This Table Shows How Many Male And Female
Holbox
Mar 22, 2025 · 6 min read
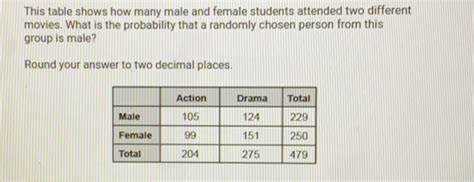
Table of Contents
- This Table Shows How Many Male And Female
- Table of Contents
- Decoding the Data: A Deep Dive into Male and Female Demographics
- The Significance of Male and Female Demographics
- Understanding Different Presentation Formats
- The Crucial Role of Context in Interpretation
- Applications Across Various Fields
- Ethical Considerations
- Conclusion
- Latest Posts
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
Decoding the Data: A Deep Dive into Male and Female Demographics
This article explores the multifaceted world of analyzing demographic data, specifically focusing on the interpretation and application of tables showing the distribution of males and females within a given population. We will dissect the significance of such data, delve into various presentation formats, and discuss the crucial role of context in accurate interpretation. Furthermore, we'll examine how this seemingly simple data informs crucial decisions in numerous fields.
The Significance of Male and Female Demographics
Understanding the proportion of males and females within a population is fundamental to numerous disciplines. From urban planning and resource allocation to healthcare and marketing, this seemingly simple data point holds immense power. The sex ratio, often expressed as the number of males per 100 females, is a key indicator of societal health and development. Deviations from the norm can reveal significant societal trends, such as:
- Healthcare disparities: A skewed sex ratio might indicate health challenges specific to one sex, requiring targeted interventions.
- Economic implications: The distribution of males and females within the workforce profoundly impacts economic growth and development.
- Social structures: Cultural norms and practices significantly influence the sex ratio, reflecting deep-seated societal values.
- Political representation: An unbalanced sex ratio might signal imbalances in political representation and participation.
Analyzing the raw numbers alone is rarely sufficient; contextual factors are paramount. We must understand the age group, geographic location, and socio-economic background to accurately interpret the significance of the data. A high proportion of males in a specific age group might be entirely normal, while the same ratio across all ages could indicate a serious issue.
Understanding Different Presentation Formats
Data on male and female distributions can be presented in various formats, each with its strengths and weaknesses. Common formats include:
-
Simple Tables: These present raw numbers of males and females, often categorized by age group or other relevant variables. While simple, they lack visual impact and can be difficult to grasp for large datasets. Example: A table showing the number of male and female students in each year of a university.
-
Bar Charts: These provide a visual representation of the data, making comparisons easier. Different colored bars can represent males and females, clearly illustrating their relative proportions. Example: A bar chart comparing the male and female workforce participation rate in different sectors.
-
Pie Charts: These are effective for displaying the proportion of males and females within the total population. Each segment represents the percentage of each sex, providing a quick visual understanding of the overall distribution. Example: A pie chart showing the male and female distribution in a specific city.
-
Line Graphs: Useful for displaying changes in the sex ratio over time. These graphs illustrate trends and allow for analysis of fluctuations in the proportion of males and females. Example: A line graph showing the changing sex ratio of a country over several decades.
-
Heatmaps: For more complex data sets, heatmaps can visualize the distribution of males and females across multiple variables simultaneously. This allows for the identification of clusters and patterns within the data. Example: A heatmap showing the distribution of males and females across different income brackets and age groups.
The choice of presentation format depends on the specific data, the intended audience, and the message the presenter wishes to convey. A simple table might suffice for a small dataset, while a more sophisticated visual representation is necessary for complex datasets with multiple variables.
The Crucial Role of Context in Interpretation
As previously emphasized, context is paramount in interpreting data on male and female distributions. Consider the following scenarios:
Scenario 1: A village in a developing country shows a significantly higher number of males than females. This could be due to several factors, including gender-selective abortions, higher mortality rates among females due to poor healthcare access, and emigration of women seeking better opportunities.
Scenario 2: A university's engineering department shows a significantly higher number of males than females. This could be attributed to various factors, including gender stereotypes and biases in the field, a lack of female role models, and insufficient outreach efforts to attract female students.
Scenario 3: A retirement community shows a significantly higher number of females than males. This is often attributed to higher life expectancy among women, resulting in a larger proportion of older women surviving their spouses.
The same raw data—a skewed sex ratio—can have completely different interpretations depending on the context. Therefore, a thorough understanding of the population being studied, including its age, geographic location, socio-economic status, and cultural background, is essential for drawing accurate conclusions. Failing to consider context can lead to misleading and potentially harmful interpretations.
Applications Across Various Fields
The analysis of male and female demographic data plays a critical role in numerous fields, including:
-
Public Health: Understanding the distribution of males and females is crucial for designing effective public health initiatives. Targeted programs can be developed to address health disparities between the sexes, improving overall health outcomes. For instance, understanding the prevalence of specific diseases in one sex over another helps focus preventative measures and resource allocation.
-
Urban Planning: Accurate demographic data informs urban planning decisions, ensuring the provision of adequate infrastructure and services to meet the needs of both males and females. This includes considerations such as transportation, housing, recreational facilities, and healthcare access. A city with a large female population might require more daycare facilities, for example.
-
Education: Understanding the distribution of males and females in different educational levels is crucial for designing effective educational policies and interventions. Addressing gender gaps in education requires a nuanced understanding of the factors contributing to these imbalances.
-
Marketing and Advertising: Market research frequently utilizes demographic data to tailor marketing strategies and advertising campaigns. Understanding consumer behavior based on sex is essential for targeting specific products or services effectively.
-
Economics: Labor market analysis heavily relies on data on the distribution of males and females in the workforce. This allows economists to analyze gender wage gaps, understand employment trends, and assess the overall impact of gender on economic growth.
Ethical Considerations
The collection and analysis of data on male and female distributions must be conducted ethically and responsibly. Data privacy must be protected, and the potential for bias in data collection and interpretation must be carefully considered. Transparency in data reporting is crucial, ensuring that the limitations and potential biases of the data are clearly communicated.
Conclusion
Analyzing data on male and female distributions is far more complex than simply comparing numbers. It requires a deep understanding of the context, careful consideration of the chosen presentation format, and a strong awareness of ethical considerations. The insights derived from such analyses are crucial for informed decision-making across a wide range of disciplines, contributing to more equitable and effective policies and practices that benefit society as a whole. By combining quantitative analysis with qualitative understanding, we can unlock the full potential of this seemingly simple data to improve lives and shape a better future. The key takeaway is to always view the numbers within the broader context of societal factors, cultural norms, and historical trends to ensure a thorough and accurate interpretation. This holistic approach ensures that the data serves its purpose – informing progress and facilitating positive change.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Is Not A Source For Osha Standards
Mar 24, 2025
-
Theo Needs To Enter A New Income
Mar 24, 2025
-
Rank The Structures In Order Of Decreasing Electrophilic Strength
Mar 24, 2025
-
One Of The Three Economic Questions Deals With Deciding
Mar 24, 2025
-
Suppose A Gene Has Two Alleles
Mar 24, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about This Table Shows How Many Male And Female . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
