An Unfavorable Materials Quantity Variance Indicates That
Holbox
Mar 15, 2025 · 5 min read
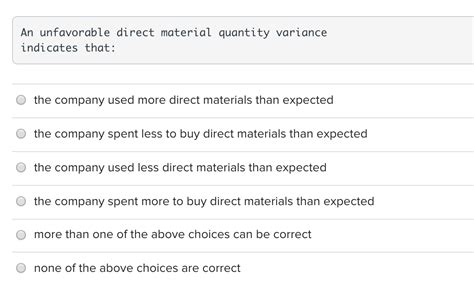
Table of Contents
An Unfavorable Materials Quantity Variance Indicates That… Trouble Ahead?
An unfavorable materials quantity variance signals a potential problem in your production process. It means you've used more raw materials than you planned for, leading to increased costs and potentially impacting your profitability. Understanding the root causes of this variance is crucial for effective cost management and process improvement. This article will delve deep into the meaning, implications, and investigation of unfavorable materials quantity variances, providing you with the tools to identify and rectify the issues they highlight.
Understanding Materials Quantity Variance
Before diving into the specifics of an unfavorable variance, let's establish a solid understanding of what a materials quantity variance is. It's the difference between the actual quantity of materials used in production and the standard quantity that should have been used, multiplied by the standard cost per unit of material.
Formula: (Actual Quantity - Standard Quantity) x Standard Price
Favorable Variance: This occurs when the actual quantity used is less than the standard quantity. It indicates efficiency and cost savings.
Unfavorable Variance: This is the focus of our discussion. It happens when the actual quantity used is more than the standard quantity, resulting in higher-than-expected material costs.
Causes of an Unfavorable Materials Quantity Variance
Several factors can contribute to an unfavorable materials quantity variance. Pinpointing the exact cause requires careful investigation, often involving a multi-faceted approach:
1. Inefficient Production Processes:
- Poorly maintained machinery: Malfunctioning equipment can lead to material waste and spoilage, significantly increasing the quantity used.
- Inadequate training of personnel: Lack of proper training can result in inefficient use of materials, leading to excess consumption. This includes errors in material handling, cutting, and assembly.
- Suboptimal workflow: Inefficient processes, bottlenecks, and poorly designed layouts can force workers to use more materials than necessary to achieve production goals.
- Lack of preventative maintenance: Ignoring scheduled maintenance on equipment increases the likelihood of breakdowns and subsequent material waste.
2. Material Defects & Spoilage:
- Poor quality raw materials: Using substandard materials might lead to higher rejection rates and increased consumption of materials to compensate for defects. Stricter quality control at the procurement stage is key.
- Improper storage conditions: Incorrect storage of materials can cause deterioration, spoilage, and damage, leading to increased consumption.
- Excessive handling: Repeated handling of materials increases the risk of damage and waste. Improving material handling practices can mitigate this issue.
3. Inaccurate Standard Costs:
- Outdated standards: Standard costs should be regularly reviewed and updated to reflect current market conditions and production efficiencies. Using outdated standards can mask inefficiencies and lead to inaccurate variance analysis.
- Unrealistic standards: Setting overly optimistic or unattainable standards can create an illusion of efficiency, masking underlying inefficiencies. Standards must be realistic and achievable.
4. Changes in Product Specifications:
- Design modifications: Changes in product design can require more materials than initially planned, leading to an unfavorable variance.
- Increased complexity: A more intricate product design inevitably requires more materials and increases the likelihood of material waste.
5. External Factors:
- Supply chain disruptions: Delays or shortages in material supply can force the use of alternative materials or methods, resulting in higher consumption.
- Seasonal variations: Seasonal fluctuations in material prices and availability can impact the quantity used.
Investigating and Addressing Unfavorable Materials Quantity Variances
Identifying the root cause is paramount to addressing the issue effectively. A systematic approach is recommended:
1. Data Analysis:
- Detailed Variance Report: Analyze the variance report for specific details, identifying which materials and production processes contributed most to the unfavorable variance.
- Production Records: Review production records for evidence of machine downtime, material defects, or other anomalies.
- Inventory Records: Cross-reference production records with inventory data to identify potential discrepancies in material usage.
2. On-Site Investigation:
- Production Floor Observation: Direct observation of the production process can reveal inefficiencies not apparent from data analysis alone. Look for bottlenecks, poor material handling, or other issues.
- Employee Interviews: Gather feedback from production workers to understand their perspectives on the issues contributing to the variance.
- Machine Inspections: Inspect machinery for signs of wear and tear, malfunction, or improper calibration.
3. Corrective Actions:
Once the root cause(s) are identified, implement appropriate corrective actions. This might include:
- Improving employee training: Provide better training on efficient material handling techniques and waste reduction strategies.
- Upgrading equipment: Invest in new equipment or perform necessary maintenance on existing machinery.
- Implementing a preventative maintenance program: A robust maintenance schedule minimizes downtime and material waste.
- Streamlining production processes: Optimize workflows, eliminate bottlenecks, and improve the layout of the production floor.
- Improving material quality control: Implement stricter quality checks on incoming raw materials to minimize defects.
- Enhancing inventory management: Implement better inventory control and storage practices to minimize spoilage and waste.
- Revising standard costs: Regularly update standard costs to reflect current market conditions and production efficiencies.
Preventing Future Unfavorable Variances
Proactive measures are crucial for preventing the recurrence of unfavorable materials quantity variances.
- Regular monitoring and analysis: Continuous monitoring of material usage and variance analysis will enable early detection of potential problems.
- Benchmarking: Compare your material usage against industry best practices to identify areas for improvement.
- Employee empowerment: Encourage employees to identify and report potential issues, fostering a culture of continuous improvement.
- Technological advancements: Explore technologies such as automated material handling systems and real-time production monitoring tools.
- Continuous improvement initiatives: Implement methodologies such as Lean Manufacturing or Six Sigma to systematically identify and eliminate waste.
The Financial Impact of Unfavorable Variances
Ignoring unfavorable materials quantity variances can have serious financial implications. The increased material costs directly impact profitability, reducing margins and potentially impacting the bottom line. This can lead to:
- Reduced profitability: Higher material costs directly translate to lower profits.
- Loss of competitiveness: Increased production costs make it difficult to compete on price.
- Inventory write-offs: Spoiled or unusable materials represent a direct loss of investment.
- Potential job losses: In severe cases, unsustainable cost increases might necessitate workforce reductions.
Conclusion
An unfavorable materials quantity variance is a significant indicator of underlying problems within a production process. It is not simply an accounting anomaly; it's a red flag demanding investigation and corrective action. By systematically investigating the root causes, implementing appropriate corrective measures, and establishing robust preventative strategies, businesses can effectively manage material costs, improve production efficiency, and protect their profitability. Remember that proactive management, continuous improvement, and a data-driven approach are key to long-term success in minimizing these variances and ensuring a healthy bottom line.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
A Flexible Budget Performance Report Compares
Mar 15, 2025
-
During The Breakfast Rush An Angry Customer
Mar 15, 2025
-
Is The Characteristic Of The Individuals Within The Population
Mar 15, 2025
-
Converting Nfa To Dfa Theorem 1 39
Mar 15, 2025
-
The Waiting Times Between A Subway Departure
Mar 15, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about An Unfavorable Materials Quantity Variance Indicates That . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
