Manufacturing Costs Include Direct Materials Direct Labor And
Holbox
Mar 14, 2025 · 6 min read
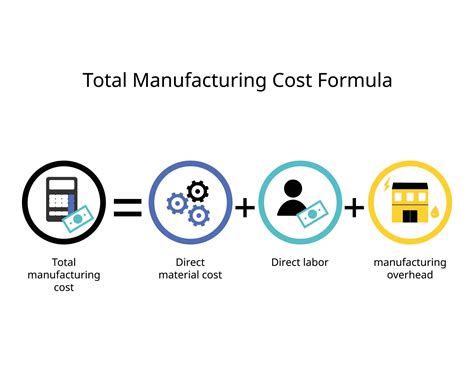
Table of Contents
Manufacturing Costs: A Deep Dive into Direct Materials, Direct Labor, and More
Understanding manufacturing costs is crucial for any business involved in production. Accurate cost accounting allows for informed pricing decisions, efficient resource allocation, and ultimately, profitability. This comprehensive guide explores the key components of manufacturing costs, focusing on direct materials, direct labor, and the often-overlooked yet vital indirect costs. We'll also touch upon cost accounting methods and strategies for minimizing manufacturing expenses.
The Trifecta of Manufacturing Costs: Direct Materials, Direct Labor, and Manufacturing Overhead
The core components of manufacturing costs are generally categorized into three main buckets:
1. Direct Materials
Direct materials are the raw materials, components, and supplies that are directly used in the production process and can be easily traced to the finished product. Think of the wood in a chair, the fabric in a shirt, or the steel in a car. These are tangible and directly identifiable components. Accurate tracking of direct materials is vital for several reasons:
- Cost Control: Efficiently managing inventory and tracking usage helps prevent waste and minimizes material costs. This includes implementing robust inventory management systems and regularly reviewing material usage reports.
- Pricing Decisions: Accurate costing of direct materials directly impacts the final price of the product. Understanding these costs allows for realistic pricing that ensures profitability.
- Quality Control: Tracking materials helps identify potential sources of defects or quality issues, leading to improvements in the production process and reduced waste.
Examples of Direct Materials:
- Food Processing: Flour, sugar, fruits, vegetables for bakery products or processed foods.
- Textile Manufacturing: Cotton, silk, wool, synthetic fibers for clothing or home textiles.
- Automotive Manufacturing: Steel, aluminum, rubber, plastics for vehicle components.
- Electronics Manufacturing: Integrated circuits, resistors, capacitors, printed circuit boards.
Challenges in Managing Direct Materials:
- Price Volatility: Fluctuations in raw material prices can significantly affect manufacturing costs. Implementing strategies like hedging or long-term contracts can mitigate this risk.
- Inventory Management: Balancing inventory levels to meet demand without excessive storage costs is crucial. Effective inventory management systems are essential for maintaining optimal stock levels.
- Supply Chain Disruptions: Unexpected delays or disruptions in the supply chain can halt production and lead to significant cost increases. Diversifying suppliers and building strong relationships are crucial for resilience.
2. Direct Labor
Direct labor refers to the wages, salaries, and benefits paid to employees who are directly involved in the manufacturing process. These are the individuals who physically work on transforming raw materials into finished products. This includes assembly line workers, machine operators, and skilled technicians whose time and effort can be directly attributed to a specific product.
Importance of Effective Direct Labor Management:
- Productivity: Optimizing labor processes, providing appropriate training, and implementing efficient scheduling can improve worker productivity and reduce labor costs.
- Employee Morale: A positive work environment and fair compensation can significantly impact employee morale and productivity, contributing to lower labor costs in the long run.
- Skill Development: Investing in training and development programs can enhance employee skills, improve product quality, and reduce errors, resulting in lower labor costs and higher output.
Examples of Direct Labor:
- Construction: Wages paid to carpenters, electricians, and plumbers working on a building project.
- Clothing Manufacturing: Salaries of seamstresses, cutters, and other workers directly involved in garment production.
- Furniture Manufacturing: Wages of workers assembling furniture pieces, applying finishes, and conducting quality checks.
- Pharmaceutical Manufacturing: Salaries of technicians and scientists involved in the production and quality control of medications.
Challenges in Managing Direct Labor:
- Labor Shortages: In certain industries, finding and retaining skilled workers can be challenging. This necessitates competitive compensation and benefits packages.
- Wage Inflation: Increases in minimum wage and other labor costs can impact the overall manufacturing expenses. Strategies for improving efficiency and productivity can help offset these increases.
- Worker Safety: Maintaining a safe work environment is crucial for both ethical and legal reasons. Investing in safety measures can help prevent accidents and reduce associated costs.
3. Manufacturing Overhead
Manufacturing overhead encompasses all indirect costs associated with the production process. These costs are difficult to directly trace to a specific product but are essential for production. Unlike direct materials and direct labor, they aren't easily attributed to a single unit.
Components of Manufacturing Overhead:
- Indirect Labor: Salaries of supervisors, maintenance personnel, quality control inspectors, and other support staff who are not directly involved in transforming raw materials.
- Factory Rent: Cost of renting or leasing the manufacturing facility.
- Utilities: Electricity, water, gas, and other utility costs consumed during production.
- Depreciation: The allocation of the cost of equipment and machinery over their useful life.
- Insurance: Insurance premiums covering factory buildings, equipment, and liability.
- Factory Supplies: Cleaning supplies, lubricants, and other indirect materials used in the factory.
- Maintenance and Repairs: Costs associated with maintaining and repairing factory equipment.
Effective Management of Manufacturing Overhead:
- Cost Allocation: Implementing an appropriate method for allocating overhead costs to products is crucial for accurate cost accounting. Common methods include machine hours, direct labor hours, and activity-based costing.
- Efficiency Improvements: Identifying and eliminating wasteful spending in areas like utilities and maintenance can significantly reduce overhead costs.
- Technology Adoption: Investing in advanced technologies such as automation and robotics can improve efficiency and reduce labor and maintenance costs.
Cost Accounting Methods
Several cost accounting methods are used to track and manage manufacturing costs. The choice of method depends on the complexity of the production process and the level of detail required.
- Job Order Costing: This method tracks costs for each individual job or project. It’s ideal for businesses that produce unique or customized products.
- Process Costing: This method averages costs across a large number of identical units produced. It’s suitable for businesses that produce standardized products in large quantities.
- Activity-Based Costing (ABC): This method allocates overhead costs based on specific activities performed in the production process. It provides a more accurate picture of costs compared to traditional methods, especially for complex manufacturing environments.
Strategies for Minimizing Manufacturing Costs
Minimizing manufacturing costs without compromising quality is a continuous challenge for businesses. Here are some key strategies:
- Lean Manufacturing: This philosophy focuses on eliminating waste and maximizing efficiency throughout the production process. Techniques include just-in-time inventory, kaizen (continuous improvement), and value stream mapping.
- Supply Chain Optimization: Building strong relationships with suppliers, negotiating favorable pricing, and optimizing logistics can significantly reduce material costs.
- Technology Adoption: Investing in automation, robotics, and other technologies can improve efficiency, reduce labor costs, and enhance quality control.
- Process Improvement: Continuously analyzing and improving production processes can identify bottlenecks and inefficiencies, leading to cost savings.
- Waste Reduction: Implementing programs to reduce waste in materials, energy, and labor can significantly lower manufacturing costs. This includes implementing recycling programs and reducing energy consumption.
- Employee Training and Development: Investing in training and development programs can improve employee skills, reduce errors, and boost productivity, leading to lower labor costs.
- Quality Control: Implementing robust quality control measures can reduce waste, rework, and defects, ultimately minimizing costs.
Conclusion
Understanding and managing manufacturing costs is fundamental to the success of any production business. By carefully analyzing direct materials, direct labor, and manufacturing overhead, and by implementing appropriate cost accounting methods and cost-reduction strategies, businesses can achieve greater profitability and long-term sustainability. The continuous pursuit of efficiency, quality, and innovation remains crucial in navigating the complexities of manufacturing cost management. Regular review and adaptation of these strategies are essential to remain competitive in today's dynamic business landscape.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
A Backup Of Sewage In The Operations Storeroom Is Considered
Mar 14, 2025
-
One Drawback That Is Particuaty Relevent To
Mar 14, 2025
-
Molecular Formula Consistent With Mass Spec C3h6br2
Mar 14, 2025
-
Determine Which Is The Larger Species
Mar 14, 2025
-
Modern Real Estate Practice Workbook 5th Edition
Mar 14, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Manufacturing Costs Include Direct Materials Direct Labor And . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
