Distinguish Between Infrasonic And Ultrasonic Sound Waves
Holbox
Mar 22, 2025 · 6 min read
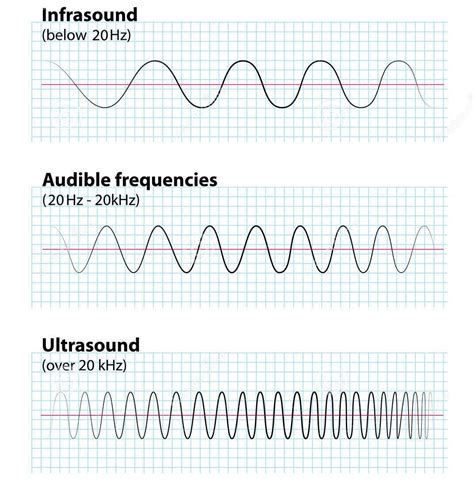
Table of Contents
Distinguishing Infrasonic and Ultrasonic Sound Waves: A Deep Dive into the Extremes of Audible Sound
Sound, a fundamental aspect of our daily lives, is a form of energy that travels as waves. While we perceive sound within a specific frequency range, the world of acoustic waves extends far beyond the limits of human hearing. This article delves into the fascinating realms of infrasound and ultrasound, exploring their properties, sources, effects, and applications. We will definitively distinguish between these two types of sound waves, highlighting their key differences and similarities.
Understanding the Basics: Frequency and Human Hearing
Before diving into infrasound and ultrasound, let's establish a baseline understanding of sound frequency. Frequency, measured in Hertz (Hz), represents the number of sound wave cycles that pass a given point per second. The human ear can typically perceive sounds within the range of 20 Hz to 20,000 Hz. Sounds below 20 Hz are classified as infrasound, while those above 20,000 Hz are known as ultrasound.
The Audible Spectrum: A Narrow Window
It's crucial to remember that the audible spectrum is a relatively narrow band compared to the full range of sound wave frequencies found in nature and generated by various technologies. The vast majority of sound waves fall outside the range of human perception. This is where the study of infrasound and ultrasound becomes particularly significant.
Infrasound: The Low-Frequency Rumble
Infrasound, with its frequencies below 20 Hz, is often described as a low-frequency rumble or vibration. These waves are characterized by their long wavelengths, which allow them to travel long distances with minimal attenuation (loss of energy). This characteristic makes infrasound particularly interesting for various scientific and practical applications.
Sources of Infrasound: Natural and Man-made
Several natural phenomena generate infrasound. These include:
- Earthquakes: Seismic activity produces powerful infrasonic waves that can travel thousands of kilometers, providing valuable data for seismologists.
- Volcanoes: Eruptions generate intense infrasonic waves, providing early warning signals and insights into volcanic activity.
- Meteorological events: Strong winds, thunderstorms, and even auroras can produce infrasonic waves.
- Ocean waves: Large ocean waves crashing on the shore or during storms create infrasonic waves detectable over vast distances.
Man-made sources of infrasound include:
- Explosions: Large explosions, such as nuclear detonations or industrial blasts, generate intense infrasonic waves.
- Transportation: Large vehicles like airplanes, trains, and heavy machinery produce infrasonic noise as a byproduct of their operation.
- Industrial processes: Certain industrial processes, such as wind turbines and some types of machinery, generate infrasonic noise.
Effects of Infrasound on Humans and the Environment
While humans generally cannot consciously hear infrasound, some studies suggest potential physiological effects at high intensities. These effects might include feelings of unease, pressure on the chest, or even nausea. The long-term effects of exposure to high-intensity infrasound are still under investigation. It is crucial to remember that the effects of infrasound depend heavily on intensity and duration of exposure. Low levels of infrasound are likely to have minimal or no noticeable effects.
The impact of infrasound on the environment is largely unknown, but the potential for disruption of animal communication and behavior warrants further research.
Ultrasound: The High-Frequency World
Ultrasound, with its frequencies above 20,000 Hz, lies beyond the range of human hearing. Its short wavelengths allow for highly focused beams of energy, making it incredibly valuable for various applications.
Sources of Ultrasound: Natural and Man-made
Naturally occurring ultrasound is less common than infrasound but does occur in some instances. Examples include:
- Animal vocalizations: Certain animals, such as bats and dolphins, utilize ultrasound for echolocation and communication. This has driven significant biological research related to acoustic signal processing.
- Some natural phenomena: Certain meteorological events and seismic activity may also generate weak ultrasonic signals.
Man-made ultrasound sources are ubiquitous and include:
- Medical imaging: Ultrasound is widely used in medical imaging techniques, such as sonography, providing non-invasive visualization of internal organs and tissues.
- Industrial cleaning: Ultrasonic cleaners utilize high-frequency vibrations to remove dirt and contaminants from delicate objects.
- Sonar: Sonar systems utilize ultrasound to detect and locate underwater objects.
- Welding and cutting: Ultrasonic welding and cutting techniques use high-frequency vibrations to join or cut materials with precision.
Applications of Ultrasound: A Diverse Range
The versatility of ultrasound is reflected in its diverse applications across numerous fields:
- Medicine: Beyond imaging, ultrasound is used in therapeutic applications, such as physiotherapy and lithotripsy (breaking up kidney stones). Further research is exploring the therapeutic use of focused ultrasound in cancer treatment.
- Industry: In addition to cleaning and material processing, ultrasound is used in flaw detection in materials, non-destructive testing, and process control.
- Scientific research: Ultrasound finds application in various scientific domains, including materials science, fluid dynamics, and biological research.
- Security and defense: Ultrasonic sensors play a role in various security and defense applications, including intruder detection and obstacle avoidance systems.
Effects of Ultrasound on Humans and the Environment
While ultrasound itself is inaudible, high-intensity ultrasound can have adverse effects on humans, including hearing damage (even though it's beyond the audible range, intense ultrasound can cause damage to the inner ear). However, the levels used in most common applications are generally considered safe.
Key Differences Between Infrasound and Ultrasound: A Comparison Table
| Feature | Infrasound | Ultrasound |
|---|---|---|
| Frequency Range | Below 20 Hz | Above 20,000 Hz |
| Wavelength | Long | Short |
| Attenuation | Low (travels long distances) | High (attenuates quickly) |
| Human Perception | Generally imperceptible; potential physiological effects at high intensities | Inaudible; potential physiological effects at high intensities |
| Applications | Seismology, volcano monitoring, atmospheric research | Medical imaging, industrial cleaning, sonar, material processing |
| Sources | Earthquakes, volcanoes, meteorological events, large machinery | Bats, dolphins (natural), medical equipment, industrial tools |
Conclusion: Exploring the Unheard
Infrasound and ultrasound represent the extremes of the acoustic spectrum, extending far beyond the limited range of human hearing. While imperceptible to our ears, these sound waves play significant roles in various natural phenomena and technological applications. Understanding their properties, sources, and effects is crucial for advancements in fields ranging from medical imaging to environmental monitoring and disaster prediction. Ongoing research continues to uncover new insights into the effects of these sound waves on humans, animals, and the environment, paving the way for innovative technologies and a deeper understanding of the acoustic world around us. Further study is needed to fully understand the complex interaction between these sound waves and biological systems, as well as their potential impact on our environment. The exploration of infrasound and ultrasound remains a frontier of scientific discovery, promising to reveal more about the intricate workings of our planet and the universe around us.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Of The Following Uses Of Removable Media Is Allowed
Mar 22, 2025
-
The Developing Person Through The Lifespan
Mar 22, 2025
-
The Relationship Between Sales And Profits Can Be Written As
Mar 22, 2025
-
A Construction Company Is Bidding On A Contract In Thailand
Mar 22, 2025
-
Managers Use An Internal Control System
Mar 22, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Distinguish Between Infrasonic And Ultrasonic Sound Waves . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
