The Combining Form That Means Thorax Chest Chest Cavity Is
Holbox
Mar 19, 2025 · 7 min read
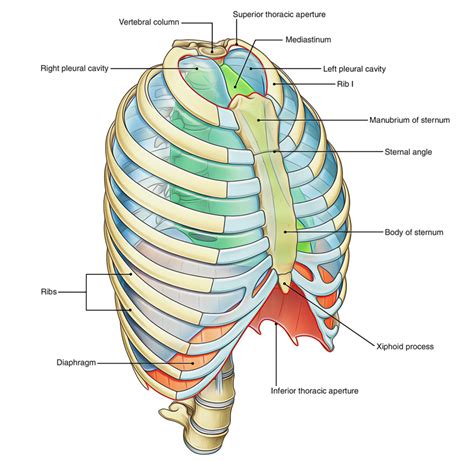
Table of Contents
The Combining Form That Means Thorax, Chest, Chest Cavity: A Comprehensive Guide
The human thorax, or chest cavity, is a vital region housing critical organs like the heart and lungs. Understanding its anatomical terminology is crucial for anyone studying medicine, anatomy, or related fields. This article delves deep into the combining form that signifies this crucial body part, exploring its etymology, usage in medical terminology, and clinical relevance. We'll uncover the richness of the language used to describe this region, going beyond simple definitions to illuminate its nuanced meaning and application.
Understanding Combining Forms in Medical Terminology
Before diving into the specific combining form, let's establish the foundational importance of combining forms in medical terminology. These linguistic building blocks, often derived from Greek or Latin roots, are essential for constructing precise and unambiguous medical terms. They act as prefixes, suffixes, or roots, each carrying specific meaning, enabling the creation of complex terms describing various anatomical structures, physiological processes, or pathological conditions. Mastering these forms is key to deciphering and understanding medical language.
Combining forms provide efficiency and precision. Instead of using lengthy descriptive phrases, concise terms built from combining forms convey intricate medical information quickly and accurately. This efficiency is vital in a healthcare setting where time and clarity are paramount.
Thorac/o-: The Combining Form for Thorax
The combining form that most directly and commonly refers to the thorax, chest, or chest cavity is thorac/o-. This form originates from the Greek word "thorax," meaning "breastplate" or "chest." Its use consistently denotes the anatomical region encompassing the area between the neck and the abdomen, including the ribs, sternum, and associated muscles and organs.
Variations and Related Combining Forms
While thorac/o- is the most prevalent and widely used combining form, it's important to note that certain variations and related terms exist. This reflects the evolution of medical terminology and the nuanced ways in which different aspects of the thoracic region may be described.
-
Pector/o-: This combining form, derived from the Latin word "pectus" meaning "breast" or "chest," is often used interchangeably with thorac/o-. However, pector/o- sometimes carries a more specific connotation, focusing on the anterior (front) aspect of the chest wall.
-
Steth/o-: Derived from the Greek word "stethos" meaning "chest," this combining form is frequently used in terms related to auscultation (listening to sounds within the body), particularly focusing on the sounds of the heart and lungs. Think of a stethoscope – the instrument's name is derived from this combining form.
These slight variations highlight the rich tapestry of medical terminology and the need for precise application of each form to accurately convey the intended anatomical region and clinical context.
Clinical Applications of Thorac/o-
The combining form thorac/o- is a cornerstone in numerous medical terms describing various aspects of the thorax, its structures, and related conditions. Let's explore some examples:
Terms Related to Thoracic Structures
-
Thoracotomy: This term combines thorac/o- with "-tomy," meaning "incision." A thoracotomy is a surgical procedure involving an incision into the chest wall, often performed to access the heart, lungs, or other thoracic organs.
-
Thoracoscopy: Combining thorac/o- with "-scopy," meaning "visual examination," thoracoscopy describes a minimally invasive surgical procedure that uses a small camera (thoracoscope) inserted through a small incision to examine the inside of the chest cavity.
-
Thoracic Cage: This straightforward term uses thorac/o- directly to denote the bony structure of the thorax, comprised of the ribs, sternum, and vertebrae.
-
Thoracic Aorta: This term describes the portion of the aorta that passes through the thorax, supplying oxygenated blood to the organs within the chest cavity.
-
Thoracic Duct: This term signifies the largest lymphatic vessel in the body, which collects lymph from the lower body and the left side of the upper body and drains it into the left subclavian vein.
Terms Related to Thoracic Conditions
-
Thoracocentesis: This term, combining thorac/o- with "-centesis," meaning "surgical puncture," refers to a procedure involving puncturing the chest wall to remove fluid from the pleural space (the space between the lungs and the chest wall). This is commonly performed to treat pleural effusions.
-
Thoracic Trauma: This broadly encompasses any injury to the chest, ranging from minor bruises to life-threatening conditions such as pneumothorax (collapsed lung) or hemothorax (blood in the pleural space). The severity of thoracic trauma can vary widely.
-
Thoracic Outlet Syndrome: This term refers to a condition characterized by compression of nerves and blood vessels in the space between the collarbone and the first rib, causing pain, numbness, and tingling in the arm and hand.
-
Thoracic Surgery: This broad term encompasses a wide range of surgical procedures performed on structures within the chest cavity, including heart surgery, lung surgery, and esophageal surgery.
Importance of Precision in Medical Terminology
The examples above illustrate the importance of precise use of combining forms like thorac/o-. Slight variations in terminology can significantly alter the meaning and clinical implications. This precision is crucial for effective communication among healthcare professionals, accurate diagnosis, and appropriate treatment planning. Ambiguity in medical terminology can have serious consequences, so mastering the nuances of combining forms is paramount.
Beyond the Combining Form: A Deeper Look at Thoracic Anatomy
Understanding thorac/o- is only one step in understanding the complexities of the thorax. A deeper comprehension requires exploring the intricate anatomical structures and physiological processes within this vital region.
Key Structures within the Thorax
-
Lungs: These paired respiratory organs are responsible for gas exchange, absorbing oxygen and releasing carbon dioxide.
-
Heart: This vital muscular organ pumps blood throughout the body, supplying oxygen and nutrients to tissues and removing waste products.
-
Trachea (windpipe): This tube connects the larynx (voice box) to the lungs, carrying air to and from the respiratory system.
-
Bronchi: The trachea branches into two bronchi, which further subdivide into smaller airways within the lungs.
-
Esophagus: This muscular tube connects the pharynx (throat) to the stomach, transporting food from the mouth to the digestive system.
-
Great Vessels: Major blood vessels, including the aorta, vena cavae, and pulmonary arteries and veins, are located within the thorax, playing a crucial role in cardiovascular function.
-
Diaphragm: This dome-shaped muscle separates the thoracic cavity from the abdominal cavity and plays a vital role in respiration.
Physiological Processes within the Thorax
The thorax is the central hub for many vital physiological processes:
-
Respiration: The lungs, trachea, bronchi, and diaphragm work together to facilitate the intake of oxygen and the expulsion of carbon dioxide.
-
Circulation: The heart pumps blood through the great vessels, ensuring efficient delivery of oxygen and nutrients to all parts of the body.
-
Protection of Vital Organs: The rib cage and sternum provide a protective barrier for the heart and lungs, shielding them from external trauma.
Further Exploration: Related Medical Specialties
Understanding the thorax involves familiarity with several key medical specialties:
-
Cardiology: This specialty focuses on the heart and cardiovascular system.
-
Pulmonology: This specialty concentrates on the respiratory system, including the lungs and airways.
-
Thoracic Surgery: This specialty involves surgical procedures performed on the organs and structures within the chest cavity.
-
Oncology: Thoracic oncologists specialize in cancers affecting the lungs, chest wall, and other structures within the thorax.
-
Critical Care Medicine: Physicians in this specialty often manage patients with severe thoracic injuries or illnesses.
Conclusion: The Enduring Significance of Thorac/o-
The combining form thorac/o- serves as a powerful testament to the precision and efficiency of medical terminology. Its consistent use, combined with a deep understanding of thoracic anatomy and physiology, equips healthcare professionals, students, and anyone interested in human biology with the essential vocabulary to navigate the complexities of this vital region of the body. From simple anatomical descriptions to complex clinical diagnoses, the significance of thorac/o- and its related terms in medical discourse remains paramount. Remember, continuous learning and a focus on precision are vital for those seeking to master medical terminology and its application in healthcare.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
The Knee Jerk Reflex Is An Example Of A
Mar 19, 2025
-
What Can Tangled Lead Wires Lead To
Mar 19, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Is A Third Party Network Analysis Tool
Mar 19, 2025
-
C A Mo Debe Almacenarse La Basura Y Los Art A Culos Reciclables
Mar 19, 2025
-
A Major Advantage Of Licensing Is
Mar 19, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about The Combining Form That Means Thorax Chest Chest Cavity Is . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
