Ring Opening Arrow Pushing Mechanism Under Basic Conditions
Holbox
Mar 17, 2025 · 5 min read
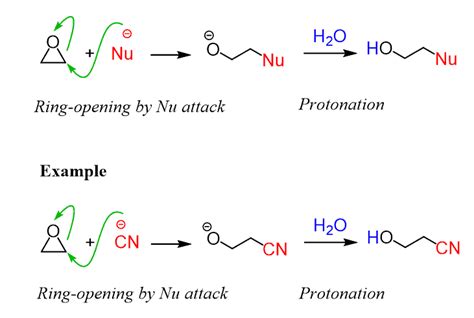
Table of Contents
Ring-Opening Reactions under Basic Conditions: A Comprehensive Guide to Arrow Pushing Mechanisms
Ring-opening reactions are fundamental transformations in organic chemistry, offering versatile routes to synthesize a wide array of functionalized molecules. Understanding the underlying mechanisms, particularly under basic conditions, is crucial for predicting reaction outcomes and designing efficient synthetic strategies. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of ring-opening mechanisms under basic conditions, utilizing arrow-pushing formalism to illustrate the electron flow involved in these reactions. We will explore various ring systems and the nuances of base-induced ring opening.
Understanding Basic Conditions in Ring-Opening Reactions
Before diving into specific mechanisms, it's essential to define "basic conditions" in the context of ring-opening reactions. These conditions typically involve the presence of a strong base, such as hydroxide (OH⁻), alkoxide (RO⁻), or amide (NR₂⁻) ions. These bases facilitate ring opening by abstracting a proton from a suitable site within the ring system, generating a nucleophilic species capable of undergoing ring scission. The strength of the base, the solvent, and the temperature all play significant roles in determining the reaction pathway and the final products.
Key Mechanisms of Base-Induced Ring Opening
Several mechanisms govern base-induced ring opening, each with its own characteristics and applications. The most common mechanisms include:
1. Nucleophilic Attack on an Electrophilic Carbon: Epoxides and Aziridines
Epoxides (three-membered cyclic ethers) and aziridines (three-membered cyclic amines) are particularly susceptible to base-induced ring opening due to the inherent ring strain. The highly strained three-membered ring makes these compounds highly reactive towards nucleophiles.
Mechanism: Under basic conditions, the base abstracts a proton (often from the nucleophile itself, creating a more powerful nucleophile), increasing the nucleophilicity of the nucleophile. The nucleophile then attacks the less substituted carbon atom of the epoxide or aziridine (SN2-type attack). This attack results in the cleavage of the C-O or C-N bond and the formation of a new carbon-nucleophile bond.
Example: Epoxide Ring Opening
Let's consider the ring opening of an epoxide with a hydroxide ion:
O
/ \
/ \ + OH⁻ ---> HO-CH₂-CH₂-OH
C----C
Arrow-Pushing:
- The lone pair of electrons on the oxygen of the hydroxide ion attacks the less hindered carbon of the epoxide.
- Simultaneously, the C-O bond in the epoxide breaks, and the electrons move to the oxygen atom, generating an alkoxide ion.
- Protonation of the alkoxide ion by water (or another proton source) yields the final diol product.
Example: Aziridine Ring Opening
Similar mechanism applies to aziridine ring opening.
2. β-Elimination: Cyclopropanes and Other Strained Rings
Cyclopropanes and other strained rings can undergo base-induced ring opening via a β-elimination pathway. This mechanism involves the abstraction of a proton from a carbon atom adjacent to the ring, leading to the formation of a carbanion. The carbanion then undergoes elimination to open the ring, forming an alkene.
Mechanism:
- The base abstracts a proton from a carbon atom adjacent to the ring (β-carbon).
- The electrons from the C-H bond form a double bond, breaking the ring.
Example: Cyclopropane Ring Opening
The ring opening of a cyclopropane with a strong base such as tert-butoxide (t-BuO⁻) often involves a β-elimination.
Arrow Pushing:
- The base abstracts a proton from a carbon adjacent to the ring.
- The electrons from the C-H bond form a double bond with one of the carbon atoms in the ring, breaking the ring.
3. Concerted Mechanisms: Specific Ring Systems
Some ring systems undergo ring opening via concerted mechanisms, where bond breaking and bond formation occur simultaneously in a single step. This often involves a cyclic transition state. Examples include certain lactones and lactams under specific basic conditions. The detailed mechanism depends heavily on the specific ring system and base used.
Factors Influencing Base-Induced Ring Opening
Several factors influence the outcome of base-induced ring opening reactions:
- Base Strength: Stronger bases generally favor faster reaction rates and can lead to different reaction pathways.
- Steric Hindrance: Steric effects around the ring can influence the regioselectivity and stereoselectivity of the ring opening. Bulky bases might favor attack at less hindered sites.
- Solvent: The choice of solvent plays a crucial role in the solvation of the base and the intermediate species, affecting reaction rates and selectivity. Protic solvents can participate in proton transfer steps.
- Temperature: Temperature influences the reaction kinetics. Higher temperatures usually accelerate the reaction.
- Nature of the Ring System: The ring size, the presence of substituents, and the heteroatoms within the ring all influence the reactivity and mechanism of ring opening.
Applications of Base-Induced Ring Opening
Base-induced ring opening reactions are indispensable in organic synthesis, finding applications in the preparation of a vast array of molecules, including:
- Pharmaceuticals: Synthesis of various drug molecules utilizes ring-opening reactions as key steps.
- Polymers: Ring-opening polymerization (ROP) is a significant method for producing polymers with controlled architecture and properties. Many biodegradable polymers are synthesized via ROP.
- Natural Product Synthesis: Many natural products contain complex ring systems, and base-induced ring opening reactions are frequently used in their total synthesis.
- Materials Science: Functionalized molecules synthesized via ring opening are used in the design and development of novel materials.
Advanced Considerations and Future Directions
While this guide provides a foundational understanding of base-induced ring opening, more complex scenarios exist. These include:
- Regioselectivity and Stereoselectivity: Predicting and controlling the regio- and stereochemical outcome of ring opening is a critical challenge. Careful choice of base, solvent, and reaction conditions is essential.
- Catalyst-Assisted Ring Opening: The use of catalysts can enhance the efficiency and selectivity of ring-opening reactions.
- Computational Studies: Computational chemistry methods provide valuable insights into reaction mechanisms and transition states, facilitating the design of more efficient synthetic routes.
Future research will likely focus on developing new catalysts, exploring novel reaction conditions, and utilizing advanced computational techniques to further understand and control base-induced ring-opening reactions. This will lead to more efficient and sustainable synthetic methods for preparing complex molecules with applications across various fields.
Conclusion
Base-induced ring-opening reactions are powerful tools in the organic chemist's arsenal. Understanding the mechanisms governing these reactions, as illustrated by the arrow-pushing formalism, is critical for designing effective synthetic strategies. By carefully considering the various factors influencing these reactions, chemists can harness their versatility to synthesize a wide range of valuable molecules. Further research and innovation in this area will continue to expand the possibilities of this important class of reactions.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
The Image Shows A Fracture On The
Mar 18, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Is Correct Regarding The Ph Scale
Mar 18, 2025
-
Drink Tea For A Stronger Immune System Chegg
Mar 18, 2025
-
Reinforcers Have Innate Reinforcing Qualities
Mar 18, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Statements Is True About Markings
Mar 18, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Ring Opening Arrow Pushing Mechanism Under Basic Conditions . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
