Sustainable Competitive Advantage Exists When A Firm Blank______.
Holbox
Mar 16, 2025 · 6 min read
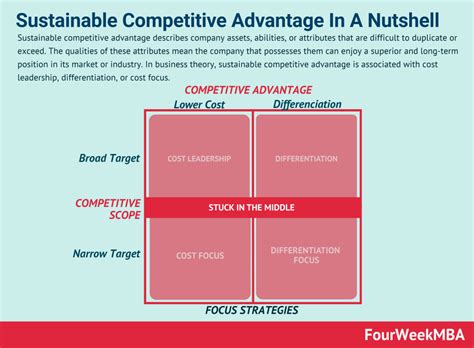
Table of Contents
Sustainable Competitive Advantage Exists When a Firm: A Deep Dive into Value Creation and Firm Performance
A sustainable competitive advantage is the holy grail for any business. It's the elusive state where a company consistently outperforms its rivals, building a resilient and enduring market position. But what exactly is a sustainable competitive advantage, and when does a firm achieve it? The answer isn't simply filling in the blank with a single word. It's a multifaceted concept rooted in a firm's ability to create and capture value in ways that are difficult for competitors to imitate or neutralize. This article explores the critical components of sustainable competitive advantage, delving into the resources, capabilities, and strategies required to achieve and maintain this coveted position.
What is a Sustainable Competitive Advantage?
A sustainable competitive advantage exists when a firm is able to consistently generate higher profits than its competitors over a prolonged period. This isn't a fleeting triumph based on a short-term market trend or a lucky break; it's a durable position built on the firm's inherent strengths and strategic acumen. Crucially, a sustainable competitive advantage is difficult for competitors to imitate or substitute. This difficulty stems from several key factors, which we will examine in detail.
The VRIN Framework: Assessing Competitive Advantage
The VRIN framework provides a useful lens for analyzing whether a firm possesses resources and capabilities that could lead to a sustainable competitive advantage. Each element is crucial:
- Valuable: The resources and capabilities must create value for customers. This value could manifest as lower prices, superior quality, unique features, or better customer service. Essentially, they must help the firm meet market demands better than competitors.
- Rare: The resources and capabilities should be uncommon; not widely possessed by competitors. If every firm has access to the same resources, there is no competitive advantage to be gained.
- Inimitable: The resources and capabilities must be difficult to imitate. This is crucial for sustainability. Competitors should face significant obstacles in replicating what the firm does. This often comes down to complex processes, unique knowledge, or strong brand recognition.
- Non-substitutable: There shouldn't be readily available strategic substitutes for the resources and capabilities. If competitors can achieve similar results through different means, the advantage is diminished.
Key Resources and Capabilities Leading to Sustainable Competitive Advantage:
Sustainable competitive advantage isn't about simply having good products; it's about possessing unique and valuable resources and capabilities. These can include:
1. Tangible Resources: These are physical assets the firm controls. Examples include:
- Efficient Manufacturing Facilities: A state-of-the-art manufacturing plant can lead to lower production costs and higher efficiency, providing a cost advantage.
- Patented Technologies: Exclusive rights to use a specific technology provide a significant barrier to entry and a source of competitive advantage.
- Strong Distribution Networks: Effective distribution channels ensure products reach customers efficiently and cost-effectively.
2. Intangible Resources: These are less visible assets, but often more valuable. They include:
- Strong Brand Reputation: A well-established brand with positive customer perception commands premium prices and increased loyalty.
- Proprietary Technology: Unique technology, beyond simple patents, can be extremely difficult to replicate.
- Organizational Culture: A strong, positive culture fosters innovation, employee engagement, and efficiency. This culture is difficult to replicate, forming a significant competitive barrier.
- Intellectual Property (IP): This encompasses patents, trademarks, copyrights, and trade secrets, providing a significant competitive edge.
3. Capabilities: These are the processes and skills a firm uses to transform resources into value. Examples include:
- Superior Innovation Capabilities: The ability to continuously develop and introduce new products or services provides a powerful advantage.
- Efficient Supply Chain Management: A well-managed supply chain ensures cost-effectiveness, responsiveness to market changes, and high quality.
- Effective Marketing and Sales: Strong marketing and sales capabilities are crucial for reaching target customers and achieving strong market share.
- Excellent Customer Service: Providing exceptional customer service builds customer loyalty and generates positive word-of-mouth marketing.
Strategies for Building Sustainable Competitive Advantage:
Building a sustainable competitive advantage requires careful planning and execution. Key strategic approaches include:
- Cost Leadership: Achieving the lowest cost of production and distribution in the industry allows firms to offer lower prices than competitors while still maintaining profitability. This requires operational efficiency, economies of scale, and effective cost management.
- Differentiation: Offering unique products or services that customers value highly allows firms to charge premium prices. This could involve superior quality, innovative features, strong branding, or excellent customer service.
- Focus: Concentrating on a specific niche market segment allows firms to develop specialized expertise and cater to the unique needs of that segment. This could involve targeting a specific customer demographic, geographical area, or product category.
- Blue Ocean Strategy: This involves creating entirely new market spaces, avoiding direct competition altogether. This approach often requires innovation and creativity, identifying unmet customer needs and developing unique offerings.
Maintaining a Sustainable Competitive Advantage:
Building a sustainable competitive advantage is only half the battle. Maintaining it requires continuous effort and adaptation:
- Continuous Innovation: Staying ahead of the curve requires continuous investment in research and development, and a commitment to innovation.
- Adaptability: The ability to adapt to changing market conditions, technological advancements, and competitive pressures is crucial for long-term success.
- Strong Organizational Culture: A supportive, innovative culture fosters employee engagement, creativity, and a commitment to excellence.
- Effective Monitoring: Continuously monitoring the competitive landscape, identifying emerging threats, and adapting strategies accordingly is critical.
Overcoming Challenges to Sustainability:
Sustaining a competitive advantage is challenging; firms face various threats:
- Imitation: Competitors will always try to copy successful strategies. Firms need to build barriers to imitation through patents, strong brands, complex processes, and superior capabilities.
- Technological Change: Rapid technological change can render existing competitive advantages obsolete. Firms must invest in R&D and adapt quickly to new technologies.
- Globalization: Increased globalization intensifies competition, making it harder to maintain a unique market position. Firms need to develop global strategies and manage international competition effectively.
- Economic Downturns: Economic recessions can severely impact demand and profitability. Firms need to develop resilient business models and manage costs effectively.
Conclusion: Sustainable Competitive Advantage – A Continuous Pursuit
In conclusion, a sustainable competitive advantage exists when a firm consistently outperforms its competitors over a prolonged period due to possessing valuable, rare, inimitable, and non-substitutable resources and capabilities, implemented through well-chosen strategies and continuously adapted to the evolving market landscape. It’s not a destination, but a journey requiring constant vigilance, innovation, and a deep understanding of both internal strengths and external forces. The key is to create value in a way that is difficult for rivals to replicate, ensuring the firm's enduring success and market leadership. The pursuit of this competitive edge demands a holistic approach, blending strategic planning, operational excellence, and a relentless focus on customer needs and market dynamics.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Name The Membranous Encasement Surrounding The Brain
Mar 17, 2025
-
What Is The Definition For The Protection Mission Area
Mar 17, 2025
-
Essentials Of Radiographic Physics And Imaging Chapter 12
Mar 17, 2025
-
On July 1st A Company Receives An Invoice For 800
Mar 17, 2025
-
Why Is It Important To Engage Communities In Preparedness Efforts
Mar 17, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Sustainable Competitive Advantage Exists When A Firm Blank______. . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
