The Image Shows A Fracture On The
Holbox
Mar 18, 2025 · 6 min read
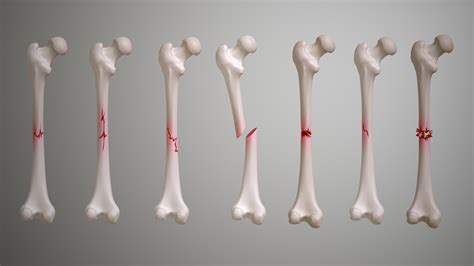
Table of Contents
Decoding the Image: Understanding Fractures from Visual Representation
The image shows a fracture—but what kind of fracture? This seemingly simple statement opens a door to a complex world of bone injuries, requiring careful analysis of the image itself and a deep understanding of fracture classification. This article delves into the intricacies of interpreting fracture images, exploring various types, their causes, and the crucial role of imaging in diagnosis and treatment planning. We'll also touch upon the significance of accurate fracture description for effective communication among healthcare professionals.
The Importance of Image Quality in Fracture Assessment
Before we delve into the specifics of fracture types, it's crucial to acknowledge the critical role of image quality. A blurry or poorly positioned X-ray, CT scan, or MRI can significantly hinder accurate diagnosis. Sharp, clear images are paramount for identifying:
- Fracture Line: The precise location and orientation of the fracture line are essential. Is it transverse, oblique, spiral, comminuted, or another type?
- Fragment Displacement: The extent to which bone fragments are separated and shifted from their original position. This significantly impacts treatment decisions.
- Soft Tissue Involvement: The image should also be assessed for signs of soft tissue swelling, hematoma (blood clot), or other injuries that might accompany the fracture.
- Associated Injuries: Sometimes, the image may reveal additional injuries, such as dislocations or other fractures in nearby bones.
Classifying Fractures: A Systematic Approach
Fractures are classified using various systems, often incorporating the fracture's location, pattern, and the degree of displacement. Some commonly used classifications include:
1. Based on Fracture Pattern:
- Transverse Fractures: These fractures occur at a right angle to the long axis of the bone. They are often caused by direct impact forces. The image might show a clean break across the bone.
- Oblique Fractures: These fractures run at an angle to the long axis of the bone. They are often caused by a twisting or shearing force. The image will show a slanted fracture line.
- Spiral Fractures: These fractures encircle the bone in a spiral pattern, typically resulting from a twisting injury. The image will demonstrate a spiral-shaped fracture line.
- Comminuted Fractures: These fractures involve multiple fragments of bone. They are often caused by high-energy impacts. The image reveals several bone pieces at the fracture site.
- Segmental Fractures: These are characterized by two or more fracture lines separating a segment of the bone.
- Avulsion Fractures: These fractures occur when a fragment of bone is pulled away from the main bone by a ligament or tendon.
- Impacted Fractures: One bone fragment is driven into another. The image may show one bone end telescoped into the other.
- Greenstick Fractures: These incomplete fractures occur primarily in children, where the bone bends and cracks but doesn't break completely. One side of the bone remains intact.
- Stress Fractures: These hairline fractures result from repetitive stress or overuse. They might be subtle and difficult to see on initial X-rays, often requiring further imaging techniques like bone scans.
- Pathologic Fractures: These fractures occur in bones weakened by underlying disease such as cancer or osteoporosis.
2. Based on Displacement:
- Non-displaced Fractures: The bone fragments remain aligned and in their normal anatomical position.
- Displaced Fractures: The bone fragments are separated and misaligned. The degree of displacement influences treatment strategy.
3. Based on Location:
Fractures are also named based on their location within the bone. For example, a fracture in the shaft of a long bone is termed a diaphyseal fracture, while a fracture at the end of the bone near a joint is called an epiphyseal fracture. Specific anatomical locations (e.g., femoral neck fracture, tibial plateau fracture) are crucial for accurate communication and targeted treatment.
The Role of Advanced Imaging Techniques
While X-rays are often the initial imaging modality used for fracture assessment, other techniques provide more detailed information:
- CT Scans: These scans provide cross-sectional images, offering a three-dimensional view of the fracture. They are especially useful in complex fractures with multiple fragments or when assessing the extent of soft tissue damage.
- MRI Scans: MRIs provide excellent visualization of soft tissues, making them valuable for assessing ligament and tendon injuries associated with the fracture. They are also useful in detecting stress fractures.
- Bone Scans: These nuclear medicine scans help identify stress fractures or other subtle fractures that may not be visible on X-rays.
Clinical Significance of Accurate Fracture Description
Precise fracture description is essential for:
- Effective Communication: Clear and concise descriptions using standardized terminology ensure that all healthcare professionals involved in the patient's care understand the nature and severity of the injury.
- Treatment Planning: The type and extent of the fracture directly influence the choice of treatment, which may range from simple immobilization with a cast or splint to more complex surgical procedures such as open reduction and internal fixation (ORIF).
- Prognosis Assessment: Accurate fracture classification aids in predicting the patient's recovery time and potential complications.
- Legal Documentation: Detailed descriptions are critical for medical-legal purposes, providing a clear record of the injury and treatment received.
Beyond the Image: The Complete Clinical Picture
Interpreting a fracture image is just one piece of the puzzle. A comprehensive clinical assessment considers:
- Patient History: Understanding the mechanism of injury, the patient's age and overall health, and any pre-existing medical conditions is crucial.
- Physical Examination: A thorough physical examination helps assess the extent of pain, swelling, and neurological function.
- Neurovascular Status: Checking for nerve and blood vessel damage is critical, as these structures can be compromised in severe fractures.
The Future of Fracture Diagnosis: Technological Advancements
Technological advancements continue to revolutionize fracture diagnosis, with the advent of:
- 3D-printed models: These models allow surgeons to plan complex procedures with greater precision.
- Advanced image processing software: Software programs can enhance image quality, aid in fracture classification, and assist in surgical planning.
- Artificial intelligence (AI): AI algorithms are increasingly being used to assist in the detection and classification of fractures, potentially improving accuracy and efficiency.
Conclusion:
The image shows a fracture, but the specific type and its implications require careful analysis. Through a systematic approach combining advanced imaging techniques, detailed clinical evaluation, and a strong understanding of fracture classification, healthcare professionals can accurately diagnose, treat, and manage fractures effectively, ultimately improving patient outcomes. Accurate interpretation, informed by image quality and comprehensive clinical data, is the cornerstone of successful fracture management. This holistic approach ensures optimal treatment planning, leading to better patient recovery and minimizing potential long-term complications. The future of fracture diagnosis is bright, with technology constantly enhancing diagnostic capabilities and pushing the boundaries of precision medicine.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Equation Is Represented By The Graph Below
Mar 18, 2025
-
A Section Of Dna Has The Base Sequence Shown In
Mar 18, 2025
-
Draw The Shear And Moment Diagrams For The Beam Chegg
Mar 18, 2025
-
Draw The Shear Diagram For The Beam Chegg
Mar 18, 2025
-
Eating Soup That Has Been Time Temperature Abused Can Result In
Mar 18, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about The Image Shows A Fracture On The . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
