Art-labeling Activity Overview Of The Cardiac Conduction System
Holbox
Mar 18, 2025 · 6 min read
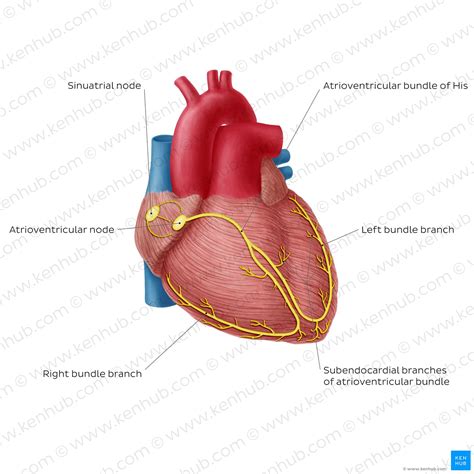
Table of Contents
Art-Labeling Activity Overview of the Cardiac Conduction System
The human heart, a tireless engine driving life itself, relies on a sophisticated electrical system for its rhythmic contractions. Understanding this intricate network, known as the cardiac conduction system, is crucial for healthcare professionals and students alike. This article provides a comprehensive overview of the cardiac conduction system, ideal for visual learners, incorporating an art-labeling activity to solidify understanding. By actively engaging with the diagrams, readers will gain a deeper appreciation for the pathways and processes that orchestrate each heartbeat.
The Symphony of the Heart: Understanding the Cardiac Conduction System
The heart doesn't simply beat randomly; its contractions are meticulously coordinated by a specialized network of cells capable of generating and conducting electrical impulses. This system ensures that the atria (upper chambers) contract before the ventricles (lower chambers), allowing for efficient blood flow through the heart and into the systemic circulation. Any disruption to this delicate balance can lead to serious cardiac arrhythmias.
Key Players in the Cardiac Conduction System:
The cardiac conduction system is composed of several key components, each playing a crucial role in generating and transmitting the electrical impulses:
-
Sinoatrial (SA) Node: Often called the "natural pacemaker," the SA node is located in the right atrium. It spontaneously generates electrical impulses at a rate of 60-100 beats per minute, setting the rhythm for the entire heart. This intrinsic rate can be influenced by the autonomic nervous system (sympathetic and parasympathetic).
-
Atrioventricular (AV) Node: Situated at the junction of the atria and ventricles, the AV node acts as a gatekeeper. It delays the electrical impulse briefly, allowing the atria to fully contract and empty their blood into the ventricles before ventricular contraction begins. This delay is critical for efficient blood flow.
-
Bundle of His (AV Bundle): This specialized pathway originates from the AV node and extends into the interventricular septum (the wall separating the ventricles). It transmits the electrical impulse rapidly to the ventricles.
-
Right and Left Bundle Branches: The Bundle of His divides into two branches, one for each ventricle. These branches further conduct the impulse towards the apex of the heart.
-
Purkinje Fibers: These extensive networks of fibers spread throughout the ventricular myocardium (heart muscle). They rapidly distribute the electrical impulse, ensuring coordinated and simultaneous contraction of the ventricular muscle.
The Art of Labeling: A Hands-On Approach to Learning
Now, let's put your knowledge to the test with an art-labeling activity. Imagine a detailed diagram of the heart, showcasing the components of the cardiac conduction system. You can find such diagrams in textbooks, online resources, or even create your own simplified version. The key is to have a visual representation to work with.
(Note: This section requires the reader to have access to a diagram of the heart depicting the cardiac conduction system. The following is a guide to the labels and their locations.)
Labeling the Key Structures:
-
Sinoatrial (SA) Node: Locate the SA node in the upper right atrium. Label it clearly. Note its position relative to the superior vena cava.
-
Atrioventricular (AV) Node: Find the AV node at the junction between the atria and ventricles. Label it and observe its proximity to the tricuspid valve.
-
Bundle of His (AV Bundle): Trace the Bundle of His as it descends from the AV node into the interventricular septum. Label it clearly.
-
Right Bundle Branch: Identify the right bundle branch extending into the right ventricle. Label it accordingly.
-
Left Bundle Branch: Locate the left bundle branch branching off from the Bundle of His into the left ventricle. Label it.
-
Purkinje Fibers: Observe the extensive network of Purkinje fibers spreading through both ventricles. Indicate their widespread distribution with a label.
-
Atria: Label the left and right atria. Pay attention to the anatomical structures within the atria such as the crista terminalis and the fossa ovalis.
-
Ventricles: Label the left and right ventricles and observe their thicker muscular walls.
Beyond the Basics: Understanding the Electrocardiogram (ECG)
The electrical activity of the heart can be measured using an electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG). The ECG provides a visual representation of the heart's electrical impulses, reflecting the activity of the cardiac conduction system. Understanding the ECG waves (P wave, QRS complex, T wave) helps diagnose various cardiac conditions.
ECG Waves and the Conduction System:
-
P wave: Represents atrial depolarization (electrical activation) initiated by the SA node.
-
PR interval: Reflects the time it takes for the impulse to travel from the SA node to the ventricles, including the AV nodal delay. Prolongation of this interval may indicate AV nodal dysfunction.
-
QRS complex: Represents ventricular depolarization (electrical activation) spread through the Bundle of His, bundle branches, and Purkinje fibers. Widening of this complex can signify conduction delays or abnormalities in the ventricles.
-
ST segment: Represents the early phase of ventricular repolarization (electrical recovery). Changes in this segment can indicate myocardial ischemia (reduced blood flow to the heart muscle).
-
T wave: Represents ventricular repolarization. Abnormal T wave morphology can suggest electrolyte imbalances or cardiac ischemia.
Analyzing ECG waveforms is essential for diagnosing various cardiac arrhythmias, including:
- Sinus tachycardia: Fast heart rate originating from the SA node.
- Sinus bradycardia: Slow heart rate originating from the SA node.
- Atrial fibrillation: Irregular, rapid atrial activity.
- Atrial flutter: Rapid, regular atrial activity.
- Ventricular tachycardia: Rapid, irregular ventricular activity.
- Ventricular fibrillation: A life-threatening condition characterized by chaotic ventricular activity.
- Heart Blocks: Various degrees of blockage in the conduction pathway, interfering with the transmission of impulses from the atria to the ventricles.
Clinical Significance and Further Exploration
Understanding the cardiac conduction system is pivotal in diagnosing and managing various cardiovascular diseases. Healthcare professionals use this knowledge to interpret ECGs, diagnose arrhythmias, and guide treatment strategies. For instance, knowledge of conduction pathways is crucial in interpreting the location of myocardial infarctions (heart attacks) based on ECG findings. Furthermore, interventions such as cardiac pacemakers and implantable cardioverter-defibrillators (ICDs) directly target components of the cardiac conduction system to restore or maintain normal heart rhythm.
Further exploration into the cardiac conduction system could include studying the cellular mechanisms of impulse generation and propagation, the role of ion channels, and the effects of various medications on the heart's rhythm. Advanced topics might include the impact of autonomic nervous system modulation on heart rate and the pathophysiology of specific arrhythmias. In essence, the cardiac conduction system is a richly complex and fascinating area of study that warrants continuous investigation.
Conclusion: Mastering the Heart's Electrical Symphony
This article has provided a detailed overview of the cardiac conduction system, emphasizing its importance in maintaining a healthy heart rhythm. Through the art-labeling activity, readers have actively engaged with the visual representation of the system, strengthening their understanding of the various components and their interactions. A solid grasp of the cardiac conduction system is essential for healthcare professionals and students alike. By appreciating the intricate interplay of the SA node, AV node, Bundle of His, bundle branches, and Purkinje fibers, one gains a deeper understanding of the heart's electrical symphony – the rhythm that sustains life itself. Continued study and exploration of this fascinating system will only enhance appreciation for its vital role in maintaining human health.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
A Characteristic Of A Fixed Asset Is That It Is
Mar 18, 2025
-
Please Match The Organism With Its Fermentation Product
Mar 18, 2025
-
Strainers Are Present In Which Type Of Rescue Scene
Mar 18, 2025
-
Luisa Has Multiple Tasks To Work On
Mar 18, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Is The Most Difficult To Inactivate
Mar 18, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Art-labeling Activity Overview Of The Cardiac Conduction System . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
