Material Handling:
- 2. Workflow Optimization:
- 3. Space Utilization:
- 4. Flexibility and Scalability:
- 5. Safety and Ergonomics:
- Different Types of Facility Layouts
- 1. Product Layout (Line Flow):
- 2. Process Layout (Functional Layout):
- 3. Fixed-Position Layout:
- 4. Cellular Layout (Group Technology):
- 5. Combined Layout:
- Factors to Consider When Designing a Facility Layout
- 1. Product or Service Characteristics:
- 2. Production Volume and Variety:
- 3. Space Constraints:
- 4. Technology and Equipment:
- 5. Material Handling Systems:
- 6. Environmental Factors:
- 7. Budgetary Constraints:
- Implementing and Evaluating Facility Layout
- 1. Data Collection and Analysis:
- 2. Layout Design and Planning:
- 3. Simulation and Modeling:
- 4. Implementation and Transition:
- 5. Evaluation and Improvement:
- Advanced Concepts in Facility Layout
- 1. Computer-Aided Facility Design (CAFD):
- 2. Simulation and Modeling Techniques:
- 3. Lean Manufacturing Principles:
- 4. Ergonomic Design:
- Conclusion: The Ongoing Evolution of Facility Layout
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
The Idea of Facility Layout: Optimizing Space, Flow, and Efficiency
The idea behind facility layout is simple yet profound: to arrange the physical elements within a facility to optimize workflow, minimize costs, and maximize efficiency. It's more than just arranging desks or machines; it's a strategic process that impacts everything from productivity and employee satisfaction to customer experience and profitability. A well-designed facility layout can significantly reduce wasted time and resources, improve safety, and enhance the overall operational effectiveness of any organization. This comprehensive guide delves into the core principles of facility layout, exploring various approaches, considerations, and best practices to help you design a layout that meets your specific needs.
Understanding the Core Principles of Facility Layout
Effective facility layout is grounded in several key principles:
1. Material Handling:
This is a cornerstone of facility layout. The goal is to minimize the distance and effort required to move materials, products, or information throughout the facility. Efficient material handling reduces bottlenecks, lowers transportation costs, and improves overall throughput. Analyzing material flow is crucial in determining the best placement of workstations, equipment, and storage areas. Consider factors like the weight, volume, and fragility of materials when planning your layout.
2. Workflow Optimization:
Analyzing the sequence of operations and the flow of materials is essential for streamlining processes. The layout should facilitate a smooth and logical flow of work, minimizing backtracking and unnecessary movement. This involves understanding the relationships between different departments, workstations, and processes to create a cohesive and efficient system.
3. Space Utilization:
Maximizing space utilization is crucial, especially in expensive real estate markets. The layout should efficiently utilize available space, minimizing wasted areas and ensuring that all areas serve a productive purpose. This includes considering storage solutions, aisle widths, and the overall arrangement of equipment and workstations. Efficient space planning leads to reduced operational costs and improved profitability.
4. Flexibility and Scalability:
A well-designed facility layout anticipates future growth and changes. It should be adaptable to accommodate changes in production volume, technology, or product lines. A flexible layout allows for easier expansion, reconfiguration, and adaptation to evolving business needs. This ensures that the layout remains efficient and effective even as the organization grows and changes.
5. Safety and Ergonomics:
Safety and employee well-being are paramount. The layout should prioritize safety by minimizing hazards, providing ample space for movement, and ensuring easy access to emergency exits. Ergonomic considerations should also be incorporated to minimize strain and fatigue, resulting in improved employee health and productivity. Proper lighting, ventilation, and comfortable workstations contribute to a safer and healthier work environment.
Different Types of Facility Layouts
There are several types of facility layouts, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. The best choice depends on the specific needs and characteristics of the organization.
1. Product Layout (Line Flow):
This layout arranges workstations in a sequence corresponding to the steps in the production process. It's ideal for high-volume, standardized production, such as assembly lines. The advantages include high efficiency, low unit costs, and simplified material handling. However, it lacks flexibility and can be vulnerable to disruptions.
2. Process Layout (Functional Layout):
This layout groups similar machines or equipment together based on their function. It's suitable for low-volume, customized production, where a variety of products are manufactured. The advantage is flexibility, allowing for handling a range of products. However, material handling can be complex and inefficient, potentially leading to increased lead times.
3. Fixed-Position Layout:
This layout keeps the product stationary while workers and equipment move around it. It's used for large, immobile products such as ships or buildings. It's effective for projects where the product is too large or complex to move. However, coordination and material handling can be challenging.
4. Cellular Layout (Group Technology):
This layout groups machines or equipment into cells based on product families. It combines the advantages of both product and process layouts, providing a balance between efficiency and flexibility. It's ideal for medium-volume production with a moderate variety of products. Careful planning is required to form efficient and balanced cells.
5. Combined Layout:
Many facilities use a combination of layout types to optimize different aspects of their operations. For instance, a manufacturing facility might use a product layout for high-volume production and a process layout for specialized components. This hybrid approach provides flexibility and efficiency depending on the specific production requirements.
Factors to Consider When Designing a Facility Layout
Several critical factors influence the design of an effective facility layout:
1. Product or Service Characteristics:
The nature of the products or services offered significantly impacts the layout. High-volume, standardized products require a different layout than low-volume, customized products. Consider factors like product size, weight, and fragility, as well as the complexity of the production process.
2. Production Volume and Variety:
High-volume production generally calls for a product layout, while low-volume, high-variety production benefits from a process layout. Understanding the production volume and the variety of products or services is crucial for selecting the appropriate layout type.
3. Space Constraints:
The available space and its configuration influence the layout design. Existing building structures, available land, and other spatial limitations must be considered. This often involves optimizing the use of vertical space and maximizing floor area utilization.
4. Technology and Equipment:
The types of equipment used and their space requirements play a significant role in layout design. Consider the size, weight, and power requirements of machines, as well as the need for specialized utilities and infrastructure.
5. Material Handling Systems:
The choice of material handling systems, such as conveyors, forklifts, or automated guided vehicles (AGVs), impacts the layout. The layout must accommodate the chosen system and ensure efficient movement of materials.
6. Environmental Factors:
Environmental considerations, such as lighting, ventilation, temperature control, and noise levels, affect employee comfort and productivity. The layout should incorporate features that contribute to a safe and pleasant work environment.
7. Budgetary Constraints:
The cost of implementing the layout, including equipment purchases, construction, and relocation, must be carefully considered. A detailed cost analysis is essential to ensure that the chosen layout is both effective and affordable.
Implementing and Evaluating Facility Layout
Implementing a new or revised facility layout is a complex process requiring careful planning and execution.
1. Data Collection and Analysis:
Gather comprehensive data on production processes, material flow, equipment requirements, and space constraints. Analyze this data to identify bottlenecks, inefficiencies, and areas for improvement.
2. Layout Design and Planning:
Develop several potential layout options using different layout techniques and software tools. Evaluate these options based on criteria such as cost, efficiency, and flexibility.
3. Simulation and Modeling:
Use simulation software to model the chosen layout and test its performance under different scenarios. This helps identify potential problems and refine the design before implementation.
4. Implementation and Transition:
Implement the chosen layout in stages to minimize disruption to ongoing operations. Provide adequate training to employees on the new layout and procedures.
5. Evaluation and Improvement:
Continuously monitor the performance of the layout after implementation and identify areas for improvement. Regular evaluation and adjustment ensure that the layout remains effective and efficient over time.
Advanced Concepts in Facility Layout
Beyond the basic principles and layout types, several advanced concepts enhance facility layout optimization:
1. Computer-Aided Facility Design (CAFD):
CAFD software enables the creation and analysis of multiple layout alternatives, optimizing space utilization and material flow. These tools allow for dynamic adjustments and "what-if" scenarios, supporting data-driven decision-making.
2. Simulation and Modeling Techniques:
Sophisticated simulation models predict the performance of different layouts under various conditions, identifying bottlenecks and optimizing resource allocation. Discrete event simulation and agent-based modeling are powerful techniques used in this context.
3. Lean Manufacturing Principles:
Integrating lean principles into facility layout eliminates waste, streamlines processes, and improves efficiency. This involves minimizing unnecessary movement, reducing inventory, and improving workflow.
4. Ergonomic Design:
Prioritizing ergonomics ensures a comfortable and safe work environment, boosting employee productivity and morale. This involves considering workstation design, lighting, ventilation, and the reduction of repetitive strain injuries.
Conclusion: The Ongoing Evolution of Facility Layout
The idea of facility layout is not a static concept; it's a dynamic and evolving process. As businesses adapt to changing market conditions, technological advancements, and evolving customer needs, facility layouts must adapt as well. By integrating advanced technologies, lean principles, and a focus on continuous improvement, organizations can create facility layouts that are not only efficient and effective but also adaptable to future challenges. A well-designed layout is a strategic investment that significantly impacts operational efficiency, profitability, and long-term success. The continuous refinement and optimization of facility layout are essential components of sustainable and thriving businesses.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about The Idea Of Facility Layout Is To . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.