Distribution Intensity Is Commonly Divided Into Three Levels
Holbox
Mar 18, 2025 · 5 min read
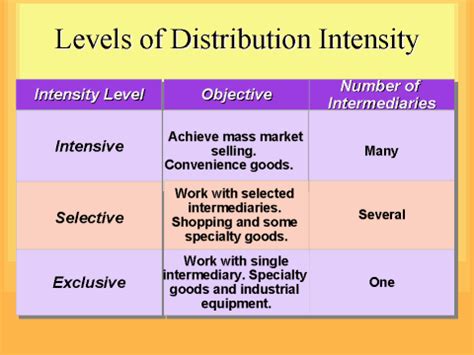
Table of Contents
Distribution Intensity: A Deep Dive into Intensive, Selective, and Exclusive Strategies
Distribution intensity is a crucial element of a company's marketing strategy. It dictates the availability of a product or service to the target market. Understanding the nuances of distribution intensity is critical for achieving optimal market penetration and maximizing sales. This concept is commonly divided into three levels: intensive, selective, and exclusive distribution. Each strategy has its own advantages and disadvantages, and selecting the right one depends heavily on factors like product type, target market, competitive landscape, and marketing budget.
Intensive Distribution: Saturating the Market
Intensive distribution aims for maximum market coverage. The goal is to make the product available in as many outlets as possible. Think everyday items like candy bars, soft drinks, or newspapers. You can find these products practically everywhere – supermarkets, convenience stores, gas stations, even vending machines.
Advantages of Intensive Distribution:
- Increased Sales Volume: By saturating the market, companies dramatically increase the likelihood of a purchase. Consumers encounter the product at numerous locations, increasing impulse buys and overall sales.
- Enhanced Brand Awareness: Constant visibility through widespread availability builds strong brand recognition and familiarity among consumers.
- Convenience for Consumers: Easy accessibility is a major draw for consumers, especially for frequently purchased items.
- Competitive Advantage: A broad reach can discourage competitors from entering the market or limit their effectiveness.
Disadvantages of Intensive Distribution:
- Lower Profit Margins: Intensive distribution often involves agreements with numerous retailers, leading to lower profit margins per unit due to discounts and volume-based agreements.
- Loss of Control over Branding and Messaging: When a product is available through countless channels, maintaining consistent branding and messaging becomes challenging. Retailers may not always adhere to the brand's guidelines perfectly.
- Increased Logistics and Distribution Costs: Managing a vast distribution network requires significant investment in logistics, warehousing, and transportation.
- Potential for Channel Conflict: Conflicts can arise between different retailers, such as price wars or disagreements over inventory allocation.
Suitable Products for Intensive Distribution:
Products suitable for intensive distribution are typically:
- Low-priced, frequently purchased goods: Items consumers buy regularly and don't require much deliberation.
- Non-durable goods: Items with a short shelf life.
- High-volume products: Items sold in large quantities.
Selective Distribution: Finding the Sweet Spot
Selective distribution adopts a middle ground. It involves distributing products through a limited number of retailers carefully chosen for their alignment with the brand and target market. This strategy is common for clothing brands, electronics, and moderately priced appliances. You'll find these products in selected stores rather than every corner store.
Advantages of Selective Distribution:
- Higher Profit Margins: Working with fewer retailers allows for better price negotiation and potentially higher profit margins.
- Stronger Brand Image: Partnering with carefully selected retailers helps reinforce a brand's image and enhance its perceived value.
- Greater Control over Retailing Practices: Selective distribution gives companies more influence on how their products are displayed, promoted, and sold.
- Improved Customer Service: The chosen retailers are expected to provide higher quality customer service, strengthening the brand's reputation.
Disadvantages of Selective Distribution:
- Lower Market Coverage: Reaching fewer customers compared to intensive distribution limits potential sales.
- Increased Difficulty in Reaching Target Market: Consumers might not find the product readily available, potentially leading to lost sales.
- Potential for Stockouts: If the selected retailers don't manage inventory effectively, stockouts can occur, frustrating consumers.
- Higher Distribution Costs per Unit: The cost of managing a smaller, but still significant, distribution network can be relatively high per unit sold.
Suitable Products for Selective Distribution:
Products well-suited for selective distribution typically:
- Require some level of consumer deliberation: Items that aren't impulse buys.
- Moderate to high price points: Products where consumers are willing to shop around, but brand reputation is still important.
- Products requiring specialized knowledge or expertise: Items needing informed sales assistance.
Exclusive Distribution: Preserving Exclusivity and Prestige
Exclusive distribution is the most restrictive approach. It involves granting exclusive rights to distribute a product to a single retailer or a very limited number of carefully chosen retailers within a specific geographic area. This strategy is often used for luxury goods, high-end electronics, or specialized equipment.
Advantages of Exclusive Distribution:
- Premium Branding and Image: Exclusivity enhances the product's perceived value and reinforces its premium image.
- Stronger Brand Loyalty: Limited availability creates a sense of exclusivity and can foster stronger brand loyalty.
- Maximum Control over Retailing Practices: Companies retain maximum control over pricing, display, and promotional activities.
- Higher Profit Margins: Exclusive arrangements often lead to higher profit margins due to fewer retailers and potentially higher prices.
Disadvantages of Exclusive Distribution:
- Limited Market Reach: Reaching a smaller segment of the market significantly restricts potential sales volume.
- High Dependence on Retailers: Companies are highly dependent on the performance and reliability of their exclusive partners.
- Potential for Channel Conflict: Conflicts can arise if exclusive agreements aren't clearly defined and enforced.
- Higher Risk of Stockouts or Supply Chain Issues: The limited number of distribution points increases the risk of stockouts or disruptions to the supply chain.
Suitable Products for Exclusive Distribution:
Products that are ideal for exclusive distribution typically:
- Luxury goods or high-end products: Items with a high perceived value and strong brand recognition.
- Products requiring specialized knowledge or service: Items that need expert sales assistance.
- Products with limited production capacity: Items where supply is intentionally restricted to maintain exclusivity.
Choosing the Right Distribution Intensity: A Strategic Decision
Choosing the right distribution intensity requires careful consideration of various factors. Companies should analyze:
- Product characteristics: Perishability, price point, brand image, and required after-sales service.
- Target market: Consumer behavior, purchasing habits, and geographic distribution.
- Competitive landscape: The actions of competitors and their distribution strategies.
- Company resources and capabilities: Financial resources, logistics infrastructure, and marketing expertise.
The selected distribution intensity directly impacts a product's success. A mismatch can lead to lost sales, damaged brand image, and ultimately, business failure. Companies must carefully weigh the advantages and disadvantages of each approach, tailoring their distribution strategy to their specific needs and circumstances. The optimal strategy is not a one-size-fits-all solution; it's a dynamic process requiring continuous monitoring and adaptation. Regular evaluation and adjustments are crucial for maximizing effectiveness and navigating the ever-changing marketplace. By diligently analyzing market dynamics and their own capabilities, companies can leverage the right distribution intensity to achieve sustainable growth and profitability. Understanding distribution intensity is not merely a theoretical exercise; it is a fundamental aspect of successful business operation.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Working Across Generations Has Many Benefits Including
Mar 18, 2025
-
An Organization That Pursues A Single Product Strategy
Mar 18, 2025
-
A Pizza Restaurant Buys Pre Sliced Mushrooms
Mar 18, 2025
-
Art Labeling Activity Overview Of The Cardiac Conduction System
Mar 18, 2025
-
Copy And Paste Or Type Your Submission Right Here
Mar 18, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Distribution Intensity Is Commonly Divided Into Three Levels . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
