U Varies Directly With P And Inversely With D
Holbox
Mar 18, 2025 · 6 min read
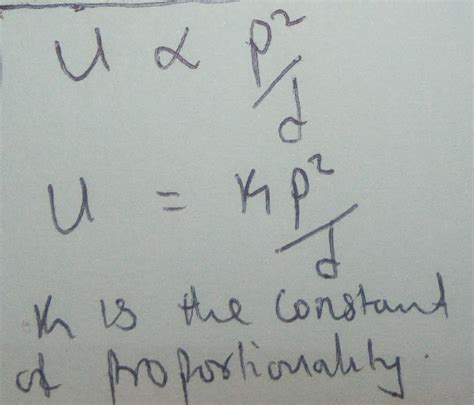
Table of Contents
U Varies Directly with P and Inversely with D: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding the relationship between variables is fundamental in many fields, from physics and engineering to economics and social sciences. This article delves deep into the concept of a variable u varying directly with p and inversely with d, exploring its mathematical representation, real-world applications, and problem-solving techniques. We'll cover everything from the basic formula to advanced applications and troubleshooting common misconceptions.
Understanding Direct and Inverse Proportionality
Before diving into the specifics of u varying directly with p and inversely with d, let's solidify our understanding of direct and inverse proportionality.
Direct Proportionality
Two variables are directly proportional if an increase in one variable leads to a proportional increase in the other, and a decrease in one leads to a proportional decrease in the other. This relationship can be represented mathematically as:
y = kx
where:
- y and x are the two variables
- k is the constant of proportionality. This constant represents the rate of change between the two variables.
For example, if you're buying apples at a fixed price per apple, the total cost (y) is directly proportional to the number of apples (x). The more apples you buy, the higher the total cost.
Inverse Proportionality
In contrast to direct proportionality, two variables are inversely proportional if an increase in one variable leads to a proportional decrease in the other, and vice-versa. This relationship is expressed mathematically as:
y = k/x
where:
- y and x are the two variables
- k is the constant of proportionality.
A classic example of inverse proportionality is the relationship between speed and travel time. If you increase your speed, your travel time decreases, and vice-versa, assuming the distance remains constant.
Combining Direct and Inverse Proportionality: The Case of u, p, and d
Now, let's tackle the core concept: u varies directly with p and inversely with d. This means u increases proportionally with p and decreases proportionally with d. The mathematical representation of this combined relationship is:
u = k * (p/d)
where:
- u, p, and d are the variables.
- k is the constant of proportionality. This constant is crucial as it determines the specific relationship between the variables. Without knowing 'k', we can only understand the type of relationship, not the precise values.
This formula encapsulates both direct and inverse proportionality. The direct proportionality is evident in the numerator (k*p) – as p increases, u increases proportionally. The inverse proportionality is present in the denominator (d) – as d increases, u decreases proportionally.
Real-World Applications
This type of relationship appears in numerous real-world scenarios. Let's explore a few:
1. Pressure, Volume, and Temperature of a Gas (Ideal Gas Law – Simplified)
While the ideal gas law (PV = nRT) is more complex, a simplified version can illustrate this principle. Imagine a scenario where the amount of gas (n) and the gas constant (R) are constant. In this case, pressure (P) can be seen as directly proportional to temperature (T) and inversely proportional to volume (V). If you increase the temperature, the pressure increases (direct proportionality), while if you increase the volume, the pressure decreases (inverse proportionality).
2. Gravitational Force
Newton's Law of Universal Gravitation states that the gravitational force (F) between two objects is directly proportional to the product of their masses (m1 and m2) and inversely proportional to the square of the distance (r) between their centers:
F = G * (m1 * m2) / r²
Here, G is the gravitational constant. This formula clearly demonstrates both direct and inverse proportionality.
3. Intensity of Light
The intensity (I) of light from a point source is inversely proportional to the square of the distance (d) from the source:
I = k/d²
This is an example of pure inverse proportionality, where 'k' is a constant related to the light source's power. As you move further from the light source, the intensity decreases rapidly.
4. Production Rate
Imagine a factory producing widgets. The production rate (u) might be directly proportional to the number of workers (p) and inversely proportional to the number of machine breakdowns (d). More workers lead to higher production, while more breakdowns decrease production.
Solving Problems Involving u = k * (p/d)
Let's illustrate how to solve problems involving this relationship with a few examples. Remember, the key is to find the constant of proportionality (k) using the given information.
Example 1:
Suppose u varies directly with p and inversely with d. When p = 6 and d = 2, u = 9. Find u when p = 10 and d = 5.
-
Find k: Substitute the initial values into the formula: 9 = k * (6/2). Solving for k, we get k = 3.
-
Use k to find u: Now, substitute k = 3, p = 10, and d = 5 into the formula: u = 3 * (10/5) = 6.
Therefore, when p = 10 and d = 5, u = 6.
Example 2:
A variable u is directly proportional to p and inversely proportional to the square of d. When p = 4 and d = 2, u = 1. Find the value of u when p = 16 and d = 4.
The formula in this case is: u = k * (p/d²)
-
Find k: 1 = k * (4/2²) => k = 1
-
Find u: u = 1 * (16/4²) = 1
Therefore, u = 1 when p = 16 and d = 4.
Advanced Applications and Considerations
The principle of u varying directly with p and inversely with d forms the basis for more complex models. Understanding the underlying relationship between variables allows for predictions and analysis of various systems.
Dealing with Multiple Inverse or Direct Proportions
You can extend this concept to situations involving multiple direct or inverse proportions. For instance, a variable might vary directly with p and q but inversely with r and s, leading to formulas like:
u = k * (p * q) / (r * s)
The approach remains the same: find the constant of proportionality (k) using initial conditions and then use it to solve for u in other scenarios.
Limitations and Assumptions
It's crucial to recognize that these models often rely on simplifying assumptions. Real-world relationships are rarely perfectly direct or inverse. Factors not explicitly included in the model might affect the outcomes. Therefore, it's essential to understand the limitations and context of any model.
For instance, in the example of the factory production rate, factors like worker efficiency, machine quality, and material availability are omitted. A more realistic model would incorporate these variables to increase accuracy.
Troubleshooting Common Mistakes
Students and professionals alike sometimes encounter common challenges when dealing with direct and inverse proportionality problems:
- Confusing direct and inverse proportionality: Carefully examine the problem statement. Identify which variables increase or decrease together and which variables have an opposite relationship.
- Incorrectly setting up the formula: Make sure you have the correct formula reflecting the direct and inverse relationships. Pay close attention to the numerator and denominator.
- Errors in algebraic manipulation: Carefully solve for the constant of proportionality and then carefully substitute values to solve for the unknown variable.
- Misinterpreting the results: Always analyze the solution in the context of the problem statement and consider the limitations of the model.
Conclusion
Understanding how variables relate to each other is crucial for problem-solving across diverse fields. The concept of a variable varying directly with one variable and inversely with another is a powerful tool for modeling real-world phenomena. By grasping the core principles, mastering the mathematical representation, and practicing problem-solving, you can effectively utilize this knowledge to analyze various systems and make accurate predictions. Remember to always analyze the limitations and assumptions associated with the models you create and always be critical of your results.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
A Legally Acceptable Id Has Which Characteristic
Mar 18, 2025
-
Ready To Eat Foods Are Defined As
Mar 18, 2025
-
Q5 1 Which Of The Following Is False
Mar 18, 2025
-
Which Description Most Accurately Summarizes The Yield Curves Shown
Mar 18, 2025
-
Why Is The Study Of Religious Beliefs Challenging For Anthropologists
Mar 18, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about U Varies Directly With P And Inversely With D . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
