Prepaid Accounts Also Called Prepaid Expenses Are
Holbox
Mar 16, 2025 · 5 min read
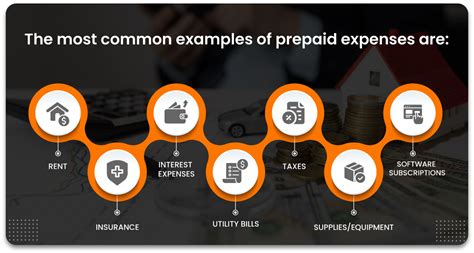
Table of Contents
Prepaid Accounts: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding and Managing Prepaid Expenses
Prepaid accounts, also known as prepaid expenses, represent a crucial aspect of financial accounting. Understanding how they function is vital for accurate financial reporting and effective business management. This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of prepaid accounts, explaining their nature, accounting treatment, and practical applications.
What are Prepaid Accounts?
Prepaid accounts are assets representing payments made for goods or services before they are consumed or utilized. Essentially, you're paying upfront for something you'll receive and use later. Think of it as an investment in future operations. This contrasts with expenses, which reflect costs incurred and consumed within the same accounting period.
The key characteristic distinguishing prepaid expenses from regular expenses lies in the future benefit. While expenses provide immediate value, prepaid accounts provide value in future periods. This future benefit is what classifies them as assets rather than expenses.
Examples of Common Prepaid Expenses:
- Insurance Premiums: Payments made for insurance coverage extending beyond the current accounting period.
- Rent: Advance rent payments covering multiple months.
- Subscriptions: Prepaid subscriptions for software, magazines, or online services.
- Office Supplies: Bulk purchases of stationery, printing paper, or other office supplies.
- Advertising: Prepaid advertising campaigns running over several months.
- Property Taxes: Advance payments for property taxes.
- Prepaid Interest: Interest paid in advance on a loan.
Accounting Treatment of Prepaid Expenses
The accounting treatment for prepaid expenses involves a two-step process:
1. Initial Recognition:
When a prepaid expense is initially paid, it's recorded as a debit to the specific prepaid account (e.g., Prepaid Insurance, Prepaid Rent) and a credit to cash or accounts payable (if purchased on credit). This increases the asset balance on the balance sheet.
Example: A company pays $12,000 for a one-year insurance policy on December 1, 2023. The journal entry would be:
| Account Name | Debit | Credit |
|---|---|---|
| Prepaid Insurance | $12,000 | |
| Cash | $12,000 | |
| To record prepaid insurance |
2. Amortization/Expense Recognition:
As the prepaid expense is used or consumed over time, a portion of it is recognized as an expense. This process is called amortization (for prepaid expenses with a lifespan exceeding one year) or expense recognition (for prepaid expenses with a shorter lifespan). This is done at the end of each accounting period (usually monthly, quarterly, or annually) to accurately reflect the expense incurred during that period.
The amount to be expensed is determined by calculating the period's usage. This calculation typically involves dividing the total prepaid expense by the number of periods it covers.
Example (continuation): For the insurance policy above, the monthly expense would be $12,000 / 12 months = $1,000. At the end of December 2023, the adjusting journal entry would be:
| Account Name | Debit | Credit |
|---|---|---|
| Insurance Expense | $1,000 | |
| Prepaid Insurance | $1,000 | |
| To record insurance expense for December |
This entry reduces the prepaid insurance asset account and increases the insurance expense account on the income statement.
Importance of Accurate Prepaid Expense Management
Proper management of prepaid expenses is crucial for several reasons:
- Accurate Financial Reporting: Incorrect accounting for prepaid expenses can lead to misstated financial statements, providing a misleading picture of the company's financial health.
- Improved Budgeting and Forecasting: Accurately tracking prepaid expenses helps in creating more accurate budgets and financial forecasts.
- Compliance with Accounting Standards: Following the correct accounting procedures for prepaid expenses is essential for compliance with Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) or International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS).
- Effective Cash Flow Management: Understanding prepaid expenses enables businesses to better manage their cash flow, ensuring sufficient funds are available for operational needs.
- Tax Optimization: Properly accounting for prepaid expenses can potentially optimize a company's tax liability.
Common Mistakes in Accounting for Prepaid Expenses
Several common errors occur when handling prepaid expenses:
- Failure to Recognize Prepaid Expenses: Sometimes, businesses fail to properly classify upfront payments as prepaid expenses, leading to overstatement of expenses in the current period.
- Incorrect Amortization/Expense Recognition: Miscalculating the amount of prepaid expense to be recognized each period leads to inaccurate expense figures.
- Ignoring the Expiration of Prepaid Expenses: Prepaid assets can expire, and businesses need to recognize this loss by writing off the unused portion. For example, if a software subscription expires without being used fully, the remaining value should be written off as a loss.
- Poor Record Keeping: Inadequate documentation of prepaid expenses can complicate the process of tracking and accounting for these assets.
Advanced Considerations:
- Materiality: For immaterial amounts, the company might choose to expense the entire amount upfront instead of amortizing it.
- Different Amortization Methods: Depending on the nature of the prepaid expense and the pattern of its benefit, different amortization methods (straight-line, declining balance, etc.) might be appropriate.
- Software and Technology: Accounting software and ERP systems significantly aid in managing and tracking prepaid expenses, automating amortization calculations and providing insightful reports.
Conclusion
Prepaid expenses are an integral part of financial accounting. Understanding their nature, proper accounting treatment, and potential pitfalls is critical for accurate financial reporting, effective financial management, and successful business operations. By meticulously tracking and accounting for these assets, businesses can ensure the integrity of their financial statements and make informed decisions based on accurate financial data. Implementing robust accounting practices and leveraging technology are crucial steps in achieving this goal. Remember to consult with qualified accounting professionals for any specific guidance related to your business's unique situation.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
The Supreme Court Concept Of Suspect Classifications Suggests That
Mar 17, 2025
-
A 90 Day Note Issued On April 10 Matures On
Mar 17, 2025
-
A Customer Arrives At A Customer Service Desk
Mar 17, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Best Describes How Deviance Is Defined
Mar 17, 2025
-
What Products Are Expected In The Ethoxide Promoted
Mar 17, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Prepaid Accounts Also Called Prepaid Expenses Are . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
