Thermostatic Expansion Valves Respond To Changes In
Holbox
Mar 15, 2025 · 6 min read
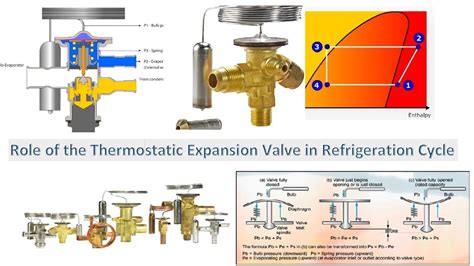
Table of Contents
Thermostatic Expansion Valves: Responding to Changes in Refrigerant Conditions
Thermostatic expansion valves (TXVs) are crucial components in refrigeration and air conditioning systems. Their primary function is to precisely regulate the flow of refrigerant into the evaporator, ensuring optimal system performance and efficiency. Unlike simpler expansion devices like capillary tubes, TXVs dynamically respond to several key factors, adapting the refrigerant flow to maintain a consistent evaporator temperature and superheat. This article will delve deep into the intricacies of TXVs, exploring the various factors they respond to and how this responsiveness contributes to overall system efficiency and reliability.
Understanding the Fundamentals of TXV Operation
Before exploring the intricacies of TXV response, it's crucial to understand the basic principles of operation. A TXV essentially acts as a variable restrictor, metering the refrigerant flow based on the conditions within the evaporator. At its heart lies a sensing bulb, filled with the same refrigerant as the system. This bulb is strategically positioned to measure the refrigerant's temperature at the evaporator outlet. This temperature, along with the pressure difference across the valve, dictates the valve's position and subsequently, the refrigerant flow.
The TXV's operation hinges on a delicate balance. If the evaporator temperature is too low (indicating insufficient refrigerant), the sensing bulb's temperature also drops. This causes the refrigerant inside the bulb to contract, reducing the pressure exerted on a diaphragm within the valve. This allows the valve to open wider, increasing refrigerant flow into the evaporator. Conversely, if the evaporator temperature is too high (indicating excessive refrigerant), the bulb's temperature rises, expanding the refrigerant within and increasing pressure on the diaphragm. The valve then closes slightly, restricting the refrigerant flow.
Key Factors Influencing TXV Response
The beauty of a TXV lies in its ability to respond dynamically to a multitude of factors, ensuring consistent evaporator conditions despite external fluctuations. Let's examine the key variables:
1. Evaporator Superheat
Superheat, the difference between the refrigerant's actual temperature and its saturation temperature at the evaporator outlet, is arguably the most critical factor affecting TXV response. Maintaining optimal superheat is essential for efficient operation. Insufficient superheat can lead to liquid refrigerant entering the compressor, causing serious damage. Conversely, excessive superheat indicates under-feeding of the evaporator, resulting in reduced cooling capacity. The TXV actively regulates the refrigerant flow to maintain a pre-set superheat value, typically between 5°F and 12°F (3°C and 7°C).
How the TXV Responds: A low superheat reading at the evaporator outlet signals the TXV sensing bulb to open wider, allowing more refrigerant into the evaporator. Conversely, high superheat causes the valve to close, reducing the flow. This continuous feedback loop ensures optimal superheat is maintained.
2. Evaporator Pressure
Evaporator pressure, while secondary to superheat in the TXV's control scheme, still significantly influences the valve's operation. Low evaporator pressure indicates a reduced refrigerant charge or a problem within the system. High evaporator pressure might signify restrictions in the refrigerant line or an overcharge.
How the TXV Responds: The TXV’s internal mechanism is designed to respond to both evaporator temperature and pressure. Low evaporator pressure, even with adequate superheat, might signal the TXV to slightly reduce its opening to prevent excessive refrigerant flow, preventing compressor flooding and preserving system stability. High evaporator pressure, regardless of superheat, will tend to partially close the valve, preventing excessive refrigerant flow and potential system overpressure.
3. Suction Line Pressure
Suction line pressure represents the refrigerant pressure at the evaporator's outlet, before it reaches the compressor. It directly relates to the refrigerant's temperature and density. Changes in suction line pressure reflect overall system load and influence the TXV's response.
How the TXV Responds: A drop in suction line pressure usually signals a higher system load or reduced refrigerant charge. The TXV responds by opening slightly more, increasing the refrigerant flow into the evaporator and attempting to meet the increased demand. Conversely, an increase in suction line pressure prompts the valve to close slightly, reducing refrigerant flow.
4. Ambient Temperature
External ambient temperature significantly impacts the refrigeration cycle’s overall heat load. In hotter environments, the system has to work harder to maintain a constant temperature, affecting refrigerant demand.
How the TXV Responds: Higher ambient temperatures increase the evaporator's heat load. Consequently, the TXV senses a greater demand for refrigerant and responds by opening wider to ensure the evaporator is adequately supplied. Conversely, lower ambient temperatures lessen the heat load, prompting the valve to adjust accordingly.
5. Refrigerant Charge
The total amount of refrigerant in the system plays a crucial role in system performance. An insufficient refrigerant charge can lead to reduced cooling capacity and potentially damage the compressor due to liquid slugging. An overcharge can result in excessive pressure and reduced efficiency.
How the TXV Responds: While the TXV doesn't directly measure refrigerant charge, its operation is heavily influenced by it. An undercharge manifests as reduced evaporator pressure and insufficient superheat, prompting the TXV to open more, attempting to compensate. An overcharge leads to high suction pressure and superheat, causing the TXV to partially restrict refrigerant flow.
Factors Affecting TXV Performance and Troubleshooting
Several factors can affect the TXV's ability to accurately respond to the aforementioned conditions. Understanding these aspects is crucial for troubleshooting and maintaining optimal system performance:
-
Dirt and Debris: Accumulation of dirt, debris, or moisture in the sensing bulb or valve can impede its operation, resulting in inaccurate metering. Regular system maintenance is essential to prevent such issues.
-
Malfunctioning Sensing Bulb: A faulty sensing bulb can fail to accurately reflect the evaporator's temperature and superheat, causing inaccurate refrigerant control and potential system damage.
-
Spring Tension: The spring within the TXV regulates its sensitivity to pressure changes. Improper spring tension can lead to either over- or under-feeding of the evaporator.
-
Incorrect TXV Sizing: An improperly sized TXV for the specific application can lead to operational problems. It's crucial to select a TXV with the appropriate capacity and operating range for the system.
-
Refrigerant Type: Different refrigerants have varying properties, influencing TXV calibration and operation. It's imperative to use the correct TXV for the specific refrigerant employed.
TXV vs. Other Expansion Devices
Compared to other expansion devices like capillary tubes and orifice tubes, TXVs offer significant advantages in terms of responsiveness and adaptability.
-
Capillary Tubes: Capillary tubes are fixed restriction devices, incapable of dynamically adjusting refrigerant flow based on changing conditions. They are less efficient and prone to malfunctions under varying loads.
-
Orifice Tubes: Similar to capillary tubes, orifice tubes are fixed restriction devices. They're simpler and cheaper than TXVs, but lack the adaptability to changing load conditions.
The superior responsiveness of TXVs makes them ideal for applications requiring precise temperature control and efficient operation across a wide range of load conditions.
Conclusion: The Unsung Hero of Refrigeration Systems
Thermostatic expansion valves represent a crucial component within modern refrigeration and air conditioning systems. Their sophisticated design and ability to respond dynamically to changes in various parameters ensure efficient, reliable, and consistent operation. Understanding the key factors that influence TXV response, along with potential troubleshooting aspects, is essential for technicians and engineers alike involved in refrigeration system design, installation, and maintenance. While often overlooked, the TXV's precise control of refrigerant flow is a cornerstone of efficient and effective cooling, highlighting its role as the unsung hero of refrigeration technology. Proper maintenance, selection, and understanding of the TXV's operational principles are vital for maximizing system performance and longevity.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Is The Characteristic Of The Individuals Within The Population
Mar 15, 2025
-
Converting Nfa To Dfa Theorem 1 39
Mar 15, 2025
-
The Waiting Times Between A Subway Departure
Mar 15, 2025
-
A Improvement In Production Technology Will Shift The
Mar 15, 2025
-
Select The Nmr Spectrum That Corresponds Best To P Anisidine
Mar 15, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Thermostatic Expansion Valves Respond To Changes In . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
