The Responsibilities Of The Operations Manager Include
Holbox
Mar 14, 2025 · 6 min read
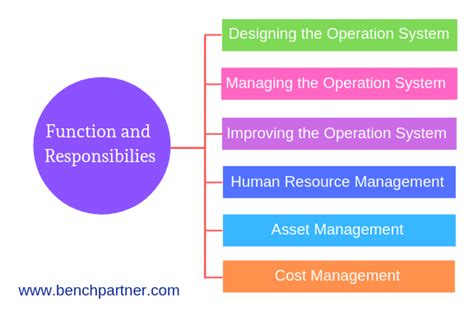
Table of Contents
The Extensive Responsibilities of an Operations Manager: A Deep Dive
The operations manager is the backbone of any successful organization. They're the orchestrators, the problem-solvers, and the strategic thinkers who ensure the smooth and efficient running of daily operations. This role transcends simple task management; it demands a multifaceted skillset, encompassing leadership, strategic planning, process improvement, and a deep understanding of the organization's overall goals. This article will delve into the diverse and extensive responsibilities of an operations manager, exploring the nuances of each area and highlighting the importance of their contribution to overall organizational success.
I. Strategic Planning and Goal Setting
One of the primary responsibilities of an operations manager is to develop and implement strategic plans aligned with the organization's overall objectives. This involves:
A. Analyzing Business Needs:
This critical first step involves deeply understanding the company's strategic goals, market trends, and competitive landscape. The operations manager must identify areas for improvement and potential growth opportunities. They need to analyze data, identify bottlenecks, and assess resource allocation to optimize operational efficiency. This analysis informs the development of actionable strategies.
B. Setting Operational Goals and Key Performance Indicators (KPIs):
Once the needs are understood, the operations manager sets specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals. These goals should directly support the organization's strategic objectives. Crucially, they must define key performance indicators (KPIs) to track progress and measure success. Examples of KPIs include production output, efficiency rates, customer satisfaction scores, and cost reduction metrics. Regular monitoring of these KPIs is essential for course correction and continuous improvement.
C. Resource Allocation and Budget Management:
Effective resource allocation is paramount. Operations managers must strategically allocate resources – including personnel, equipment, materials, and budget – to maximize efficiency and achieve set goals. This requires careful budgeting, forecasting, and cost control measures. They must anticipate future needs and ensure sufficient resources are available to meet demands.
II. Process Improvement and Optimization
A significant portion of an operations manager's role involves the continuous improvement of operational processes. This necessitates:
A. Process Mapping and Analysis:
Understanding existing operational processes is the foundation for improvement. This involves mapping out the current workflow, identifying bottlenecks, inefficiencies, and areas prone to errors. Tools like flowcharts and process diagrams are invaluable in visualizing the process and pinpointing areas for optimization.
B. Lean Manufacturing and Six Sigma Principles:
Implementing lean manufacturing principles focuses on eliminating waste and maximizing value. This involves streamlining processes, reducing lead times, and improving overall efficiency. Similarly, Six Sigma methodologies aim to minimize defects and variations in processes, ensuring consistent quality and customer satisfaction. Operations managers often utilize these principles to drive improvements.
C. Implementing and Monitoring Change:
Introducing new processes or technologies requires careful planning and execution. The operations manager manages the implementation, training staff, and monitoring the impact of changes. They need to adapt to unexpected challenges, troubleshoot problems, and ensure a smooth transition. Regular monitoring and feedback loops are crucial for ongoing optimization.
III. Leading and Managing Teams
The operations manager's role extends significantly beyond strategic planning; it's heavily focused on leading and managing teams. This involves:
A. Team Building and Motivation:
Creating a high-performing team is essential for operational success. The operations manager fosters a positive and collaborative work environment, motivates team members, and encourages teamwork. This involves recognizing achievements, addressing conflicts constructively, and providing opportunities for professional development.
B. Delegation and Empowerment:
Effective delegation is crucial for maximizing team productivity. Operations managers delegate tasks appropriately, empower team members to take ownership, and provide the necessary support and resources for success. This builds trust and confidence within the team.
C. Performance Management and Feedback:
Regular performance evaluations are essential for monitoring individual and team performance. The operations manager provides constructive feedback, identifies training needs, and addresses performance issues promptly and fairly. They implement performance improvement plans and celebrate successes.
D. Recruitment and Training:
Operations managers often play a role in the recruitment and training of new team members. They define job requirements, conduct interviews, and onboard new hires. They develop training programs to enhance skills and knowledge, ensuring the team possesses the necessary competencies for effective operation.
IV. Technology and Innovation
In today's dynamic business environment, technology plays a vital role in operational efficiency. The operations manager is responsible for:
A. Implementing and Managing Technology:
This involves evaluating and implementing new technologies to automate processes, improve efficiency, and enhance productivity. This could range from enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems to specialized software for production or logistics management.
B. Data Analysis and Reporting:
Leveraging data analytics to gain insights into operational performance is crucial. Operations managers utilize data to identify trends, optimize processes, and make informed decisions. They create reports and dashboards to monitor key performance indicators and communicate progress to stakeholders.
C. Staying Current with Industry Trends:
The operational landscape is constantly evolving. Operations managers must stay abreast of the latest technologies, industry best practices, and emerging trends to ensure their organization remains competitive. This requires continuous learning and engagement with industry publications and events.
V. Compliance and Risk Management
Ensuring compliance with relevant regulations and mitigating operational risks is a crucial responsibility. This includes:
A. Regulatory Compliance:
Operations managers must ensure adherence to all applicable laws, regulations, and industry standards. This might involve safety regulations, environmental regulations, or data privacy laws. They develop and implement procedures to ensure compliance and address any potential violations promptly.
B. Risk Assessment and Mitigation:
Identifying and mitigating operational risks is crucial for business continuity. This involves conducting risk assessments, identifying potential threats, and developing strategies to minimize their impact. This includes implementing contingency plans for unexpected events.
C. Safety and Security:
Maintaining a safe and secure work environment is paramount. Operations managers implement safety protocols, conduct regular safety inspections, and ensure compliance with occupational health and safety regulations. They also implement security measures to protect company assets and data.
VI. Communication and Collaboration
Effective communication and collaboration are essential for successful operations management. This involves:
A. Internal Communication:
Maintaining clear and consistent communication within the team and across different departments is crucial for seamless operations. This involves regular team meetings, clear communication of goals and expectations, and prompt responses to queries.
B. External Communication:
Communicating with external stakeholders, such as suppliers, customers, and regulatory bodies, is equally important. Operations managers handle communication, build relationships, and address issues promptly and professionally.
C. Reporting and Stakeholder Management:
Regularly reporting on operational performance to senior management and other stakeholders is crucial. Operations managers prepare reports, present findings, and address any concerns effectively. They manage expectations and build strong relationships with stakeholders.
VII. Continuous Improvement and Learning
The role of an operations manager is never static; it demands continuous improvement and learning. This includes:
A. Regular Performance Reviews:
Analyzing operational performance regularly is essential. This involves reviewing KPIs, identifying areas for improvement, and implementing corrective actions.
B. Seeking Feedback:
Actively seeking feedback from team members, customers, and other stakeholders provides valuable insights into areas needing improvement. This feedback loop is essential for continuous improvement.
C. Professional Development:
Operations managers must stay updated on industry best practices and advancements. This involves participating in professional development opportunities, attending conferences, and engaging in continuous learning.
In conclusion, the responsibilities of an operations manager are multifaceted and demanding. They are the driving force behind efficient and effective operations, leading teams, optimizing processes, and ensuring organizational success. This role demands a diverse skill set, encompassing strategic thinking, leadership, problem-solving, and a deep understanding of the business environment. The successful operations manager is a critical asset to any organization, ensuring smooth operations and contributing significantly to overall profitability and growth.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
A Medical Record Is An Example Of
Mar 14, 2025
-
Minor Violations May Be Granted Upwards Of Days For Correction
Mar 14, 2025
-
Which One Of The Following Statements Is Correct
Mar 14, 2025
-
Experiment 3 Radioactivity Effect Of Distance And Absorbers
Mar 14, 2025
-
Rn Targeted Medical Surgical Cardiovascular Online Practice 2023
Mar 14, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about The Responsibilities Of The Operations Manager Include . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
