Overhead May Be Applied Based On
Holbox
Apr 02, 2025 · 7 min read
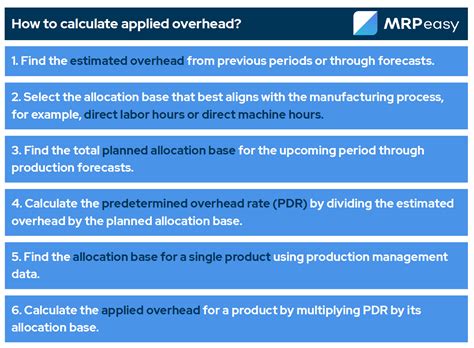
Table of Contents
- Overhead May Be Applied Based On
- Table of Contents
- Overhead May Be Applied Based On: A Comprehensive Guide to Overhead Allocation Methods
- What are Overhead Costs?
- Common Methods of Overhead Allocation
- 1. Direct Labor Cost Method
- 2. Direct Labor Hours Method
- 3. Machine Hours Method
- 4. Activity-Based Costing (ABC) Method
- 5. Plantwide Overhead Rate Method
- 6. Departmental Overhead Rate Method
- Choosing the Right Overhead Allocation Method
- Refining Overhead Allocation: Best Practices
- Conclusion
- Latest Posts
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
Overhead May Be Applied Based On: A Comprehensive Guide to Overhead Allocation Methods
Overhead costs are a critical aspect of any business, representing expenses not directly tied to producing a specific product or service. Effectively allocating these costs is crucial for accurate pricing, profitability analysis, and informed decision-making. However, the method used to allocate overhead can significantly impact the financial picture. This article delves into various methods of overhead allocation, exploring their strengths, weaknesses, and suitability for different business contexts. Understanding these methods is vital for businesses aiming to optimize their cost management and gain a clearer understanding of their profitability.
What are Overhead Costs?
Before diving into allocation methods, let's clarify what constitutes overhead. Overhead costs, also known as indirect costs, are expenses necessary for running a business but aren't directly traceable to individual products or services. Examples include:
- Rent and Utilities: Costs associated with the space where operations occur.
- Salaries of Support Staff: Pay for administrative personnel, security, and cleaning staff.
- Depreciation of Equipment: The gradual reduction in the value of assets over time.
- Insurance Premiums: Coverage for property, liability, and workers' compensation.
- Marketing and Advertising: Costs associated with promoting products or services.
- Research and Development: Expenses for innovation and improving existing offerings.
These expenses are essential for business operations but aren't easily linked to specific products. This necessitates the use of allocation methods to distribute them across the different cost objects (e.g., products, departments, projects).
Common Methods of Overhead Allocation
Several methods exist for allocating overhead costs. The choice of method depends on factors such as the nature of the business, the complexity of its operations, and the desired level of accuracy. Here are some of the most prevalent techniques:
1. Direct Labor Cost Method
This is a simple and widely used method where overhead is allocated based on the proportion of direct labor costs incurred for each product or service. The formula is:
Overhead Allocation Rate = Total Overhead Costs / Total Direct Labor Costs
Overhead Applied to a Product = Overhead Allocation Rate * Direct Labor Cost of the Product
Advantages:
- Simplicity: Easy to understand and implement.
- Relatively Low Cost: Requires minimal data collection and calculations.
Disadvantages:
- Inaccuracy: Assumes a direct relationship between direct labor and overhead, which may not always hold true. If a product requires little direct labor but substantial machine time, it might be under-costed.
- Inefficient for Automated Processes: Less suitable for businesses with high levels of automation, where direct labor costs are a small percentage of total costs.
2. Direct Labor Hours Method
Similar to the direct labor cost method, this approach uses the number of direct labor hours as the allocation base. The formula is:
Overhead Allocation Rate = Total Overhead Costs / Total Direct Labor Hours
Overhead Applied to a Product = Overhead Allocation Rate * Direct Labor Hours for the Product
Advantages:
- Simplicity: Simple to understand and implement.
- Better than Direct Labor Cost for Varied Wage Rates: Accounts for differences in labor rates, providing a slightly more accurate allocation.
Disadvantages:
- Inaccuracy: Still relies on a potentially inaccurate assumption that overhead is directly proportional to labor hours. It fails to consider other factors influencing overhead.
- Inefficient for Automated Processes: Like the direct labor cost method, it's less suitable for businesses with high automation.
3. Machine Hours Method
This method is particularly relevant for manufacturing companies that rely heavily on machinery. Overhead is allocated based on the number of machine hours used to produce each product. The formula is:
Overhead Allocation Rate = Total Overhead Costs / Total Machine Hours
Overhead Applied to a Product = Overhead Allocation Rate * Machine Hours for the Product
Advantages:
- Suitable for Automated Processes: More accurate than labor-based methods for businesses with significant automation.
- Better Reflection of Overhead Drivers: Better reflects the relationship between overhead and the actual resource consumption in machine-intensive environments.
Disadvantages:
- Less Relevant for Labor-Intensive Businesses: Less applicable to businesses where labor costs are the primary driver of overhead.
- Requires Accurate Machine Hour Tracking: Accurate tracking of machine hours is crucial for reliable allocation.
4. Activity-Based Costing (ABC) Method
This is a more sophisticated method that assigns overhead costs based on activities that consume resources. It identifies cost pools (groups of similar overhead costs) and assigns overhead costs to these pools based on their activities. Each activity is then allocated to products based on the consumption of that activity.
Advantages:
- High Accuracy: Provides a more accurate representation of the actual overhead consumed by each product or service.
- Better Cost Management: Identifies cost drivers, facilitating improved cost control and decision-making.
- Improved Pricing Strategies: Enables more accurate product pricing based on actual resource consumption.
Disadvantages:
- Complexity: Requires significant data collection and analysis, making it more time-consuming and costly to implement.
- Requires Strong IT Infrastructure: Often relies on robust information systems for data tracking and analysis.
5. Plantwide Overhead Rate Method
This method uses a single overhead rate for the entire plant or organization. While simple, it lacks the granularity of other methods and can lead to significant distortions.
Advantages:
- Simplicity: Easiest method to implement and understand.
Disadvantages:
- Significant Inaccuracy: Ignores variations in overhead consumption across different departments or products.
- Distorted Product Costs: Can lead to inaccurate product costs, impacting pricing and profitability analysis.
6. Departmental Overhead Rate Method
This method improves on the plantwide rate by calculating separate overhead rates for each department. This addresses some of the inaccuracies of the plantwide method but still might not capture the nuances of overhead consumption within a department.
Advantages:
- Improved Accuracy: More accurate than the plantwide method, reflecting departmental differences in overhead consumption.
Disadvantages:
- Still Relatively Inaccurate: Doesn't consider variations in overhead consumption within a department.
Choosing the Right Overhead Allocation Method
The selection of an appropriate overhead allocation method is critical for accurate cost accounting and informed decision-making. The optimal choice depends on several factors:
- Company Size and Complexity: Smaller, simpler businesses might find the direct labor cost or machine hours method sufficient. Larger, more complex businesses might benefit from ABC costing.
- Industry: Manufacturing companies might favor the machine hours or ABC methods, while service-based businesses might find direct labor cost or activity-based methods more suitable.
- Level of Automation: Highly automated businesses might benefit from machine hours or ABC methods, while labor-intensive businesses might rely on direct labor cost or hours methods.
- Desired Accuracy: ABC costing offers the highest accuracy but requires more resources. Simpler methods offer lower accuracy but are less resource-intensive.
- Availability of Data: The chosen method should be feasible given the available data and the resources for data collection and analysis.
It's important to remember that no single method is universally superior. The best approach is the one that offers the most accurate and cost-effective allocation of overhead costs for a particular business. Regularly reviewing and refining the allocation method is crucial to ensure its ongoing suitability.
Refining Overhead Allocation: Best Practices
Effective overhead allocation goes beyond simply selecting a method. Here are some best practices to enhance accuracy and efficiency:
- Accurate Cost Tracking: Maintain meticulous records of all overhead costs, ensuring accurate classification and categorization.
- Regular Review and Adjustment: Periodically review and adjust the allocation method to ensure it remains aligned with the business's changing operations and cost structures.
- Consideration of Multiple Cost Drivers: While a single allocation base might suffice for some businesses, others might benefit from using multiple cost drivers to capture a wider range of overhead consumption patterns.
- Technology Integration: Leverage technology, such as ERP systems, to automate data collection, processing, and allocation.
- Cross-Functional Collaboration: Involve personnel from different departments to ensure the allocation method reflects their specific needs and perspectives.
Conclusion
Overhead allocation is a crucial aspect of cost accounting and business management. Selecting the appropriate method and adhering to best practices can significantly improve the accuracy of cost information, supporting better decision-making in areas such as pricing, resource allocation, and profitability analysis. Understanding the strengths and weaknesses of each method enables businesses to make informed choices that align with their specific operational context and objectives. By adopting a proactive and data-driven approach, businesses can harness the power of effective overhead allocation to enhance their overall financial performance and competitive advantage.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Once A Corrective Action Plan Is Started
Apr 04, 2025
-
The Green Upper Triangle Has An Area Of
Apr 04, 2025
-
Consider The Phase Diagram Shown Below
Apr 04, 2025
-
What Is The Conjugate Acid Of Nh3
Apr 04, 2025
-
Companies Use Job Cost Sheets To Track The Costs Of
Apr 04, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Overhead May Be Applied Based On . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
