Put The Following Mitosis And Cytokinesis Images In Order
Holbox
Mar 18, 2025 · 5 min read
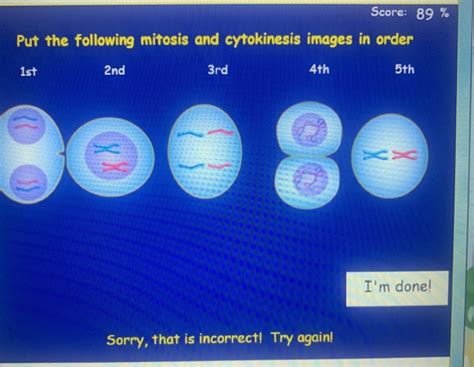
Table of Contents
Putting Mitosis and Cytokinesis Images in Order: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding the stages of mitosis and cytokinesis is fundamental to grasping cell division and the life cycle of eukaryotic organisms. This guide will walk you through the process, explaining each phase and providing tips for correctly ordering images depicting these crucial cellular events. We'll also explore the subtle differences between plant and animal cell cytokinesis.
What are Mitosis and Cytokinesis?
Mitosis is the process of nuclear division, where a single cell divides into two identical daughter cells. This process is essential for growth, repair, and asexual reproduction in organisms. Cytokinesis, on the other hand, is the division of the cytoplasm, resulting in two separate daughter cells. While mitosis focuses on the nucleus, cytokinesis completes the cell division process.
Mitosis is further divided into several distinct phases:
- Prophase: Chromosomes condense and become visible, the nuclear envelope breaks down, and the mitotic spindle begins to form.
- Prometaphase: Kinetochores (protein structures on chromosomes) attach to microtubules of the spindle.
- Metaphase: Chromosomes align at the metaphase plate (the equator of the cell).
- Anaphase: Sister chromatids separate and move to opposite poles of the cell.
- Telophase: Chromosomes arrive at the poles, the nuclear envelope reforms, and chromosomes decondense.
Cytokinesis, the final stage of the cell cycle, follows telophase. It involves the division of the cytoplasm, resulting in two separate daughter cells. The mechanism of cytokinesis differs slightly between plant and animal cells.
Identifying Key Features in Microscopic Images
To correctly sequence images of mitosis and cytokinesis, you need to learn to identify specific visual cues. Here’s a breakdown of the visual characteristics of each stage:
1. Interphase (Pre-Mitosis):
- Appearance: The nucleus is clearly visible, and chromosomes are not individually distinguishable. The chromatin appears as a diffuse material within the nucleus. The cell appears generally relaxed, with no visible mitotic spindle.
- Key Features: Undifferentiated chromatin, intact nuclear membrane.
2. Prophase:
- Appearance: Chromosomes begin to condense and thicken, becoming visible as distinct structures. The nuclear envelope is still largely intact, although it may begin to fragment.
- Key Features: Condensed chromosomes, intact (or partially fragmented) nuclear envelope, early spindle formation.
3. Prometaphase:
- Appearance: The nuclear envelope has completely broken down. Chromosomes continue to condense and become even more distinct. Kinetochores attach to microtubules of the mitotic spindle.
- Key Features: Fragmented nuclear envelope, condensed chromosomes, kinetochore attachment to spindle microtubules.
4. Metaphase:
- Appearance: Chromosomes align along the metaphase plate, an imaginary plane equidistant from the two poles of the cell. The chromosomes are at their most condensed state.
- Key Features: Chromosomes aligned at the metaphase plate, highly condensed chromosomes.
5. Anaphase:
- Appearance: Sister chromatids separate and move towards opposite poles of the cell. The cell elongates.
- Key Features: Sister chromatids separating, movement towards poles, cell elongation.
6. Telophase:
- Appearance: Chromosomes reach the poles, decondense, and become less visible. The nuclear envelope reforms around each set of chromosomes. The mitotic spindle disappears.
- Key Features: Chromosomes at poles, nuclear envelope reformation, decondensed chromosomes, spindle disappearance.
7. Cytokinesis (Animal Cells):
- Appearance: A cleavage furrow forms, constricting the cell membrane and pinching the cytoplasm into two separate daughter cells.
- Key Features: Cleavage furrow formation, constriction of cell membrane.
7. Cytokinesis (Plant Cells):
- Appearance: A cell plate forms in the center of the cell, expanding outwards until it reaches the cell wall, dividing the cytoplasm into two.
- Key Features: Cell plate formation, expansion of cell plate.
Sequencing Mitosis and Cytokinesis Images: A Step-by-Step Approach
-
Identify Interphase: Start by identifying the image showing the cell in interphase – the resting phase before mitosis begins. This image will have a clear, intact nucleus with diffuse chromatin.
-
Look for Chromosome Condensation: Next, look for images showing progressive chromosome condensation. Prophase will show slightly condensed chromosomes, while prometaphase and metaphase will exhibit highly condensed chromosomes.
-
Find the Metaphase Plate: The metaphase image will show chromosomes aligned at the metaphase plate. This is a crucial landmark in the sequence.
-
Observe Chromosome Separation: Anaphase is characterized by the separation of sister chromatids and their movement towards opposite poles.
-
Look for Nuclear Envelope Reformation: Telophase shows the reformation of the nuclear envelope around the separated chromosomes.
-
Distinguish Cytokinesis: Finally, identify the image depicting cytokinesis. In animal cells, this will be marked by a cleavage furrow; in plant cells, by a cell plate.
-
Check for Consistency: Once you've arranged the images, review the sequence to ensure a logical progression from interphase to cytokinesis.
Troubleshooting Common Mistakes
- Confusing Prophase and Metaphase: Remember that prophase shows chromosomes condensing and the nuclear envelope breaking down, while metaphase shows chromosomes aligned at the metaphase plate.
- Misinterpreting Anaphase: Ensure that you are identifying the actual separation of sister chromatids, not just their movement.
- Overlooking Cytokinesis: Cytokinesis is a critical part of the process, so ensure you correctly identify the image depicting the division of the cytoplasm.
- Differentiating Plant and Animal Cytokinesis: Understand the differences in how plant and animal cells divide their cytoplasm.
Advanced Considerations: Variations and Exceptions
While the stages of mitosis and cytokinesis are generally consistent across eukaryotic cells, variations can exist. For instance, the duration of each phase can vary depending on the cell type and environmental conditions. Furthermore, certain cell types may exhibit unusual mitotic behaviors. Understanding these nuances is vital for accurate interpretation of microscopic images.
Variations in Chromosome Number: Different organisms have different numbers of chromosomes. This will affect the visual appearance of the chromosomes during mitosis.
Variations in Spindle Organization: The arrangement of the mitotic spindle can vary slightly between different species and cell types.
Atypical Mitosis: In some cases, errors can occur during mitosis, resulting in abnormal chromosome segregation or cell division. Identifying these atypical patterns requires a deeper understanding of cellular processes.
Utilizing Resources for Enhanced Learning
While this guide provides a comprehensive overview, further exploration of educational resources will solidify your understanding. Textbooks, online tutorials, and interactive simulations can all contribute to your mastery of this complex subject. Consider exploring various microscopic images from different cell types to expand your visual recognition skills. The more images you analyze, the more proficient you will become in sequencing them accurately.
By thoroughly understanding the visual cues of each mitotic stage and practicing with various images, you'll develop the skills to confidently order images of mitosis and cytokinesis, providing a clear understanding of this fundamental cellular process. Remember, consistent practice is key to mastering the intricate details and achieving accuracy in your analysis.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Identify The Differential Equation Solved By
Mar 18, 2025
-
Radiolucent Lesion Apical To Tooth 30
Mar 18, 2025
-
A Legally Acceptable Id Has Which Characteristic
Mar 18, 2025
-
Ready To Eat Foods Are Defined As
Mar 18, 2025
-
Q5 1 Which Of The Following Is False
Mar 18, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Put The Following Mitosis And Cytokinesis Images In Order . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
