Least Common Multiple Of 5 And 6
Holbox
Mar 09, 2025 · 5 min read
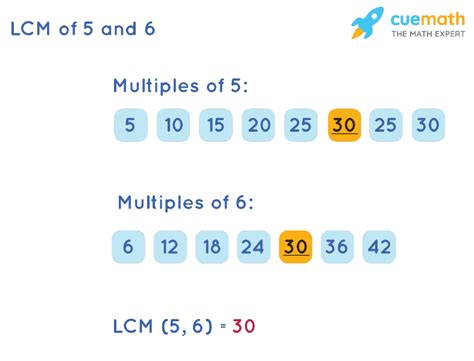
Table of Contents
Unveiling the Least Common Multiple (LCM) of 5 and 6: A Deep Dive
The concept of the Least Common Multiple (LCM) is a fundamental element in number theory and has far-reaching applications in various mathematical fields and real-world scenarios. This article delves deep into understanding the LCM, specifically focusing on the LCM of 5 and 6, exploring different methods of calculation, and highlighting its practical significance.
Understanding Least Common Multiples (LCM)
Before we tackle the specific case of 5 and 6, let's establish a solid understanding of LCMs. The least common multiple of two or more integers is the smallest positive integer that is divisible by all the integers. In simpler terms, it's the smallest number that is a multiple of all the given numbers.
For example, consider the numbers 2 and 3. Multiples of 2 are 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12... Multiples of 3 are 3, 6, 9, 12, 15... The common multiples are 6, 12, 18... The smallest of these common multiples is 6, therefore, the LCM of 2 and 3 is 6.
Understanding LCMs is crucial for various mathematical operations, including:
- Simplifying fractions: Finding the LCM of the denominators allows for easy addition and subtraction of fractions.
- Solving problems involving cycles or periodic events: Determining when events will coincide again (e.g., two buses arriving at a stop simultaneously).
- Working with ratios and proportions: LCM helps in scaling ratios to find equivalent values.
Calculating the LCM of 5 and 6: Multiple Approaches
Now, let's focus on calculating the LCM of 5 and 6. We can use several methods to achieve this:
1. Listing Multiples Method
This is the most straightforward approach, especially for smaller numbers. We list the multiples of each number until we find the smallest common multiple.
- Multiples of 5: 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 35...
- Multiples of 6: 6, 12, 18, 24, 30, 36...
The smallest number that appears in both lists is 30. Therefore, the LCM of 5 and 6 is 30.
2. Prime Factorization Method
This method is more efficient for larger numbers. We first find the prime factorization of each number:
- Prime factorization of 5: 5 (5 is a prime number)
- Prime factorization of 6: 2 x 3
To find the LCM, we take the highest power of each prime factor present in the factorizations and multiply them together:
LCM(5, 6) = 2 x 3 x 5 = 30
This method is particularly useful when dealing with larger numbers where listing multiples becomes cumbersome. It provides a systematic and efficient way to determine the LCM.
3. Greatest Common Divisor (GCD) Method
The LCM and GCD (Greatest Common Divisor) of two numbers are closely related. The product of the LCM and GCD of two numbers is equal to the product of the two numbers themselves.
First, let's find the GCD of 5 and 6 using the Euclidean algorithm:
- Divide 6 by 5: 6 = 1 x 5 + 1
- Divide 5 by 1: 5 = 5 x 1 + 0
The GCD is the last non-zero remainder, which is 1.
Now, we can use the formula:
LCM(a, b) = (a x b) / GCD(a, b)
LCM(5, 6) = (5 x 6) / 1 = 30
This method is powerful because it leverages the relationship between LCM and GCD, providing an alternative route to the solution.
Applications of LCM(5,6) = 30 in Real-World Scenarios
The LCM of 5 and 6, which is 30, has practical applications in various situations:
1. Scheduling and Time Management
Imagine two machines operating on a cycle. Machine A completes a cycle every 5 minutes, while Machine B completes a cycle every 6 minutes. To find when both machines will complete a cycle simultaneously, we need to find the LCM(5,6) = 30. Both machines will complete a cycle together after 30 minutes.
2. Pattern Recognition
Consider a repeating pattern where one element repeats every 5 units and another element repeats every 6 units. The LCM (30) indicates the length of the smallest repeating segment where both patterns align perfectly.
3. Fraction Operations
When adding or subtracting fractions with denominators 5 and 6, finding the LCM (30) allows for the conversion to a common denominator, simplifying the calculation. For instance, adding 1/5 and 1/6 requires finding a common denominator, which is 30. Therefore, 1/5 becomes 6/30 and 1/6 becomes 5/30. Adding these results in 11/30.
4. Gear Ratios and Mechanical Systems
In mechanical systems with gears, the LCM helps determine when different gears will be aligned perfectly, crucial for efficient energy transfer and preventing wear and tear.
5. Modular Arithmetic and Cryptography
LCMs play a vital role in modular arithmetic, a branch of mathematics with applications in cryptography and computer science. Understanding LCMs is crucial for solving congruences and working with cyclic groups.
Beyond the Basics: Extending LCM Concepts
The concept of LCM extends beyond just two numbers. We can find the LCM of multiple numbers using similar methods. The prime factorization method is particularly efficient for larger sets of numbers. For instance, to find the LCM of 5, 6, and 10, we find the prime factorization of each number:
- 5 = 5
- 6 = 2 x 3
- 10 = 2 x 5
The LCM will be 2 x 3 x 5 = 30.
Conclusion: The Importance of Understanding LCM
The LCM, and specifically the LCM of 5 and 6, is not just an abstract mathematical concept; it's a powerful tool with tangible real-world applications. Understanding its calculation and significance is crucial for students and professionals across various disciplines. Whether you are simplifying fractions, scheduling events, or working with mechanical systems, mastering the concept of LCM provides a valuable skill set for problem-solving and efficient operations. This detailed exploration has aimed to demystify the concept of LCM, showcasing its versatility and practicality in a comprehensive manner. Further exploration into related concepts like GCD and modular arithmetic will only enhance your understanding and appreciation for this fundamental mathematical idea.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is 2 And 1 2 As A Decimal
Mar 10, 2025
-
What Is 58 Degrees Fahrenheit In Celsius
Mar 10, 2025
-
How Many Inches Are In 6 Feet
Mar 10, 2025
-
How Many Valence Electrons Does Zn Have
Mar 10, 2025
-
How Do You Say Go To In Spanish
Mar 10, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Least Common Multiple Of 5 And 6 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
