Replace With An Expression That Will Make The Equation Valid
Holbox
Mar 24, 2025 · 5 min read
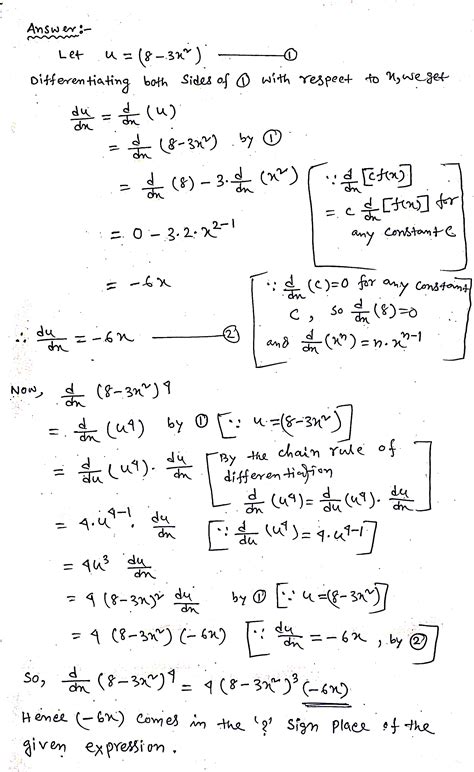
Table of Contents
- Replace With An Expression That Will Make The Equation Valid
- Table of Contents
- Replace With an Expression: Mastering Equation Validation
- Understanding Equation Validity
- Common Scenarios Requiring Expression Replacement
- 1. Solving Equations:
- 2. Simplifying Expressions:
- 3. Equivalent Fractions and Ratios:
- 4. Substituting Values:
- Strategies for Replacing Expressions
- Advanced Techniques and Considerations
- Error Avoidance and Troubleshooting
- Conclusion
- Latest Posts
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
Replace With an Expression: Mastering Equation Validation
Mathematical equations, the bedrock of scientific and logical reasoning, demand precision. A single misplaced symbol, a wrong operator, or an incorrect value can render an entire equation invalid. The challenge, therefore, lies not just in understanding the equation but in possessing the skills to replace elements to achieve validity. This isn't just about finding the right answer; it's about understanding the underlying principles and developing problem-solving strategies. This comprehensive guide delves into various techniques for replacing expressions within equations to ensure validity. We’ll explore different types of equations, common pitfalls, and advanced strategies to help you master this crucial skill.
Understanding Equation Validity
Before delving into techniques for replacing expressions, it's crucial to understand what constitutes a valid equation. An equation is considered valid if it maintains the equality between its left-hand side (LHS) and right-hand side (RHS). This means that after performing all the necessary operations on both sides, the result on the LHS must be numerically equivalent to the result on the RHS.
Key Aspects of Equation Validity:
- Equality: The fundamental principle is that the LHS must always equal the RHS.
- Order of Operations (PEMDAS/BODMAS): Parentheses/Brackets, Exponents/Orders, Multiplication and Division (from left to right), Addition and Subtraction (from left to right). Failure to adhere to this order can lead to incorrect results and invalidate the equation.
- Properties of Equality: Understanding properties like the addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division properties of equality is essential for manipulating equations without compromising validity. These properties allow you to perform operations on both sides of the equation simultaneously while maintaining equality.
- Variable Consistency: If variables are used, they must maintain consistent values throughout the equation. Substituting a different value for the same variable will invalidate the equation unless it's a valid mathematical substitution based on previously established relationships.
Common Scenarios Requiring Expression Replacement
Many scenarios in mathematics require replacing expressions to validate an equation. Let's examine some common ones:
1. Solving Equations:
This is arguably the most frequent scenario. Solving equations involves manipulating the equation algebraically until the variable (or unknown) is isolated on one side, revealing its value. This involves strategically replacing expressions to simplify and isolate the variable.
Example: 2x + 5 = 11
To solve for 'x', we need to replace expressions:
- Subtract 5 from both sides: 2x + 5 - 5 = 11 - 5 => 2x = 6
- Divide both sides by 2: 2x / 2 = 6 / 2 => x = 3
Replacing "2x + 5" with "11" and "2x" with "6" are examples of valid replacements within this process.
2. Simplifying Expressions:
Simplifying expressions aims to reduce the complexity of an equation without altering its value. This often involves combining like terms, factoring, expanding brackets, or applying algebraic identities. Replacing complex expressions with their simplified equivalents ensures equation validity.
Example: 3(x + 2) + 2x - 4
We can replace the expression with its simplified equivalent:
- Expand the brackets: 3x + 6 + 2x - 4
- Combine like terms: 5x + 2
Replacing "3(x + 2) + 2x - 4" with "5x + 2" maintains the equation's validity.
3. Equivalent Fractions and Ratios:
In fractions and ratios, equivalent expressions can replace existing ones without altering the equation's validity. This often involves simplifying fractions to their lowest terms or finding common denominators.
Example: (1/2)x + (1/4)x = 3
To simplify, we replace the fractional coefficients with an equivalent expression:
- Find a common denominator: (2/4)x + (1/4)x = 3
- Combine like terms: (3/4)x = 3
4. Substituting Values:
Sometimes, an equation contains variables that have known values. Replacing these variables with their numerical values helps validate the equation or find a solution.
Example: y = mx + c (where m=2 and c=3)
If x = 4, we can replace 'm', 'c', and 'x' with their values to solve for 'y':
y = 2(4) + 3 => y = 11
Strategies for Replacing Expressions
Here are some key strategies to ensure valid replacements:
- Maintain Equality: Any replacement must maintain the equality between the LHS and RHS.
- Apply Algebraic Rules: Use algebraic properties like distributive property, commutative property, associative property, etc., to simplify and replace expressions correctly.
- Check Your Work: Always verify your replacements by substituting the new expressions and checking if the equality still holds.
- Use Systematic Approaches: Follow a methodical approach, especially when dealing with complex equations. Break down the problem into smaller, manageable steps.
- Consider All Possible Solutions: Some equations have multiple solutions; ensure you explore and identify all possible valid replacements.
Advanced Techniques and Considerations
- Trigonometric Identities: In trigonometric equations, substituting equivalent trigonometric expressions using identities (e.g., sin²x + cos²x = 1) is crucial for simplification and validation.
- Logarithmic and Exponential Equations: Similar to trigonometric equations, manipulating logarithmic and exponential equations requires knowledge of their properties and the use of appropriate identities for valid replacements.
- Complex Numbers: When working with complex numbers, special care must be taken to ensure that all operations, including replacements, adhere to the rules governing complex number arithmetic.
- Matrices and Vectors: Replacing expressions in matrix and vector equations demands an understanding of matrix operations, including multiplication, addition, and inversion.
Error Avoidance and Troubleshooting
- Common Mistakes: Be cautious of common errors such as forgetting to apply the order of operations, incorrectly distributing negative signs, making mistakes in algebraic manipulation, and overlooking hidden simplifications.
- Systematic Debugging: If an equation doesn't validate after a replacement, meticulously review each step. Try substituting numerical values to pinpoint the error location.
- Seek External Review: If you're struggling, seeking a second opinion from a peer or tutor can be invaluable. A fresh perspective often highlights overlooked mistakes.
Conclusion
Replacing expressions within equations to maintain validity is a fundamental skill in mathematics. It requires a solid understanding of algebraic principles, order of operations, and equation properties. By mastering the strategies and techniques outlined in this guide, you'll significantly improve your ability to solve equations, simplify expressions, and confidently navigate more complex mathematical challenges. Remember to always maintain equality, use systematic approaches, and verify your work to ensure accuracy. Practice regularly to enhance your skill and proficiency in this crucial mathematical technique. The ability to validate equations through expression replacement is not only essential for academic success but also vital for practical applications in various fields, including science, engineering, and computer programming. So continue to practice, hone your skills, and enjoy the rewarding journey of mastering this important mathematical process.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
The Blood Platelet Counts Of A Group
Mar 26, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Research Designs Will Allow Cause And Effect Conclusions
Mar 26, 2025
-
A Means That Government Spending And Taxes Are Equal
Mar 26, 2025
-
How Can An Operation Prevent Cross Contamination In A Self Service Area
Mar 26, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Is An Intensive Property
Mar 26, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Replace With An Expression That Will Make The Equation Valid . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
