Magnetic Field Of U Shaped Magnet
Holbox
Mar 10, 2025 · 6 min read
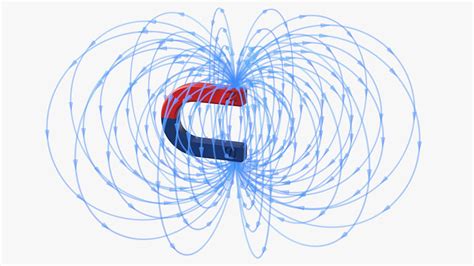
Table of Contents
The Magnetic Field of a U-Shaped Magnet: A Deep Dive
The humble U-shaped magnet, a staple in science classrooms and countless applications, holds a fascinating complexity within its seemingly simple form. Understanding its magnetic field is key to harnessing its power and predicting its behavior. This article will explore the magnetic field of a U-shaped magnet in detail, examining its properties, its interaction with other magnetic objects, and its applications. We'll delve into the physics behind the field, explore visualizations, and discuss practical implications.
Understanding the Basics: Magnetic Poles and Field Lines
Before diving into the specifics of a U-shaped magnet, let's refresh our understanding of fundamental magnetic concepts. Every magnet possesses two poles: a north pole and a south pole. These poles are inseparable; you cannot have a north pole without a south pole. The magnetic field is the region surrounding a magnet where its magnetic influence is felt. We visualize this field using magnetic field lines, which are imaginary lines that represent the direction and strength of the magnetic field at each point. These lines always emerge from the north pole and loop around to enter the south pole. The closer the lines are together, the stronger the magnetic field.
The U-Shaped Magnet's Distinctive Field
A U-shaped magnet is essentially a bar magnet bent into a U shape. This seemingly simple modification significantly alters the distribution and concentration of its magnetic field. The most striking difference is the stronger field concentrated between the poles. The curved shape guides the field lines, focusing them into a relatively narrow region between the poles. This concentration enhances the magnet's ability to attract ferromagnetic materials and perform various tasks requiring a strong localized magnetic field.
Visualizing the Field Lines
Imagine the field lines emanating from the north pole of the U-shaped magnet. They curve outwards, then inwards towards the south pole, creating a concentrated region of flux density between the poles. This concentrated flux is what allows U-shaped magnets to lift heavier objects than a similarly sized straight bar magnet. A simple visualization helps: picture a river flowing from one pole to the other – the river is narrower and faster (stronger field) in the region between the poles.
Comparing to a Bar Magnet
While both U-shaped and bar magnets have north and south poles, the field configuration differs significantly. A bar magnet has a more dispersed field, radiating in all directions. The U-shaped design effectively channels this field, creating a powerful, localized field in the gap between the poles. This concentrated field is crucial for various applications where a strong, focused magnetic force is essential.
Factors Affecting the Magnetic Field Strength
Several factors influence the strength of the magnetic field produced by a U-shaped magnet:
-
Magnet Material: The material used to construct the magnet significantly affects its strength. Stronger magnetic materials, like neodymium magnets (NdFeB), produce much more powerful fields than weaker materials, such as alnico magnets.
-
Magnet Size and Shape: Larger magnets generally produce stronger fields. However, the shape plays a critical role. The U-shape itself contributes to the field's concentration, increasing the field strength in the gap between the poles.
-
Temperature: Temperature significantly impacts a magnet's strength. Most magnets lose some of their magnetic properties as temperature increases – this is known as Curie temperature. Above the Curie temperature, the magnet loses its magnetism entirely.
-
Presence of Ferromagnetic Materials: Placing ferromagnetic materials near the U-shaped magnet can alter the field lines. The materials will become magnetized themselves, enhancing or redirecting the magnetic field.
Applications Leveraging the U-Shaped Magnet's Field
The unique properties of a U-shaped magnet's field make it ideal for a wide range of applications, including:
-
Lifting and Holding: The strong, localized field makes U-shaped magnets excellent for lifting and holding ferromagnetic objects. This is utilized in various industrial applications, such as lifting scrap metal or holding components during assembly.
-
Magnetic Sensors: The concentrated field between the poles allows for sensitive detection of small changes in magnetic fields. This principle is used in various sensors, including those in automotive speedometers and electronic compasses.
-
Electric Motors and Generators: U-shaped magnets play a crucial role in the design of some electric motors and generators. The configuration of the magnets creates a rotating magnetic field, essential for the motor's operation.
-
Magnetic Switches and Relays: The attraction force between the poles can be utilized to actuate switches and relays, providing a contactless method for controlling electrical circuits.
-
Loudspeakers and Headphones: Some speaker and headphone designs incorporate U-shaped magnets to provide the magnetic field necessary to move the voice coil and produce sound.
-
Scientific Instruments: U-shaped magnets are used in various scientific instruments, such as mass spectrometers and particle accelerators, to guide charged particles or create precise magnetic fields for experiments.
-
Educational Demonstrations: The U-shaped magnet is a common tool in educational settings, making magnetic field demonstrations easily understandable. Its simple shape and concentrated field provide a clear illustration of magnetic field lines and their behavior.
Exploring the Field: Experiments and Observations
Several simple experiments can help visualize and understand the U-shaped magnet's field:
-
Iron Filings Experiment: Sprinkling iron filings onto a sheet of paper placed over a U-shaped magnet reveals the pattern of magnetic field lines. The filings will align along the field lines, providing a visual representation of the field's shape and intensity.
-
Magnetic Compass Experiment: Moving a magnetic compass around the magnet shows the direction of the field at various points. The compass needle will align itself with the local field lines, indicating the direction of the magnetic field.
-
Attraction and Repulsion Experiments: Experimenting with different ferromagnetic objects of varying sizes and shapes helps illustrate the relationship between distance, field strength, and the force of attraction.
Advanced Considerations: Magnetic Flux Density and Calculations
For a more detailed understanding, we can delve into the concept of magnetic flux density (B), often measured in Tesla (T). The magnetic flux density represents the strength of the magnetic field at a specific point. Calculating the exact magnetic flux density for a U-shaped magnet is complex, requiring advanced mathematical techniques and considering factors such as magnet geometry and material properties. However, finite element analysis (FEA) software can provide accurate simulations and visualizations of the magnetic field.
Conclusion: The Power of the U-Shaped Design
The U-shaped magnet, while seemingly simple, demonstrates the powerful impact of shaping a magnetic material to enhance and concentrate its field. This concentrated field makes it a versatile tool across numerous applications, from everyday items to sophisticated scientific instruments. By understanding its magnetic field properties, we can fully harness its power and continue to innovate its uses. Further exploration into advanced magnetic materials and more precise computational modeling will undoubtedly lead to even more creative and effective applications of this fundamental magnetic configuration. The seemingly simple U-shaped magnet offers a wealth of scientific insights and technological possibilities, illustrating the remarkable interplay between physics and engineering.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
I Am Sorry In French Language
Mar 10, 2025
-
Weight Of A Cubic Foot Of Water
Mar 10, 2025
-
Is A Pencil A Conductor Or Insulator
Mar 10, 2025
-
How Do We Calculate Energy Efficiency
Mar 10, 2025
-
A Life Cycle Of A Sea Turtle
Mar 10, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Magnetic Field Of U Shaped Magnet . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
