Two Important Advantages Of Secondary Data Are That They Are
Holbox
Mar 28, 2025 · 6 min read
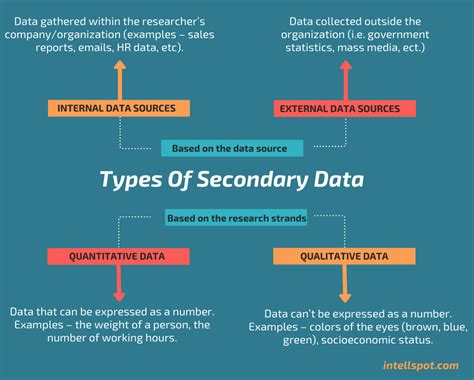
Table of Contents
- Two Important Advantages Of Secondary Data Are That They Are
- Table of Contents
- Two Important Advantages of Secondary Data: Cost-Effectiveness and Time Efficiency
- Cost-Effectiveness: Saving Money on Data Collection
- High Costs of Primary Data Collection
- Secondary Data: A Budget-Friendly Alternative
- Cost Savings in Action: A Case Study
- Time Efficiency: Speeding Up the Research Process
- Time-Consuming Aspects of Primary Data Collection
- Secondary Data: A Time-Saving Boon
- Time Efficiency in Action: An Example
- Combining Primary and Secondary Data for Optimal Results
- Challenges of Using Secondary Data: Critical Considerations
- Conclusion: Harnessing the Power of Secondary Data
- Latest Posts
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
Two Important Advantages of Secondary Data: Cost-Effectiveness and Time Efficiency
Secondary data, pre-existing data collected by someone other than the researcher, offers invaluable benefits in research and analysis. While primary data collection provides firsthand insights, secondary data boasts two significant advantages: cost-effectiveness and time efficiency. These advantages are crucial for researchers and businesses seeking to gather insights quickly and affordably without compromising the quality of their analysis. This article delves deeper into these key benefits, exploring their implications and providing examples to illustrate their practical application.
Cost-Effectiveness: Saving Money on Data Collection
One of the most compelling advantages of utilizing secondary data is its significant cost savings. Collecting primary data involves substantial expenses, including:
High Costs of Primary Data Collection
-
Personnel Costs: Employing interviewers, data entry staff, and project managers adds significantly to the overall budget. The cost escalates with the complexity of the research and the size of the sample population.
-
Recruitment and Incentive Costs: Finding and incentivizing participants, especially for targeted groups, can be expensive. Offering monetary compensation, gift cards, or other incentives can quickly deplete resources.
-
Data Collection Method Costs: Different methods—surveys (online, phone, mail), interviews (face-to-face, telephone), observations, and experiments—each involve varying levels of cost. For example, conducting face-to-face interviews requires travel expenses and interviewer time, increasing the overall cost.
-
Data Processing and Cleaning Costs: Preparing raw data for analysis is a time-consuming and labor-intensive process. Data cleaning involves identifying and correcting errors, inconsistencies, and missing values, adding to the cost.
-
Equipment and Software Costs: Investing in software for data collection, analysis, and management contributes to the financial burden. This includes survey platforms, statistical software, and other specialized tools.
Secondary Data: A Budget-Friendly Alternative
In contrast, secondary data often comes at a significantly lower cost, or even free. Many sources offer publicly available datasets, reports, and statistics. Examples include:
-
Government Agencies: Statistical offices (like the U.S. Census Bureau or the UK's Office for National Statistics) provide a wealth of demographic, economic, and social data at minimal or no cost.
-
Academic Databases: Repositories such as JSTOR, ScienceDirect, and Google Scholar contain numerous research papers and studies offering valuable data for analysis. While access might require institutional subscriptions, the cost is often shared across researchers and institutions, making it more affordable.
-
Industry Associations: Trade associations and industry bodies often publish market research reports and statistical analyses related to their sectors. These resources can be invaluable for understanding industry trends and competitive landscapes.
-
Commercial Data Providers: While some commercial providers charge for their data, they often offer more affordable and readily accessible options compared to conducting extensive primary research. These providers may specialize in specific areas, making their data particularly valuable for focused research.
Cost Savings in Action: A Case Study
Imagine a market research project aiming to understand consumer preferences for a new product. Conducting primary research (surveys, focus groups) would involve significant costs in participant recruitment, data collection, and analysis. However, leveraging existing market research reports from industry associations or publicly available consumer trend data could significantly reduce these costs. The researcher can focus resources on analysis and interpretation rather than the expensive primary data collection process.
Time Efficiency: Speeding Up the Research Process
Beyond cost savings, the second crucial advantage of secondary data lies in its time efficiency. The process of gathering primary data is inherently time-consuming, whereas secondary data is readily available, saving researchers valuable time and accelerating the entire research process.
Time-Consuming Aspects of Primary Data Collection
-
Design and Development: Creating questionnaires, interview guides, or observation protocols requires careful planning and development, which can be time-consuming. Pilot testing and revisions add to the duration.
-
Data Collection: The process of gathering data through surveys, interviews, or observations can take weeks, months, or even years, depending on the research design and sample size.
-
Data Processing and Cleaning: Preparing the raw data for analysis—cleaning, coding, and transforming it—is a lengthy process that requires considerable time and effort.
-
Analysis and Interpretation: Analyzing the collected data and drawing meaningful conclusions is a complex and time-intensive process.
Secondary Data: A Time-Saving Boon
Secondary data drastically shortens the research timeline by eliminating the time-consuming phases of primary data collection, allowing researchers to:
-
Focus on Analysis: With readily available data, researchers can dedicate more time to analyzing the data, interpreting the findings, and drawing valuable insights.
-
Faster Turnaround: Utilizing existing datasets drastically reduces the research timeline, enabling quicker decision-making and timely responses to market changes or emerging trends.
-
Access to Historical Data: Secondary data offers access to historical trends and patterns, providing context and insights that would be impossible to obtain through primary data collection alone. This historical context enriches the analysis and facilitates informed decision-making.
Time Efficiency in Action: An Example
Consider a company planning a new marketing campaign. Instead of spending months conducting surveys to gauge consumer preferences, the company can utilize existing social media analytics, market research reports, and consumer trend data to quickly gain a comprehensive understanding of their target audience and preferences. This allows them to develop a targeted and effective marketing campaign in a significantly shorter timeframe.
Combining Primary and Secondary Data for Optimal Results
While secondary data offers significant advantages in terms of cost and time, it's important to note that it's not always a perfect substitute for primary data. Often, the most effective approach involves combining both primary and secondary data. This mixed-methods approach offers the best of both worlds:
-
Secondary Data Provides Context: Secondary data can provide a foundational understanding of the research topic, establishing a context for primary data collection.
-
Primary Data Addresses Specific Gaps: Primary data can be used to fill any gaps or address specific questions that secondary data cannot answer.
-
Triangulation for Enhanced Validity: Combining both data sources allows for triangulation, enhancing the validity and reliability of the findings.
For example, a researcher investigating customer satisfaction might initially utilize secondary data from customer reviews and social media to identify key themes and areas of concern. Then, they could conduct primary research (surveys or interviews) to delve deeper into these specific issues, gathering more detailed insights and perspectives.
Challenges of Using Secondary Data: Critical Considerations
While cost-effectiveness and time efficiency are significant advantages, it’s crucial to be aware of potential limitations:
-
Data Relevance: Secondary data may not always perfectly align with the specific research question or objectives. Researchers must carefully assess the relevance and suitability of the data.
-
Data Quality: The quality and accuracy of secondary data can vary significantly depending on the source. Researchers need to critically evaluate the data's credibility and potential biases.
-
Data Accessibility: Accessing certain types of secondary data may require subscriptions, fees, or permissions.
-
Data Integrity: Ensuring the data's integrity is vital, as errors or inconsistencies can impact the research findings.
Overcoming these challenges requires careful planning, thorough data validation, and a critical approach to data interpretation.
Conclusion: Harnessing the Power of Secondary Data
Secondary data represents a powerful resource for researchers and businesses seeking efficient and cost-effective ways to gather insights. Its advantages in terms of cost savings and time efficiency are undeniable. By carefully selecting appropriate data sources, critically evaluating data quality, and understanding its limitations, researchers can leverage secondary data to accelerate their research, enhance their analysis, and ultimately achieve their research objectives more effectively. Combined with primary data collection, secondary data creates a robust and comprehensive approach to research and analysis. Understanding and effectively utilizing these two significant advantages will undoubtedly enhance the overall efficacy and efficiency of any research endeavor.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Holes Essentials Of Human Anatomy And Physiology
Apr 01, 2025
-
The Term Deviance Can Be Defined As
Apr 01, 2025
-
Which Molecule Is Expected To Have The Smallest Pka
Apr 01, 2025
-
Which Could Be The Function Graphed Below
Apr 01, 2025
-
Art Labeling Activity Gross Anatomy Of The Stomach
Apr 01, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Two Important Advantages Of Secondary Data Are That They Are . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
