A Medical Record Is An Example Of
Holbox
Mar 16, 2025 · 7 min read
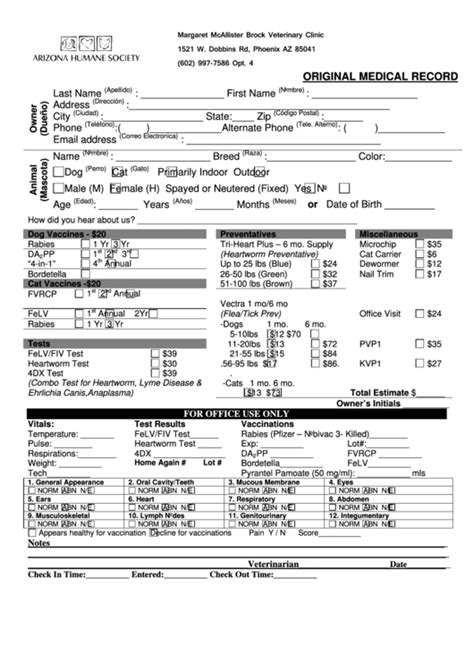
Table of Contents
- A Medical Record Is An Example Of
- Table of Contents
- A Medical Record Is an Example of: A Deep Dive into Healthcare Data and its Implications
- What Constitutes a Medical Record?
- 1. Patient Demographics and Identifying Information:
- 2. Medical History:
- 3. Physical Examination Findings:
- 4. Diagnostic Test Results:
- 5. Treatment Plans and Progress Notes:
- 6. Consultations and Referrals:
- 7. Medication Records:
- 8. Immunization Records:
- 9. Discharge Summaries:
- A Medical Record as an Example of Data Security and Privacy:
- A Medical Record as an Example of Evidence-Based Medicine:
- A Medical Record as an Example of Interoperability:
- A Medical Record as an Example of Legal and Ethical Considerations:
- A Medical Record as an Example of Continuous Improvement:
- A Medical Record as an Example of Data-Driven Healthcare:
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
A Medical Record Is an Example of: A Deep Dive into Healthcare Data and its Implications
A medical record is much more than just a collection of notes; it's a dynamic, comprehensive chronicle of an individual's health journey. It serves as a cornerstone of healthcare, informing treatment decisions, tracking progress, and ensuring continuity of care. Understanding what a medical record is an example of requires exploring its multifaceted nature, its legal implications, and its crucial role in the modern healthcare system.
What Constitutes a Medical Record?
A medical record is an example of a complex, legally significant document. It's not merely a chronological list of appointments; rather, it's a meticulously compiled collection of data encompassing various aspects of a patient's health. This includes:
1. Patient Demographics and Identifying Information:
This foundational element includes details such as the patient's name, date of birth, address, contact information, and insurance details. Accurate identification is paramount to prevent errors and ensure the right patient receives the correct care. This is an example of data essential for administrative purposes and for linking various aspects of the medical record.
2. Medical History:
A comprehensive medical history details past illnesses, surgeries, allergies, medications, and family history. This section provides context for current health concerns and helps healthcare providers assess risk factors. This is an example of longitudinal data, crucial for understanding a patient's overall health trajectory.
3. Physical Examination Findings:
Detailed notes from physical examinations document vital signs (blood pressure, heart rate, temperature, respiration rate), physical assessments of different body systems, and any abnormalities detected. This section forms an example of objective data, crucial for monitoring changes in a patient's condition.
4. Diagnostic Test Results:
This section includes results from laboratory tests (blood work, urine analysis), imaging studies (X-rays, CT scans, MRIs), and other diagnostic procedures. These results are an example of quantifiable data, offering objective evidence of the patient's health status.
5. Treatment Plans and Progress Notes:
This section documents the healthcare provider's assessment, diagnosis, treatment plan, and progress notes outlining the patient's response to treatment. It's an example of subjective and objective data combined, showcasing the interplay between the provider's assessment and the patient's response.
6. Consultations and Referrals:
Notes from consultations with specialists or referrals to other healthcare providers are included, demonstrating a collaborative approach to care. This is an example of interdisciplinary data, highlighting the collaborative nature of modern healthcare.
7. Medication Records:
A complete list of current and past medications, including dosages and administration routes, is crucial for preventing drug interactions and ensuring medication safety. This is an example of time-sensitive data, requiring meticulous updating and accuracy.
8. Immunization Records:
Documentation of vaccinations received is essential for tracking immunization status and ensuring preventive care. This is an example of preventive healthcare data, crucial for public health initiatives.
9. Discharge Summaries:
Upon discharge from a hospital or other healthcare facility, a summary of the patient's stay, diagnosis, treatment, and instructions for follow-up care is provided. This is an example of transition-of-care data, ensuring continuity of care after discharge.
A Medical Record as an Example of Data Security and Privacy:
The information contained within a medical record is highly sensitive and confidential. As such, medical records are prime examples of data subject to stringent privacy regulations, including HIPAA in the United States and GDPR in Europe. These regulations are designed to:
- Protect patient privacy: Ensuring that only authorized individuals have access to medical records.
- Prevent unauthorized disclosure: Implementing security measures to safeguard against breaches and unauthorized access.
- Maintain data integrity: Ensuring the accuracy and completeness of the information contained within the record.
- Provide patients with control over their data: Allowing patients to access, correct, and amend their medical information.
A breach in medical record security can have devastating consequences, both for the patient and the healthcare provider. Therefore, robust security measures, including encryption, access control, and audit trails, are essential. The medical record serves as a powerful example of how sensitive data needs to be handled with utmost care and precaution.
A Medical Record as an Example of Evidence-Based Medicine:
Medical records are indispensable for evidence-based medicine. They provide the raw data that fuels research, informing the development of new treatments, diagnostic procedures, and healthcare policies. By analyzing trends and patterns within large datasets of medical records, researchers can:
- Identify risk factors for diseases: Understanding the factors that contribute to the development of specific conditions.
- Evaluate the effectiveness of treatments: Assessing the efficacy of various interventions.
- Improve healthcare outcomes: Implementing evidence-based practices to improve patient care.
The anonymization and aggregation of medical record data play a pivotal role in this process, allowing for meaningful analysis without compromising patient confidentiality. This exemplifies the wider application of healthcare data in furthering medical knowledge and driving improvements in healthcare delivery.
A Medical Record as an Example of Interoperability:
In an increasingly interconnected healthcare landscape, the ability to share medical information seamlessly between different healthcare providers and systems is crucial. The medical record serves as an example of the need for interoperability – the ability of different systems to exchange and use data effectively. Interoperability challenges include:
- Standardization of data formats: Ensuring that different systems use compatible formats for storing and exchanging medical information.
- Security and privacy concerns: Maintaining patient confidentiality while enabling data sharing.
- Integration of different systems: Connecting various healthcare systems and databases to allow for seamless data flow.
Overcoming these challenges is essential to improve care coordination, reduce medical errors, and enhance patient outcomes. The evolution of electronic health records (EHRs) and health information exchange (HIE) initiatives are examples of efforts to improve interoperability.
A Medical Record as an Example of Legal and Ethical Considerations:
Medical records hold significant legal weight. They serve as crucial evidence in medical malpractice cases, insurance claims, and disability determinations. Therefore, maintaining accurate, complete, and well-documented records is essential for legal compliance. Moreover, ethical considerations are paramount, including:
- Patient autonomy: Respecting patients' rights to access and control their medical information.
- Confidentiality: Protecting the privacy of patient information.
- Truthfulness and accuracy: Ensuring the accuracy and completeness of the information recorded.
- Professional responsibility: Adhering to professional standards and guidelines.
Failure to uphold these ethical and legal considerations can have serious consequences, including legal repercussions, loss of professional license, and reputational damage. The medical record, therefore, stands as a potent example of the intersection between healthcare, law, and ethics.
A Medical Record as an Example of Continuous Improvement:
Medical records are not static documents. They are continuously evolving, reflecting advancements in medical knowledge, technology, and healthcare practices. The implementation of electronic health records (EHRs) is a prime example of this evolution, bringing significant changes to how medical information is stored, accessed, and managed. Continuous improvement in medical record-keeping focuses on:
- Enhanced data security: Implementing robust security measures to prevent breaches and unauthorized access.
- Improved interoperability: Facilitating the seamless exchange of information between different healthcare systems.
- Streamlined workflows: Improving efficiency and reducing administrative burden.
- Patient engagement: Empowering patients to access and manage their own medical information.
The ongoing development and refinement of medical record systems demonstrate a commitment to using technology to enhance patient care, improve efficiency, and maintain the highest standards of data security and privacy. This continuous evolution highlights the dynamic and forward-looking nature of medical records within the healthcare system.
A Medical Record as an Example of Data-Driven Healthcare:
The vast amount of data contained within medical records is increasingly utilized to drive improvements in healthcare delivery. Analyzing aggregated and anonymized medical record data can reveal valuable insights into:
- Population health trends: Identifying health disparities and informing public health initiatives.
- Disease prediction and prevention: Developing predictive models to identify individuals at high risk for specific conditions.
- Personalized medicine: Tailoring treatment plans to individual patient needs and characteristics.
- Resource allocation: Optimizing the allocation of healthcare resources to improve efficiency and effectiveness.
This data-driven approach emphasizes the importance of medical records not merely as individual patient chronicles but also as valuable resources for improving healthcare at a broader population level. It exemplifies the shift toward a more proactive, data-informed approach to healthcare.
In conclusion, a medical record is not simply a collection of documents; it's a multifaceted example of crucial data management, legal compliance, ethical considerations, and technological advancement in the healthcare industry. Its importance extends far beyond individual patient care, influencing research, policymaking, and the future of healthcare as a whole. Understanding the full scope of a medical record requires recognizing its complex and dynamic nature, emphasizing the need for continuous improvement and robust security measures to protect patient privacy and ensure the highest standards of care.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about A Medical Record Is An Example Of . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.