Managers Can Use The Vrio Framework To
Holbox
Apr 02, 2025 · 6 min read
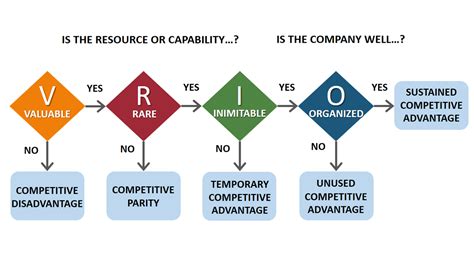
Table of Contents
- Managers Can Use The Vrio Framework To
- Table of Contents
- Managers Can Use the VRIO Framework To Gain a Competitive Advantage
- Understanding the VRIO Framework
- Valuable: Does the resource or capability add value?
- Rare: Is the resource or capability rare among competitors?
- Inimitable: Is the resource or capability costly to imitate?
- Organized: Is the firm organized to exploit the resource or capability?
- Applying the VRIO Framework: A Practical Guide
- Case Study: Applying VRIO to Apple
- Conclusion: The VRIO Framework for Sustainable Competitive Advantage
- Latest Posts
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
Managers Can Use the VRIO Framework To Gain a Competitive Advantage
The business world is a relentless battlefield, a constant struggle for survival and dominance. In this cutthroat environment, managers are constantly searching for ways to gain a competitive edge. One powerful tool that can help achieve this is the VRIO framework. This framework, a strategic analysis tool, helps managers assess the resources and capabilities of their organization to determine their potential for creating sustainable competitive advantage. By understanding and effectively utilizing the VRIO framework, managers can make informed decisions, optimize resource allocation, and ultimately, propel their organizations to success.
Understanding the VRIO Framework
The VRIO framework is an acronym that stands for Valuable, Rare, Inimitable, and Organized. Each of these criteria represents a critical lens through which managers should assess a resource or capability to determine its strategic significance. Let's break down each component:
Valuable: Does the resource or capability add value?
A resource or capability is valuable if it helps a firm exploit opportunities or neutralize threats in its environment. This means it must contribute positively to a firm's ability to increase its revenue or reduce its costs. Examples of valuable resources include:
- Strong Brand Reputation: A well-established brand can command premium prices and attract loyal customers.
- Patented Technology: Exclusive access to patented technology provides a significant competitive advantage.
- Efficient Supply Chain: A streamlined supply chain can reduce costs and improve delivery times.
- Skilled Workforce: A highly skilled and experienced workforce can produce higher-quality products and services.
Managers must thoroughly analyze the market and competitive landscape to determine if a specific resource is truly adding value. A seemingly valuable resource in one market might be irrelevant or even detrimental in another.
Rare: Is the resource or capability rare among competitors?
Even if a resource or capability is valuable, it won't provide a sustainable competitive advantage if it's widely available to competitors. Rarity is what creates a temporary monopoly. If many firms possess the same resource, the competitive landscape will be largely leveled. For example, while skilled workers are valuable, a large pool of readily available skilled labor diminishes their rarity and thus their strategic importance.
Examples of rare resources or capabilities might include:
- Unique Geographic Location: Access to a prime location with exceptional visibility or proximity to key resources.
- Exclusive Distribution Network: A highly efficient and extensive distribution network that competitors struggle to replicate.
- Specialized Knowledge: Deep expertise in a niche market or technology that is difficult to acquire.
Assessing rarity necessitates detailed competitive intelligence gathering and market analysis. Managers need to understand not only their own resources but also the resources controlled by their competitors.
Inimitable: Is the resource or capability costly to imitate?
A truly valuable and rare resource will only provide a sustainable competitive advantage if it's difficult for competitors to imitate. Imitation can take various forms, including direct duplication, substitution, or strategic emulation. Resources that are costly to imitate are often protected by factors such as:
- Path Dependency: A resource built over time through unique historical events or strategic choices.
- Causal Ambiguity: The reasons for the resource's success are not clearly understood, making it difficult to replicate.
- Social Complexity: The resource relies on complex social relationships, culture, or trust that are difficult to reconstruct.
Intellectual property protection (patents, copyrights, trademarks) is also a significant factor in inimitability. Managers need to identify and build resources that possess these characteristics to secure a longer-lasting competitive edge.
Organized: Is the firm organized to exploit the resource or capability?
Even if a resource is valuable, rare, and inimitable, it won't generate a competitive advantage if the firm isn't organized to effectively utilize it. This requires appropriate organizational structures, processes, and management systems to effectively leverage the resource. For example, a company might possess a valuable patented technology but fail to commercialize it due to internal organizational inefficiencies.
Factors that contribute to effective organization include:
- Strong Management Team: A capable leadership team to guide and coordinate the utilization of the resource.
- Efficient Processes: Well-defined and efficient processes for production, marketing, and distribution.
- Supportive Culture: A company culture that fosters innovation, collaboration, and efficiency.
Without proper organization, even the most valuable resources can remain dormant and untapped, failing to contribute to competitive advantage.
Applying the VRIO Framework: A Practical Guide
The VRIO framework is not simply a theoretical model; it's a practical tool for managers to analyze their organization's resources and capabilities. Here's a step-by-step guide:
-
Identify Key Resources and Capabilities: Begin by identifying all the resources and capabilities within the organization. This should include tangible assets (equipment, facilities), intangible assets (brand reputation, intellectual property), and human capital (skills, knowledge).
-
Assess Value: For each resource or capability, analyze its value. Does it contribute to increasing revenue or reducing costs? Use market analysis, customer feedback, and financial data to support your assessment.
-
Determine Rarity: Analyze the competitive landscape. How many competitors possess this resource or capability? If it's readily available, its competitive impact is likely limited.
-
Evaluate Inimitability: Assess the difficulty of imitation. Are there barriers to imitation such as path dependency, causal ambiguity, or social complexity? Consider the potential for substitution and strategic emulation.
-
Analyze Organization: Determine if the organization is effectively structured and organized to exploit the resource or capability. Evaluate management systems, processes, and organizational culture.
-
Develop Strategic Implications: Based on your VRIO analysis, determine the strategic implications. A resource that is valuable, rare, inimitable, and organized represents a sustainable competitive advantage. Resources that are lacking in one or more of these areas need to be addressed through strategic initiatives. This may involve investing in new resources, improving existing capabilities, restructuring the organization, or divesting from underperforming assets.
Case Study: Applying VRIO to Apple
Apple provides an excellent example of leveraging the VRIO framework. Let's analyze some of their key resources:
-
Brand Reputation: Apple has a powerful and highly valuable brand reputation known for innovation and quality. This is valuable, rare, relatively inimitable (due to its long-standing history and strong brand equity), and Apple is highly organized to leverage this through superior marketing and product design. This represents a sustainable competitive advantage.
-
Ecosystem: The Apple ecosystem, encompassing iPhones, iPads, Macs, and services like the App Store and Apple Music, is valuable due to its user loyalty and revenue generation potential. This is rare and quite inimitable due to its network effects and strong brand loyalty. Apple is excellently organized to manage and expand this ecosystem. This is another key source of sustainable competitive advantage.
-
Design and User Experience: Apple’s focus on sleek design and intuitive user experience is valuable, relatively rare compared to competitors, and somewhat inimitable because it's deeply ingrained in the company's culture and design philosophy. The company is highly organized to maintain its commitment to design excellence.
Conclusion: The VRIO Framework for Sustainable Competitive Advantage
The VRIO framework offers managers a powerful tool for analyzing their organization's resources and capabilities to identify and build sustainable competitive advantages. By systematically assessing each resource through the lens of value, rarity, inimitability, and organization, managers can make informed decisions, optimize resource allocation, and ultimately drive their organizations towards greater success in the competitive marketplace. The framework isn't a one-time exercise; it's an ongoing process of evaluation and adaptation crucial for maintaining a competitive edge in a dynamically evolving business environment. Regular application of the VRIO framework allows for proactive adjustments and strategic maneuvering, positioning the organization for long-term success and growth. Remember to continuously monitor the competitive landscape and reassess your resources to maintain relevance and competitiveness.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Drag And Drop Each Structure To The Correct Location
Apr 07, 2025
-
Which Of The Events Occur During Eukaryotic Translation Elongation
Apr 07, 2025
-
Place The Events Of Synaptic Transmission In Order
Apr 07, 2025
-
A Person Pulls Equally Hard On Two
Apr 07, 2025
-
Biochemical Tests For Food Macromolecules Labster
Apr 07, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Managers Can Use The Vrio Framework To . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.