Can Mutations Show Convergent Evolution Worksheet Answer Key
Holbox
Mar 28, 2025 · 6 min read
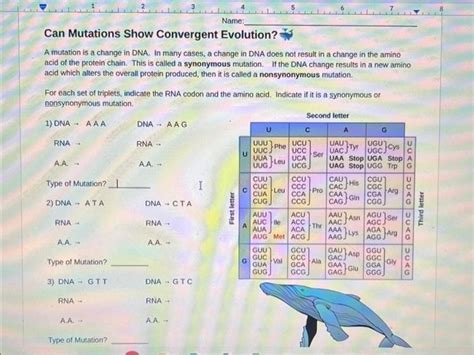
Table of Contents
Can Mutations Show Convergent Evolution? A Deep Dive into Worksheet Answers and Beyond
Convergent evolution, the independent evolution of similar traits in different species, is a fascinating aspect of biology. Understanding how this occurs at a genetic level, particularly through mutations, is crucial to grasping the mechanisms of evolutionary change. This article will delve deep into the question of whether mutations can demonstrate convergent evolution, providing detailed explanations to accompany common worksheet answers and expanding upon the underlying principles.
H2: What is Convergent Evolution?
Convergent evolution occurs when distantly related species develop similar traits as a result of adapting to similar environments or ecological niches. These similarities are analogous, not homologous. Homologous structures share a common ancestor, while analogous structures evolved independently. Think of the wings of birds, bats, and insects: while all serve the purpose of flight, their underlying structures are vastly different, reflecting their independent evolutionary origins. This difference is key to understanding how mutations play a role.
H3: The Role of Mutations
Mutations, changes in an organism's DNA sequence, are the raw material of evolution. They introduce variation into a population, providing the foundation upon which natural selection can act. Beneficial mutations, those that enhance an organism's survival and reproduction in a given environment, are more likely to be passed on to subsequent generations. This process, over vast stretches of time, can lead to the development of novel traits.
H2: How Mutations Contribute to Convergent Evolution
The crucial point is that convergent evolution isn't about identical mutations producing identical traits. Instead, it's about different mutations in different lineages leading to functionally similar outcomes. Different genetic pathways can achieve the same phenotypic result.
H3: Example 1: Flight in Birds and Bats
Consider the evolution of flight in birds and bats. Birds' wings are formed by modifications of their forelimbs, involving specific genetic changes affecting bone development, feather formation, and muscle attachment. Bats, on the other hand, achieve flight through a different genetic pathway, involving modifications to their forelimbs that result in the formation of a patagium, a membrane of skin stretched between their elongated fingers. While the function is identical (flight), the underlying genetic mechanisms are distinct. Different mutations in different lineages resulted in analogous structures.
H3: Example 2: Echolocation in Bats and Dolphins
Another compelling example is echolocation in bats and dolphins. Both use sound waves to navigate and hunt in dark or murky environments. However, the genes and developmental pathways involved in echolocation evolved independently in these two lineages. Specific genes related to hearing, sound production, and neural processing underwent mutations in both bats and dolphins, but the specific mutations were likely different. The convergence lies in the functional outcome – effective echolocation – rather than the exact genetic changes.
H2: Interpreting Worksheet Answers: Common Scenarios
Many biology worksheets explore convergent evolution through simplified scenarios. Let's examine potential questions and their answers:
H3: Scenario 1: Different Mutations, Same Trait
- Question: Two different species, living in similar environments, independently evolve the ability to synthesize a specific toxin for defense. Species A achieves this through a mutation in gene X, while species B achieves it through a mutation in gene Y. Does this demonstrate convergent evolution?
- Answer: Yes. The similar phenotype (toxin production) arose through different genetic pathways (mutations in different genes), demonstrating convergent evolution. The key is the independent evolution of the same trait, despite different underlying genetic changes.
H3: Scenario 2: Similar Mutations, Different Traits
- Question: Two species share a similar mutation in gene Z. In species A, this mutation leads to increased camouflage, while in species B, it leads to enhanced resistance to a specific disease. Does this demonstrate convergent evolution?
- Answer: No. While the mutation is similar, the resulting phenotypes are different, reflecting the complex interplay of genes and environment. This showcases the importance of considering the phenotype, not just the genotype.
H3: Scenario 3: No Mutations, Similar Traits
- Question: Two species exhibit strikingly similar adaptations (e.g., streamlined body shape for swimming). However, genetic analysis reveals no significant mutations differentiating them from their respective ancestors. Can this be convergent evolution?
- Answer: This scenario is less likely to represent classic convergent evolution driven by mutations. It might suggest either: 1) the trait was already present in a common ancestor (homologous trait), and natural selection simply favored it in both lineages; or 2) the similarity is due to constraints imposed by the environment (e.g., a streamlined shape is hydrodynamically advantageous, regardless of the genetic pathway). Further research would be required to clarify.
H2: Beyond the Worksheet: The Complexity of Convergent Evolution
It's crucial to understand that the examples in worksheets simplify a highly complex process. Convergent evolution is not solely driven by individual mutations. It's a complex interplay of many factors:
-
Environmental pressures: The selective pressures of the environment play a crucial role in shaping the direction of evolution. Similar environments often favor similar adaptations, even if the genetic pathways are different.
-
Genetic drift: Random fluctuations in gene frequencies, especially in small populations, can contribute to the fixation of particular mutations, potentially leading to convergent evolution.
-
Epigenetics: Changes in gene expression without alteration of the underlying DNA sequence can also contribute to phenotypic similarities, even in the absence of identical mutations.
-
Developmental constraints: The developmental pathways of an organism can limit the types of adaptations that are possible. This can lead to convergent evolution towards a limited number of solutions, even if different genetic changes are involved.
H2: The Importance of Studying Convergent Evolution
Understanding convergent evolution is vital for several reasons:
-
Predicting future adaptations: By studying convergent adaptations in different species, we can potentially predict how species might adapt to future environmental changes.
-
Understanding evolutionary constraints: Convergent evolution can reveal the limitations on evolutionary pathways, highlighting the constraints imposed by genetics, development, and physics.
-
Developing new technologies: Biomimicry, the design of new technologies inspired by biological systems, often draws inspiration from convergent evolution. Studying the different ways nature has solved a particular problem can provide valuable insights for engineers and designers.
H2: Conclusion: Mutations as the Building Blocks
In conclusion, while mutations are not the sole driver, they are undoubtedly the fundamental building blocks of convergent evolution. Different mutations in different lineages can independently lead to similar traits through different genetic pathways. Understanding this interplay between mutations, environmental pressures, and developmental constraints is essential to fully appreciating the complex tapestry of life on Earth. Worksheets serve as a valuable starting point, offering a simplified introduction to this multifaceted evolutionary phenomenon. Remember, the key is recognizing the functional similarity of traits, even if the underlying genetic mechanisms are distinct. This nuanced understanding opens doors to a deeper appreciation of evolution's power and ingenuity.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Molecule Is Expected To Have The Smallest Pka
Apr 01, 2025
-
Which Could Be The Function Graphed Below
Apr 01, 2025
-
Art Labeling Activity Gross Anatomy Of The Stomach
Apr 01, 2025
-
Personal Eyeglasses Provide As Much Protection As
Apr 01, 2025
-
Microbiology With Diseases By Body System
Apr 01, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Can Mutations Show Convergent Evolution Worksheet Answer Key . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
