The Average Variable Cost Per Sale At H
Holbox
Mar 10, 2025 · 5 min read
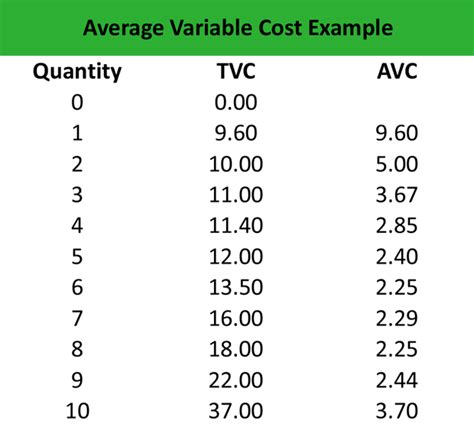
Table of Contents
Deconstructing the Average Variable Cost Per Sale at H&M: A Deep Dive
H&M, a global fashion powerhouse, operates on a vast scale, making a precise calculation of its average variable cost (AVC) per sale incredibly complex. Publicly available financial statements don't provide this granular level of detail. However, by analyzing their reported data and understanding the components of variable costs in the fast fashion industry, we can build a conceptual model to estimate and understand the factors influencing H&M's AVC per sale. This analysis will focus on identifying key variables, understanding their impact, and exploring potential future trends.
Understanding Average Variable Cost (AVC)
Before diving into H&M specifics, let's define average variable cost. AVC is the total variable costs of production divided by the number of units produced (in this case, sales). Variable costs are expenses that fluctuate directly with the volume of sales. Unlike fixed costs (rent, salaries of permanent staff), variable costs increase or decrease depending on the number of garments sold.
Key Variable Costs for H&M:
-
Raw Materials: This is arguably the largest component of H&M's variable costs. The cost of fabrics, threads, buttons, zippers, and other materials directly impacts the cost of production and fluctuates based on sales volume. Fluctuations in cotton prices, synthetic fiber costs, and global supply chain issues significantly affect this component.
-
Manufacturing Costs: H&M outsources a significant portion of its manufacturing. The cost of labor, factory overhead (electricity, machinery usage), and transportation from factories to distribution centers are all variable costs directly tied to the number of garments produced. Changes in minimum wages in manufacturing countries or fluctuations in fuel prices directly impact this cost.
-
Logistics and Distribution: Getting garments from factories to stores involves substantial variable costs. These include transportation expenses (shipping, trucking), warehousing costs (storage, handling), and the cost of last-mile delivery (if applicable for online orders). Fuel prices, warehouse capacity, and efficient logistics management are key factors here.
-
Marketing and Sales Commissions (Variable Portion): While H&M's overall marketing budget is a mix of fixed and variable costs, a portion of their marketing expenditure can be considered variable. For example, sales commissions paid to employees or performance-based marketing campaigns (online advertising based on clicks or sales) directly correlate with sales volume.
-
Direct Labor (in-store): While a portion of H&M's in-store staff costs are fixed (salaries of permanent employees), some components, like part-time staff or commission-based pay for sales associates, can be considered variable costs tied to sales volume.
Estimating H&M's AVC Per Sale: A Conceptual Model
Due to the lack of publicly available granular data, we'll construct a hypothetical model. Let's assume a simplified scenario:
Assumptions:
-
Average Selling Price (ASP): Let's assume an average selling price of $25 per garment. This is a simplification, as H&M sells a wide range of products at various price points.
-
Sales Volume: H&M sells billions of garments annually. Let's hypothetically assume 1 billion garments sold in a year.
-
Variable Cost Percentage: A reasonable estimation for the variable cost percentage in the fast fashion industry ranges from 40% to 60% of the selling price. For our model, let's assume a variable cost percentage of 50%.
Calculation:
-
Total Revenue: 1 billion garments * $25/garment = $25 billion
-
Total Variable Costs: $25 billion * 50% = $12.5 billion
-
Average Variable Cost Per Sale: $12.5 billion / 1 billion garments = $12.50 per garment
Therefore, in our simplified model, H&M's estimated AVC per sale is $12.50.
Factors Influencing H&M's AVC Per Sale:
Several factors can significantly impact H&M's actual AVC per sale:
-
Raw Material Prices: Fluctuations in cotton, polyester, and other material prices directly influence the cost of production. Increased prices lead to higher AVC.
-
Manufacturing Costs and Labor: Changes in minimum wages in manufacturing countries, factory overhead costs, and transportation expenses from overseas factories directly affect the AVC.
-
Supply Chain Efficiency: Effective supply chain management, including optimized logistics and inventory management, can significantly reduce variable costs.
-
Currency Fluctuations: H&M operates globally, so exchange rate fluctuations between currencies can affect the cost of imported materials and manufacturing.
-
Technological Advancements: Automation in manufacturing and improved technologies in logistics can lead to reduced variable costs.
-
Sustainability Initiatives: H&M's commitment to more sustainable materials and practices might increase initial raw material costs, potentially impacting the AVC in the short term. However, it could potentially lower costs in the long run through improved efficiency and reduced waste.
Analyzing the Impact of External Factors:
-
Geopolitical Instability: Global events, like trade wars or pandemics, can significantly disrupt supply chains and lead to increased variable costs due to delays and shortages.
-
Economic Conditions: Economic downturns can impact consumer spending, potentially reducing sales volume and increasing the AVC per sale if fixed costs are spread over fewer units.
-
Competition: Intense competition in the fast fashion industry forces H&M to maintain competitive pricing, potentially squeezing profit margins and impacting the AVC.
Future Trends and Implications:
-
Increased Automation: The adoption of automation in manufacturing will likely reduce labor costs, lowering the AVC.
-
Sustainable Sourcing: The shift towards sustainable and ethical sourcing practices might lead to higher raw material costs initially, but long-term benefits could outweigh the initial increase.
-
Supply Chain Diversification: H&M might diversify its manufacturing base to reduce reliance on single regions and mitigate risks associated with geopolitical instability.
-
E-commerce Growth: The increasing dominance of online sales necessitates investments in efficient e-commerce logistics, impacting variable costs related to delivery and warehousing.
Conclusion:
Determining the precise average variable cost per sale for H&M is challenging without internal data. However, by understanding the key components of variable costs in the fast fashion industry and constructing a conceptual model, we can gain insights into the factors influencing H&M's AVC. The interplay between raw material prices, manufacturing costs, logistics, and external factors significantly impacts this crucial metric. By proactively managing these elements and adapting to future trends like automation and sustainable sourcing, H&M can optimize its cost structure and maintain its competitiveness in the ever-evolving global fashion landscape. Further research utilizing financial modeling techniques and deeper industry analysis would be required for a more precise and comprehensive understanding of H&M's AVC per sale.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
You Are Placing Teams In Your Office Building
Mar 10, 2025
-
Find The Expansion Using Combinatorial Reasoning
Mar 10, 2025
-
What Are The Two Parts Of A Mac Address Called
Mar 10, 2025
-
Discuss The Difference Between R And P
Mar 10, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Statements Is Are Correct
Mar 10, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about The Average Variable Cost Per Sale At H . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
