In Activity Based Costing An Activity Measure Is
Holbox
Mar 27, 2025 · 7 min read
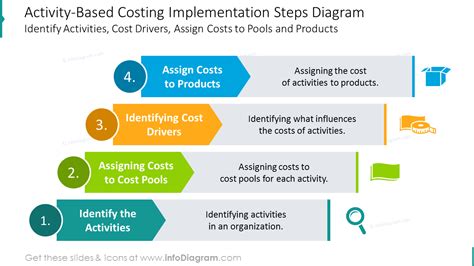
Table of Contents
- In Activity Based Costing An Activity Measure Is
- Table of Contents
- In Activity-Based Costing, an Activity Measure Is: The Key to Accurate Cost Allocation
- Understanding the Role of Activity Measures in ABC
- Examples of Activity Measures
- Selecting the Right Activity Measure: Key Considerations
- Activity Measures and Cost Pools
- Dealing with Multiple Cost Drivers
- Challenges in Implementing Activity Measures
- Overcoming Challenges and Ensuring Success
- Conclusion: Activity Measures – The Foundation of Accurate ABC
- Latest Posts
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
In Activity-Based Costing, an Activity Measure Is: The Key to Accurate Cost Allocation
Activity-based costing (ABC) is a powerful costing method that moves beyond traditional approaches by focusing on activities as the fundamental cost drivers. Unlike traditional methods that often rely on simplistic volume-based measures like direct labor hours, ABC digs deeper to pinpoint the specific activities that consume resources and drive costs. A crucial element of this process is the activity measure, the metric used to quantify the consumption of resources by each activity. Understanding what an activity measure is, and how to select and apply the right one, is critical to the success of ABC.
This comprehensive guide will explore the intricacies of activity measures in ABC, providing you with a solid understanding of their role, different types, and best practices for selecting and implementing them effectively.
Understanding the Role of Activity Measures in ABC
In essence, an activity measure is a quantifiable metric that reflects the volume or intensity of an activity performed. It serves as the link between the cost of an activity and the products or services that consume it. The accuracy of cost allocation in ABC heavily depends on the choice and precision of these measures. An incorrectly chosen activity measure can lead to inaccurate cost assignments, flawed pricing decisions, and ultimately, compromised profitability.
The primary role of an activity measure is to:
- Assign costs accurately: By quantifying activity consumption, the activity measure allows for a more precise allocation of indirect costs (overhead) to products or services based on their actual consumption of resources.
- Identify cost drivers: The selection of an appropriate activity measure helps pinpoint the activities that are the most significant cost drivers within the organization. This identification allows for better management and control of costs.
- Improve decision-making: Accurate cost information derived from well-chosen activity measures empowers managers to make informed decisions regarding pricing, product mix, process improvement, and resource allocation.
Examples of Activity Measures
The type of activity measure used depends entirely on the specific activity being considered. There is no one-size-fits-all solution. Here are several examples of common activity measures:
-
Number of units produced: This is a suitable measure for activities directly related to production volume, such as machine setup, material handling, and quality inspection. However, it's crucial to note that this simplistic measure may not capture the complexities of activities involving diverse product lines or varying production processes.
-
Number of orders processed: This is appropriate for activities related to order fulfillment, such as order entry, invoicing, and shipping. It reflects the workload associated with each order, regardless of the size or complexity.
-
Number of machine hours: A useful measure for activities directly related to machine usage, such as machine maintenance and depreciation. This measure accounts for the time a machine is operational, regardless of the number of units produced.
-
Number of engineering hours: This measure is suitable for activities related to product design and engineering support. It captures the time spent on design, testing, and problem-solving.
-
Number of customer interactions: A suitable measure for activities related to customer service, such as phone calls, emails, and on-site visits. It reflects the level of support provided to customers.
-
Number of purchase orders: This measure is useful for activities related to procurement, such as order processing, vendor communication, and receiving. It reflects the volume of purchasing activity.
-
Number of inspections: A suitable measure for activities related to quality control, reflecting the amount of quality checking performed.
-
Kilometers driven: This measure could be used for activities related to delivery or field service. It captures the distance traveled, reflecting fuel costs and wear and tear on vehicles.
-
Direct labor hours: Although traditionally used in cost allocation, this measure is sometimes incorporated into ABC, particularly in activities heavily reliant on direct labor.
Selecting the Right Activity Measure: Key Considerations
Choosing the appropriate activity measure is a crucial step in implementing ABC. The selection process requires careful consideration of several factors:
-
Causality: The chosen measure must have a clear causal relationship with the activity's cost. In other words, the higher the activity measure, the higher the activity cost should be. A strong correlation is essential for accurate cost allocation.
-
Relevance: The measure should be relevant to the specific activity being costed. An irrelevant measure will lead to inaccurate and misleading cost assignments.
-
Measurability: The activity measure must be easily and accurately measurable. Data collection should be straightforward and reliable to ensure the integrity of the ABC system.
-
Cost-effectiveness: The cost of measuring the activity should not outweigh the benefits of improved cost accuracy. Overly complex or expensive measures can negate the advantages of ABC.
-
Consistency: The chosen measure should be consistently applied over time to ensure comparability of cost data across different periods. Changes in the measure should be carefully considered and documented.
-
Complexity: The simplicity of the activity measure should be balanced with its accuracy. While simple measures are easy to implement, they may not always capture the full complexity of the activity.
-
Data Availability: Ensure readily available data exists for your chosen measure. If not, you'll need to establish a system for collecting the necessary data.
Activity Measures and Cost Pools
Activity measures are closely tied to cost pools. A cost pool is a grouping of costs related to a specific activity. The total cost of the cost pool is then allocated to products or services based on the consumption of the activity, as measured by the chosen activity measure.
For example:
- Cost Pool: Machine setup
- Activity Measure: Number of setups
- Cost Allocation: The total cost of machine setup is divided by the total number of setups, resulting in a cost per setup. This cost per setup is then allocated to each product based on the number of setups required for its production.
Dealing with Multiple Cost Drivers
Some activities might be driven by multiple factors. In such cases, it's important to identify all significant cost drivers and incorporate them into the cost allocation process. This might involve using multiple activity measures for a single cost pool or employing more sophisticated statistical techniques to determine the relative importance of each driver.
Challenges in Implementing Activity Measures
While ABC offers significant advantages, there are challenges associated with implementing effective activity measures:
-
Data Collection: Gathering accurate and reliable data for activity measures can be time-consuming and resource-intensive.
-
Cost of Implementation: Implementing an ABC system can be expensive, requiring investment in software, training, and personnel.
-
Complexity: ABC can be more complex than traditional costing methods, requiring specialized knowledge and expertise.
-
Subjectivity: In some cases, the selection of an appropriate activity measure might involve some degree of subjectivity, particularly when dealing with less quantifiable activities.
Overcoming Challenges and Ensuring Success
To overcome these challenges and ensure the success of your ABC implementation:
-
Start Small: Begin by focusing on a few key activities and gradually expand the scope of the ABC system.
-
Invest in Training: Provide adequate training to personnel involved in data collection, analysis, and cost allocation.
-
Use Technology: Leverage technology, such as specialized software, to streamline data collection and analysis.
-
Regular Review and Refinement: Regularly review and refine the ABC system based on feedback and experience.
Conclusion: Activity Measures – The Foundation of Accurate ABC
In conclusion, the activity measure is a critical component of activity-based costing. Selecting and implementing the right activity measures is essential for accurately allocating costs, identifying cost drivers, and improving decision-making. By carefully considering the factors outlined above and addressing potential challenges proactively, organizations can harness the power of ABC to gain valuable insights into their cost structures and enhance their operational efficiency and profitability. Remember, the accuracy and effectiveness of your ABC system hinges on the meticulous selection and consistent application of appropriate activity measures. Investing the necessary time and resources in this crucial aspect will yield significant returns in the form of improved cost management and enhanced business performance.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Authorized Common Stock Refers To The Total Number Of Shares
Mar 31, 2025
-
Match The Type Of Simple Epithelium With Its Description
Mar 31, 2025
-
Multiple Sclerosis And Atherosclerosis Both Refer To
Mar 31, 2025
-
A Game Is Said To Be Fair If
Mar 31, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Is The Strongest Acid
Mar 31, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about In Activity Based Costing An Activity Measure Is . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
