Question Tech 9 Select The Alkene In The Yellow Box
Holbox
Mar 15, 2025 · 6 min read
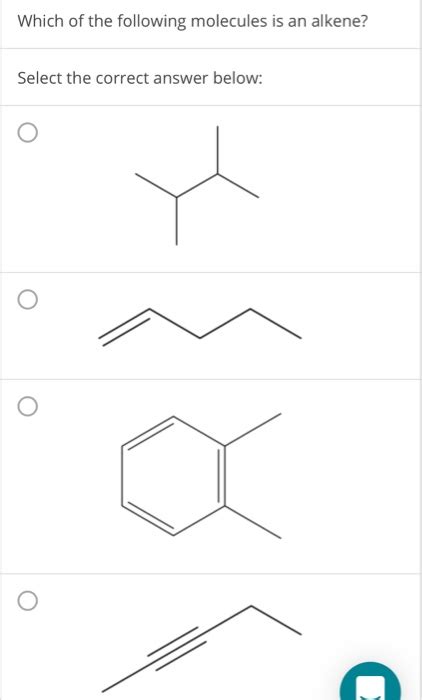
Table of Contents
Question Tech 9: Selecting the Alkene in the Yellow Box – A Deep Dive into Organic Chemistry
This article delves into the intricacies of identifying alkenes within a given set of organic compounds, specifically focusing on a hypothetical "Question Tech 9" scenario involving a yellow box highlighting potential candidates. We'll explore the fundamental characteristics of alkenes, the various methods for their identification, and strategies for approaching such a problem systematically. This detailed explanation will equip you with the knowledge to confidently tackle similar organic chemistry challenges.
Understanding Alkenes: The Double Bond Differentiator
Alkenes, also known as olefins, are unsaturated hydrocarbons characterized by the presence of at least one carbon-carbon double bond. This double bond is the key distinguishing feature that sets alkenes apart from alkanes (saturated hydrocarbons with only single bonds) and alkynes (containing at least one carbon-carbon triple bond). The presence of this double bond significantly impacts the alkene's reactivity and physical properties.
Key Properties of Alkenes:
- Unsaturation: The presence of the double bond signifies unsaturation, meaning the carbon atoms involved are not bonded to the maximum number of hydrogen atoms possible. This unsaturation is crucial for understanding reactivity.
- Planar Geometry: The atoms directly involved in the double bond (two carbons and their directly attached hydrogens) exhibit a planar geometry, meaning they lie in the same plane. This is due to the nature of the sigma and pi bonds involved.
- Reactivity: The pi bond component of the double bond is relatively weaker and more susceptible to reactions, making alkenes more reactive than alkanes. Common reactions include addition reactions (e.g., halogenation, hydration), oxidation, and polymerization.
- Isomerism: Alkenes can exhibit isomerism, both geometric (cis-trans or E-Z isomerism) and structural isomerism. This further complicates identification and requires careful consideration of the structural formula.
Identifying Alkenes: Techniques and Strategies
Several techniques can be employed to identify alkenes within a mixture of organic compounds. In the context of "Question Tech 9" and the yellow box, let's examine the most relevant:
1. Visual Inspection and Structural Formula Analysis:
This is the first and often most crucial step. Carefully examine the provided structural formulas of the compounds within the yellow box. Look for the presence of a carbon-carbon double bond (C=C). This is the definitive characteristic of an alkene. Be meticulous; a single missed double bond could lead to an incorrect identification.
2. Spectroscopic Analysis:
Advanced techniques provide conclusive evidence of the presence of a double bond. While not always applicable in a simplified "Question Tech 9" scenario, understanding these methods enhances your overall comprehension.
- Infrared (IR) Spectroscopy: Alkenes exhibit a characteristic absorption band in the IR spectrum typically between 1620-1680 cm⁻¹. This absorption arises from the stretching vibration of the C=C double bond.
- Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Spectroscopy: ¹H NMR and ¹³C NMR spectroscopy can provide valuable information about the structural environment around the double bond. Alkenyl protons (attached directly to the double bond carbons) typically resonate in a specific chemical shift range. Similarly, the carbon atoms involved in the double bond exhibit distinct chemical shifts.
- Mass Spectrometry (MS): While not directly identifying the double bond, MS provides information about the molecular weight and fragmentation pattern, which can be used in conjunction with other data to confirm the presence of an alkene.
3. Chemical Tests:
Certain chemical tests can be employed to specifically detect the presence of alkenes. While less common in modern analytical chemistry, understanding these reactions is beneficial for conceptual understanding.
- Bromine Test: Alkenes readily react with bromine (Br₂) in a colorless solution, resulting in a decolorization of the bromine solution. This is due to the addition of bromine across the double bond. This test is highly specific for unsaturated compounds containing double or triple bonds. Alkanes do not react with bromine under similar conditions.
- Baeyer's Test: Alkenes react with dilute potassium permanganate (KMnO₄) solution, causing a change in color from purple to brown. This reaction involves the oxidation of the alkene to a diol. This test is useful in distinguishing alkenes from alkanes, which do not react under these conditions.
Applying the Strategies to "Question Tech 9": A Hypothetical Example
Let's assume "Question Tech 9" presents us with five organic compounds within the yellow box:
- CH₃CH₂CH₃ (Propane – Alkane)
- CH₃CH=CH₂ (Propene – Alkene)
- CH₃CH₂CH₂OH (Propan-1-ol – Alcohol)
- CH₃C≡CH (Propyne – Alkyne)
- CH₃CH₂CHO (Propanal – Aldehyde)
Using the techniques outlined above:
-
Visual Inspection: We immediately identify CH₃CH=CH₂ (Propene) as the only compound possessing a carbon-carbon double bond (C=C). Therefore, it is the alkene.
-
Spectroscopic Analysis (Hypothetical): If spectroscopic data were provided, we'd look for the characteristic C=C stretching frequency in the IR spectrum (~1650 cm⁻¹) and specific chemical shifts in ¹H and ¹³C NMR spectra associated with the alkene group.
-
Chemical Tests (Hypothetical): The bromine test would decolorize when added to the solution containing propene, while the other compounds would not show any reaction. Similarly, Baeyer's test would change the purple solution to brown in the presence of propene.
Expanding the Scope: Complex Scenarios and Considerations
While the example above presents a straightforward case, real-world scenarios can be significantly more complex. Consider these factors when approaching more challenging problems:
- Multiple Alkenes: The yellow box might contain multiple compounds with alkene functionalities. Careful examination and potentially spectroscopic analysis would be necessary to identify all of them.
- Isomerism: Different alkenes might be isomers, differing only in the arrangement of atoms. This would necessitate careful consideration of structural formulas and potentially advanced spectroscopic analysis to distinguish between them.
- Functional Group Interferences: Other functional groups might be present in the same molecule as an alkene. Careful interpretation of the data would be essential to identify the presence of both functional groups.
- Reaction Conditions: In chemical tests, reaction conditions, such as temperature, concentration, and reaction time, can significantly affect the outcome and must be considered.
- Impurities: The sample might contain impurities that interfere with the identification process. Appropriate purification techniques might be necessary before accurate identification can be achieved.
Conclusion: Mastering Alkene Identification
Identifying alkenes successfully hinges on a robust understanding of their fundamental properties and the ability to apply various identification techniques strategically. The hypothetical "Question Tech 9" scenario serves as a valuable training ground. By systematically analyzing structural formulas, employing spectroscopic methods (when available), and understanding the principles of chemical tests, you can confidently navigate the complexities of alkene identification in organic chemistry. Remember, practice makes perfect. The more you engage with these problems, the more adept you will become at recognizing and distinguishing alkenes within a range of organic compounds. The key is meticulous attention to detail and a systematic approach to problem-solving.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Refers To The Muscles Ability To Be Stretched Or Extended
Mar 15, 2025
-
The Elevated Ridges Of The Brain Are Called The
Mar 15, 2025
-
An Example Of Rebating Would Be
Mar 15, 2025
-
Rn Mental Health Online Practice 2023 B
Mar 15, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Is Not A Type Of Hair
Mar 15, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Question Tech 9 Select The Alkene In The Yellow Box . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
