Multipurpose Trees Are Useful For What Purpose
Holbox
Mar 23, 2025 · 6 min read
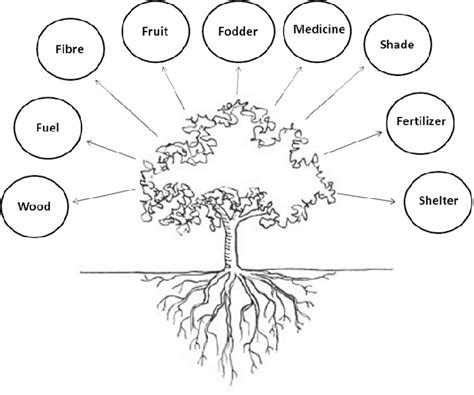
Table of Contents
- Multipurpose Trees Are Useful For What Purpose
- Table of Contents
- Multipurpose Trees: A Boon for Sustainable Living
- The Diverse Uses of Multipurpose Trees: A Deep Dive
- 1. Food Security and Nutrition:
- 2. Improved Livelihoods and Economic Opportunities:
- 3. Environmental Benefits and Ecosystem Services:
- 4. Social and Community Development:
- Selecting Appropriate Multipurpose Tree Species: Key Considerations
- Challenges and Opportunities in Multipurpose Tree Cultivation
- Conclusion: Embracing the Potential of Multipurpose Trees
- Latest Posts
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
Multipurpose Trees: A Boon for Sustainable Living
Multipurpose trees, also known as multipurpose tree species (MPTS), are a cornerstone of sustainable land management and community development. These remarkable plants offer a diverse array of benefits, extending far beyond simple shade or aesthetics. Their versatility makes them invaluable in various sectors, from agriculture and environmental conservation to economic development and social well-being. Understanding the multifaceted utility of multipurpose trees is crucial for harnessing their potential to improve livelihoods and protect our planet.
The Diverse Uses of Multipurpose Trees: A Deep Dive
The true strength of multipurpose trees lies in their ability to serve multiple needs simultaneously. This inherent versatility makes them exceptionally valuable, especially in resource-constrained environments. Let's explore the key areas where these trees shine:
1. Food Security and Nutrition:
Fruit Production: Many multipurpose trees bear edible fruits, providing a vital source of nutrition, particularly in regions where food access is limited. Examples include mango, jackfruit, guava, and various species of citrus. The fruits can be consumed fresh, processed into jams, juices, or dried for preservation, contributing to year-round food security.
Edible Leaves and Seeds: Beyond fruits, several multipurpose trees offer nutritious leaves and seeds. Moringa, for instance, is renowned for its highly nutritious leaves, packed with vitamins and minerals. Similarly, some tree species produce edible seeds that can supplement diets with protein and essential fatty acids.
Honey Production: Many multipurpose trees are excellent sources of nectar and pollen, supporting robust honeybee populations. This translates to increased honey production, providing both a valuable food source and a source of income for local communities.
2. Improved Livelihoods and Economic Opportunities:
Timber and Fuelwood: Several multipurpose tree species yield valuable timber, suitable for construction, furniture making, and other woodworking applications. This provides a sustainable source of income and reduces reliance on unsustainable logging practices. Many also provide excellent fuelwood, reducing pressure on forests and contributing to household energy needs.
Fiber and Resin Production: Certain multipurpose trees produce fibers that are valuable for making ropes, textiles, and other materials. Others yield resins, gums, and oils used in various industrial applications, generating income and supporting local industries.
Medicinal Uses: Traditional medicine systems around the world extensively utilize multipurpose trees for their medicinal properties. Their leaves, bark, roots, and fruits often contain compounds with antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, or other therapeutic effects.
Ornamental Value: Many multipurpose trees possess ornamental value, making them suitable for landscaping and creating aesthetically pleasing environments. This is increasingly important in urban areas and tourist destinations, boosting property values and creating employment in landscaping and related sectors.
3. Environmental Benefits and Ecosystem Services:
Soil Conservation and Erosion Control: Multipurpose trees play a vital role in protecting soil from erosion. Their roots help bind the soil together, preventing runoff and landslides, particularly on slopes and in degraded areas. They also improve soil fertility by enriching it with organic matter.
Carbon Sequestration: Trees are natural carbon sinks, absorbing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and storing it in their biomass. Multipurpose trees, due to their rapid growth and longevity, can significantly contribute to carbon sequestration, mitigating climate change.
Water Management: Multipurpose trees can help manage water resources. Their canopies provide shade, reducing evaporation from the soil, and their roots enhance water infiltration, improving groundwater recharge. They can also help prevent flooding by absorbing excess water.
Biodiversity Support: Multipurpose trees provide habitat and food for a wide range of wildlife species, enhancing biodiversity. They support insect populations, birds, and other animals, contributing to a healthier ecosystem.
Windbreaks and Shelterbelts: Strategic planting of multipurpose trees can create windbreaks and shelterbelts, protecting crops and livestock from strong winds and harsh weather conditions. This can lead to increased agricultural yields and improved animal welfare.
4. Social and Community Development:
Community Forestry: Multipurpose trees are often central to community forestry initiatives, empowering local communities to manage and benefit from forest resources sustainably. This fosters a sense of ownership and responsibility, promoting long-term environmental stewardship.
Food Security and Nutritional Improvement: The provision of readily available nutritious food from multipurpose trees significantly improves the health and well-being of communities, particularly those facing food insecurity.
Income Generation and Poverty Reduction: The various income-generating opportunities associated with multipurpose trees can significantly contribute to poverty reduction and improve the economic status of rural communities.
Education and Awareness: The cultivation and management of multipurpose trees provide opportunities for education and awareness programs, promoting sustainable land management practices and environmental conservation.
Selecting Appropriate Multipurpose Tree Species: Key Considerations
The success of utilizing multipurpose trees depends on choosing species appropriate to the specific environment and needs. Several factors need careful consideration:
-
Climate and Soil Conditions: Different tree species have varying tolerances to climate and soil conditions. Selecting species adapted to the local environment is crucial for their survival and productivity.
-
Growth Rate and Maturity: The growth rate and time to maturity will influence the time frame for realizing benefits. Fast-growing species are often preferred for quick returns, while slower-growing species may offer superior timber quality.
-
Pest and Disease Resistance: Selecting pest and disease-resistant species minimizes the risk of crop failure and reduces the need for pesticides.
-
Local Knowledge and Preferences: Engaging with local communities and utilizing their traditional knowledge of suitable species and management practices is essential for ensuring project success and community acceptance.
-
Availability of Planting Material: Access to high-quality planting material, including seeds, seedlings, or cuttings, is crucial for successful establishment.
Challenges and Opportunities in Multipurpose Tree Cultivation
Despite the significant benefits, cultivating and managing multipurpose trees faces several challenges:
-
Lack of Awareness and Knowledge: Limited awareness of the potential of multipurpose trees among farmers and policymakers can hinder their adoption.
-
Inadequate Infrastructure and Support: Lack of access to appropriate technology, training, and credit can constrain the development of multipurpose tree initiatives.
-
Land Tenure and Access: Secure land tenure and access rights are essential for long-term investment in multipurpose tree cultivation.
-
Market Access and Value Chains: Developing effective market mechanisms and value chains for the products derived from multipurpose trees is crucial for ensuring profitability.
However, these challenges also present opportunities:
-
Investment in Research and Development: Further research is needed to identify and develop improved varieties of multipurpose trees suited to various environments.
-
Capacity Building and Training: Investing in training programs for farmers and other stakeholders can enhance their knowledge and skills in managing multipurpose trees.
-
Policy Support and Incentives: Government policies and incentives can encourage the wider adoption of multipurpose trees.
-
Community Participation and Ownership: Empowering communities to participate in the planning and management of multipurpose tree initiatives can promote sustainability and ownership.
Conclusion: Embracing the Potential of Multipurpose Trees
Multipurpose trees represent a powerful tool for achieving sustainable development goals. Their ability to address multiple needs simultaneously – food security, livelihood improvement, environmental protection, and community development – makes them invaluable assets in promoting sustainable land management and building resilient communities. By addressing the existing challenges and capitalizing on the opportunities, we can unlock the vast potential of multipurpose trees to contribute significantly to a more sustainable and equitable future. Their cultivation is not merely an agricultural practice; it's a holistic approach to development, encompassing economic growth, environmental stewardship, and social well-being. The integration of these remarkable trees into diverse landscapes promises a future rich in both ecological and human prosperity.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Issues And Ethics In The Helping Professions 11th Edition
Mar 26, 2025
-
How Many Different Molecules Are Drawn Below
Mar 26, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Is A Function Of Proteins
Mar 26, 2025
-
Creating Two Departments And Placing One Manager Over Each
Mar 26, 2025
-
A Simcell With A Water Permeable Membrane That Contains 20 Hemoglobin
Mar 26, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Multipurpose Trees Are Useful For What Purpose . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
