Determine The Missing Amount For Each Of The Following
Holbox
Mar 23, 2025 · 5 min read
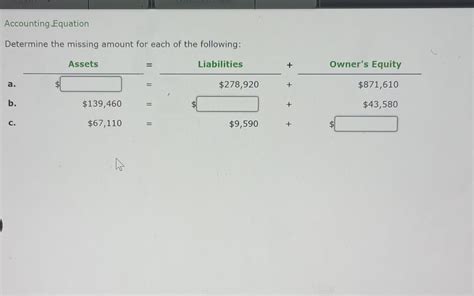
Table of Contents
- Determine The Missing Amount For Each Of The Following
- Table of Contents
- Determine the Missing Amount: A Comprehensive Guide to Accounting Equation Analysis
- Understanding the Accounting Equation: Assets = Liabilities + Equity
- Determining Missing Amounts: Step-by-Step Approach
- Practical Examples: Determining Missing Amounts in Different Scenarios
- Scenario 1: Missing Asset Value
- Scenario 2: Missing Liability Value
- Scenario 3: Missing Equity Value
- Beyond the Basic Equation: Analyzing Transactions and their Impact
- Advanced Applications: Dealing with More Complex Scenarios
- Conclusion: Mastering the Art of Determining Missing Amounts
- Latest Posts
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
Determine the Missing Amount: A Comprehensive Guide to Accounting Equation Analysis
Determining missing amounts in accounting is a fundamental skill for anyone working with financial statements. Whether you're a student, an entrepreneur, or a seasoned accountant, understanding how to solve for unknowns within the accounting equation is crucial for accurate financial reporting and decision-making. This comprehensive guide will walk you through various scenarios and techniques to effectively determine missing amounts, focusing on the core accounting equation and its implications.
Understanding the Accounting Equation: Assets = Liabilities + Equity
The accounting equation, Assets = Liabilities + Equity, forms the bedrock of double-entry bookkeeping. It represents the fundamental relationship between a company's resources (assets), its obligations to others (liabilities), and the owners' stake in the business (equity). Every transaction affects at least two accounts, ensuring the equation always remains balanced.
Assets are resources controlled by the company as a result of past events and from which future economic benefits are expected to flow to the entity. Examples include cash, accounts receivable, inventory, and equipment.
Liabilities are present obligations of the entity arising from past events, the settlement of which is expected to result in an outflow of resources embodying economic benefits. Examples include accounts payable, salaries payable, and loans payable.
Equity represents the residual interest in the assets of the entity after deducting all its liabilities. For a sole proprietorship or partnership, this is often referred to as owner's equity. For corporations, it's typically shareholder's equity and includes contributed capital and retained earnings.
Determining Missing Amounts: Step-by-Step Approach
When faced with a problem where one element of the accounting equation is missing, follow these steps:
-
Identify the Known Variables: Carefully examine the problem and list the known values for assets, liabilities, and equity.
-
Substitute the Known Values into the Equation: Replace the known variables in the accounting equation (Assets = Liabilities + Equity) with their numerical values.
-
Solve for the Unknown Variable: Use basic algebra to solve for the missing amount. This may involve addition, subtraction, multiplication, or division depending on which component is unknown.
-
Verify the Solution: Once you've calculated the missing amount, substitute all the values back into the accounting equation to verify that the equation remains balanced.
Practical Examples: Determining Missing Amounts in Different Scenarios
Let's explore various scenarios with missing amounts and illustrate how to solve them using the accounting equation.
Scenario 1: Missing Asset Value
Problem: A company has liabilities of $50,000 and equity of $100,000. Determine the value of its assets.
Solution:
-
Known Variables: Liabilities = $50,000; Equity = $100,000
-
Substitute into Equation: Assets = $50,000 + $100,000
-
Solve for Assets: Assets = $150,000
-
Verification: $150,000 (Assets) = $50,000 (Liabilities) + $100,000 (Equity) The equation balances.
Therefore, the value of the company's assets is $150,000.
Scenario 2: Missing Liability Value
Problem: A business has assets worth $200,000 and equity of $75,000. What is the amount of its liabilities?
Solution:
-
Known Variables: Assets = $200,000; Equity = $75,000
-
Substitute into Equation: $200,000 = Liabilities + $75,000
-
Solve for Liabilities: Liabilities = $200,000 - $75,000 = $125,000
-
Verification: $200,000 (Assets) = $125,000 (Liabilities) + $75,000 (Equity) The equation balances.
Therefore, the amount of the business's liabilities is $125,000.
Scenario 3: Missing Equity Value
Problem: A company reports assets totaling $300,000 and liabilities of $150,000. Calculate the value of its equity.
Solution:
-
Known Variables: Assets = $300,000; Liabilities = $150,000
-
Substitute into Equation: $300,000 = $150,000 + Equity
-
Solve for Equity: Equity = $300,000 - $150,000 = $150,000
-
Verification: $300,000 (Assets) = $150,000 (Liabilities) + $150,000 (Equity) The equation balances.
Therefore, the value of the company's equity is $150,000.
Beyond the Basic Equation: Analyzing Transactions and their Impact
The accounting equation isn't just a static formula; it dynamically reflects the impact of every business transaction. Understanding how transactions affect the equation is crucial for accurate record-keeping.
For instance, consider the following transactions:
-
Purchase of equipment with cash: This transaction decreases cash (an asset) and increases equipment (another asset). The total assets remain unchanged, and therefore, the equation remains balanced.
-
Borrowing money from a bank: This increases cash (an asset) and increases loans payable (a liability). Again, the equation remains balanced because both sides increase equally.
-
Revenue earned on credit: This increases accounts receivable (an asset) and increases revenue, which ultimately increases retained earnings (part of equity). The equation stays balanced.
-
Payment of expenses: This decreases cash (an asset) and decreases retained earnings (equity) through an expense reduction. The equation remains balanced.
By analyzing each transaction's effect on assets, liabilities, and equity, you can ensure your accounting records are accurate and the accounting equation consistently remains balanced.
Advanced Applications: Dealing with More Complex Scenarios
While the basic accounting equation provides a strong foundation, real-world accounting scenarios can be more complex. This complexity might involve:
-
Multiple asset accounts: Instead of one single asset figure, you might have to deal with several asset accounts (cash, accounts receivable, inventory, etc.). The total of all asset accounts will equal liabilities plus equity.
-
Multiple liability accounts: Similar to assets, liabilities could be broken down into several categories (accounts payable, notes payable, salaries payable, etc.). The sum of all liability accounts is then added to equity to equal the total assets.
-
Detailed equity breakdown: Equity might be further broken down into various components (common stock, retained earnings, treasury stock, etc.). You would sum all these components to arrive at the total equity figure.
In these more complex scenarios, the fundamental principle remains the same: The sum of all assets must always equal the sum of all liabilities and equity. Careful and organized accounting practices are crucial to accurately track these components and maintain the balance of the accounting equation.
Conclusion: Mastering the Art of Determining Missing Amounts
Mastering the ability to determine missing amounts within the accounting equation is essential for anyone involved in financial record-keeping and analysis. This skill provides a foundation for accurate financial reporting, sound business decision-making, and a comprehensive understanding of a company's financial health. By following the steps outlined in this guide and practicing with various scenarios, you'll develop confidence and proficiency in this critical aspect of accounting. Remember, consistent application and careful attention to detail are key to success. Continuously reviewing and understanding transactions' impact on the equation will further enhance your ability to effectively manage and interpret financial data.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Match The Assessment Tools With Their Designed Outcomes
Mar 25, 2025
-
Label The Structures Of The Knee
Mar 25, 2025
-
The Concept Of Human Resource Management Implies That Employees Are
Mar 25, 2025
-
Determine The Name Or Formula For Each Polyatomic Ion
Mar 25, 2025
-
How Can You Ensure Your Content Drives Action
Mar 25, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Determine The Missing Amount For Each Of The Following . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
