The Most Significant Hazard Associated With Splinting Is
Holbox
Mar 15, 2025 · 6 min read
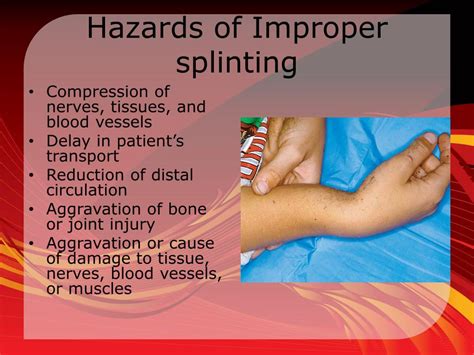
Table of Contents
The Most Significant Hazard Associated with Splinting: Compartment Syndrome
Splinting, a crucial first-aid and emergency medical procedure, aims to immobilize injured limbs, reducing pain and preventing further damage. While invaluable in managing fractures, dislocations, and soft tissue injuries, splinting carries inherent risks. The most significant hazard associated with splinting is compartment syndrome. This article will delve deep into understanding compartment syndrome, its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and crucial preventative measures related to splinting.
Understanding Compartment Syndrome
Compartment syndrome is a serious condition characterized by increased pressure within a confined muscle compartment, compromising blood supply to the tissues within. This pressure build-up can lead to muscle and nerve damage, potentially resulting in permanent disability or even limb loss if left untreated. It’s a medical emergency requiring immediate attention.
The Anatomy of Compartment Syndrome
Our limbs are divided into compartments, each containing muscles, nerves, and blood vessels encased within a tough, inelastic fascia. In healthy individuals, the pressure within these compartments remains stable. However, trauma, swelling, or bleeding after an injury can increase pressure within the compartment, exceeding the capacity of the fascia to expand. This leads to the compression of blood vessels, restricting blood flow to the muscles and nerves.
Types of Compartment Syndrome
Compartment syndrome can be broadly categorized into two main types:
-
Acute Compartment Syndrome: This is the most common and dangerous type, typically developing rapidly after a traumatic injury like a fracture, crush injury, or severe muscle contusion. The sudden increase in pressure requires immediate medical intervention.
-
Chronic Compartment Syndrome: This develops gradually and is often associated with repetitive strenuous activities like running or cycling. Symptoms typically appear during or after exercise and resolve with rest.
Causes of Compartment Syndrome Related to Splinting
Improper splinting techniques significantly increase the risk of compartment syndrome. While splinting aims to stabilize injuries, inadequate or excessively tight splinting can restrict blood flow and cause pressure build-up within the affected compartment.
How Improper Splinting Contributes
Several factors associated with improper splinting techniques contribute to the development of compartment syndrome:
-
Too-tight splinting: A splint applied too tightly restricts blood flow and venous return, leading to swelling and increased compartment pressure. This is the most common cause of splinting-related compartment syndrome. The constriction prevents the natural expansion of tissue resulting from inflammation.
-
Improper splint placement: Incorrect positioning of the splint can compress blood vessels and nerves, further hindering blood flow and contributing to pressure build-up. For example, a splint placed directly over a major artery or nerve can compromise circulation.
-
Splint too long: A splint that's too long can compress tissue beyond the injury site, restricting blood flow in unaffected areas.
-
Lack of distal pulse assessment: Failure to routinely check the distal pulses (pulse felt in the fingers or toes) after splinting significantly increases the risk. Diminished or absent distal pulses are a critical warning sign of compromised circulation.
-
Ignoring patient complaints: Dismissing the patient's complaints of increased pain, numbness, or tingling in the affected limb can be detrimental. These symptoms are early indicators of escalating compartment pressure.
Recognizing the Symptoms of Compartment Syndrome
Early recognition of compartment syndrome is critical for effective management. Symptoms often overlap with those of other injuries, making diagnosis challenging. The "six Ps" are often used as a mnemonic to remember the key symptoms:
-
Pain: This is usually disproportionate to the initial injury, intensifying even with pain medication. The pain is described as deep, throbbing, and unrelenting.
-
Pallor: The skin in the affected area becomes pale due to reduced blood flow.
-
Paresthesia: Numbness or tingling sensations develop as nerves become compressed.
-
Pulselessness: Distal pulses weaken or disappear entirely as blood supply is compromised.
-
Paralysis: Loss of muscle function indicates severe nerve compression.
-
Pressure: Increased tissue pressure within the affected compartment can be detected through palpation (physical examination).
Diagnosing Compartment Syndrome
Diagnosis involves a combination of clinical evaluation and diagnostic tests:
-
Physical Examination: The physician will assess the patient's pain level, skin color, sensation, pulses, and muscle function. They will also palpate the affected limb to detect increased tissue pressure.
-
Compartment Pressure Measurement: This involves inserting a needle into the affected compartment to measure the pressure within. This is crucial for confirming the diagnosis. Elevated pressure compared to diastolic blood pressure indicates compartment syndrome.
-
Doppler Ultrasound: This non-invasive imaging technique assesses blood flow in the affected limb. Reduced or absent blood flow supports the diagnosis.
Treatment of Compartment Syndrome
Compartment syndrome is a surgical emergency. Prompt treatment is crucial to minimize permanent damage. Treatment typically involves:
-
Fasciotomy: This surgical procedure involves making incisions in the fascia to relieve pressure and restore blood flow to the affected tissues. It allows the swollen muscles to expand and blood to circulate freely.
-
Pain Management: Analgesics (pain medications) are administered to control pain.
-
Monitoring: Close monitoring of the patient's vital signs and limb perfusion is crucial post-surgery.
Preventing Compartment Syndrome Related to Splinting
Preventing compartment syndrome related to splinting is paramount. This involves meticulous adherence to proper splinting techniques and careful monitoring of the patient.
-
Appropriate Splint Selection: Choose the right type of splint for the specific injury. Splints should be adequately padded to prevent direct pressure points.
-
Proper Splint Application: Splints should be applied snugly but not tightly. Ensure proper alignment of the limb and avoid excessive compression.
-
Regular Monitoring: Regularly assess the distal pulses, skin color, sensation, and pain level in the affected limb. Any signs of compromised circulation should be reported immediately.
-
Patient Education: Educate patients about the signs and symptoms of compartment syndrome and emphasize the importance of reporting any changes in their condition.
-
Documentation: Meticulous documentation of splinting procedures, including the type of splint used, application technique, and patient assessments, is vital for quality assurance and potential legal considerations.
Conclusion: The Critical Importance of Proper Splinting Techniques
Compartment syndrome represents a severe and potentially limb-threatening complication associated with splinting. While splinting is a life-saving procedure in managing various injuries, improper techniques significantly increase the risk of this devastating complication. By emphasizing meticulous adherence to proper splinting techniques, rigorous monitoring of the patient, and prompt recognition and treatment of compartment syndrome, healthcare professionals can significantly reduce the incidence of this potentially debilitating condition. The understanding and application of these principles are critical for ensuring patient safety and optimal outcomes. Remember, preventing compartment syndrome is far better and easier than treating it. The focus should always be on minimizing the risk through careful and consistent attention to detail in every aspect of splinting and post-splinting care. Patient comfort, safety and health should be paramount in every decision throughout the treatment process.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Question Tech 9 Select The Alkene In The Yellow Box
Mar 15, 2025
-
Question Elm Following Iupac Nomeclature Rules
Mar 15, 2025
-
Generosity Is One Of The Six Pillars Of Character
Mar 15, 2025
-
Orlando Company Began Operation In December
Mar 15, 2025
-
Match Each Description To The Corresponding Management Skill
Mar 15, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about The Most Significant Hazard Associated With Splinting Is . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
