An Anthracycline Classified As An Antitumor Antibiotic Is:
Holbox
Mar 14, 2025 · 6 min read
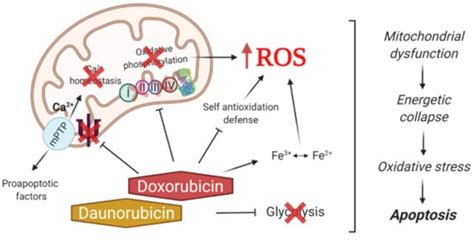
Table of Contents
Doxorubicin: A Deep Dive into This Anthracycline Antitumor Antibiotic
Anthracyclines are a family of powerful anti-cancer drugs, and among them, doxorubicin stands out as a cornerstone of cancer chemotherapy. Classified as an antitumor antibiotic, doxorubicin's mechanism of action, clinical applications, side effects, and ongoing research make it a fascinating subject for both medical professionals and those seeking to understand cancer treatment. This comprehensive article will explore doxorubicin in detail, examining its properties, uses, and limitations.
Understanding Doxorubicin: Mechanism of Action
Doxorubicin's potent anti-cancer effects stem from its ability to interfere with crucial cellular processes within rapidly dividing cancer cells. It's a topoisomerase II inhibitor, meaning it blocks the action of topoisomerase II, an enzyme essential for DNA replication and cell division. Specifically, doxorubicin intercalates into DNA, meaning it inserts itself between the DNA base pairs. This intercalation prevents topoisomerase II from properly unwinding and resealing DNA strands during replication. This leads to double-strand DNA breaks, which are highly toxic to the cell and ultimately trigger programmed cell death, or apoptosis.
The Interplay of Topoisomerase II Inhibition and DNA Damage:
The process isn't simply a matter of blocking topoisomerase II. Doxorubicin's interaction with the enzyme and DNA creates a complex that is highly susceptible to further damage. This increased vulnerability to damage significantly amplifies the drug's cytotoxic effect, leading to more effective cancer cell elimination. The precise mechanisms involved are still being investigated, but the interaction between doxorubicin, topoisomerase II, and the DNA molecule remains central to its efficacy.
Clinical Applications: Where Doxorubicin Makes a Difference
Doxorubicin's broad-spectrum anti-cancer activity makes it a vital component in the treatment of various cancers. While its use varies depending on the specific cancer type and stage, it's particularly effective in several key areas:
Breast Cancer:
Doxorubicin, often in combination with other chemotherapeutic agents like cyclophosphamide, is a cornerstone of adjuvant chemotherapy for breast cancer. This means it's used after surgery to eliminate any remaining cancer cells and reduce the risk of recurrence. Its effectiveness in both hormone receptor-positive and hormone receptor-negative breast cancers makes it a highly versatile treatment option.
Leukemia:
Doxorubicin plays a significant role in treating various types of leukemia, including acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL). It's often used in induction chemotherapy, the initial phase of treatment aimed at achieving remission, and also in consolidation therapy to further reduce the risk of relapse.
Lung Cancer:
In lung cancer, doxorubicin may be used in combination regimens for the treatment of small cell lung cancer (SCLC) and, in some cases, non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Its role is often in combination with other chemotherapeutic agents or targeted therapies, tailoring the treatment to the specific characteristics of the tumor.
Other Cancers:
Beyond these major applications, doxorubicin is also used in the treatment of other cancers, including:
- Ovarian cancer: Doxorubicin is part of many effective treatment regimens for ovarian cancer.
- Sarcomas: Doxorubicin shows efficacy in various sarcoma subtypes.
- Hodgkin's lymphoma: It's part of the treatment protocol for this type of lymphoma.
- Multiple myeloma: Used in combination therapy with other agents.
Side Effects: Managing the Challenges
While doxorubicin is a highly effective anti-cancer drug, it's associated with a range of side effects, some of which can be severe. Careful monitoring and management are crucial to mitigate these effects and ensure patient safety and well-being.
Cardiotoxicity:
The most significant and potentially life-threatening side effect of doxorubicin is cardiotoxicity. It can damage the heart muscle, leading to decreased cardiac function, congestive heart failure, and potentially fatal arrhythmias. Careful monitoring of cardiac function, including echocardiograms, is essential throughout treatment.
Myelosuppression:
Doxorubicin suppresses bone marrow function, leading to decreased production of blood cells. This can result in anemia (low red blood cell count), neutropenia (low white blood cell count, increasing the risk of infection), and thrombocytopenia (low platelet count, increasing the risk of bleeding). Regular blood tests are vital to monitor blood cell counts and adjust treatment as needed.
Mucositis:
Doxorubicin can cause inflammation and ulceration of the mucous membranes lining the mouth and gastrointestinal tract, leading to pain, difficulty swallowing, and increased risk of infection. Careful oral hygiene and supportive care are crucial to manage this side effect.
Alopecia:
Hair loss is a common side effect of doxorubicin, although it's usually temporary and hair regrowth occurs after treatment ends.
Nausea and Vomiting:
These are common side effects of chemotherapy, and effective antiemetic medications are typically used to prevent or minimize these symptoms.
Other Side Effects:
Other possible side effects include fatigue, skin rashes, liver damage, and kidney problems. The severity of these side effects varies widely among individuals.
Doxorubicin Delivery Methods: Ensuring Effective Treatment
The administration of doxorubicin is carefully controlled to maximize its therapeutic benefits while minimizing adverse effects. The most common method is intravenous infusion, allowing for precise control of the dosage and rate of administration. The drug is typically diluted in an appropriate solution before administration. Other delivery methods, such as liposomal formulations, have been developed to improve the drug's effectiveness and reduce side effects.
Liposomal Doxorubicin:
Liposomal doxorubicin encapsulates the drug within lipid vesicles, protecting it from premature degradation and allowing for targeted delivery to tumor cells. This formulation can improve the drug's efficacy and reduce its cardiotoxicity compared to conventional doxorubicin.
Ongoing Research and Future Directions: Pushing the Boundaries
Research into doxorubicin continues to explore ways to enhance its efficacy and reduce its side effects. These efforts include:
Combination Therapies:
Combining doxorubicin with other chemotherapeutic agents, targeted therapies, or immunotherapies often improves treatment outcomes. The synergistic effects of these combinations can enhance tumor cell kill while reducing the required dose of doxorubicin, potentially minimizing its toxicity.
Targeted Drug Delivery:
Researchers are investigating novel drug delivery systems aimed at targeting doxorubicin specifically to tumor cells, reducing exposure to healthy tissues and minimizing side effects. Nanotechnology-based approaches are being explored to achieve this targeted delivery.
Cardioprotection:
Significant research focuses on developing strategies to protect the heart from doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity. This includes exploring the use of cardioprotective agents that can mitigate the drug's damaging effects on the heart muscle.
Overcoming Drug Resistance:
Cancer cells can develop resistance to doxorubicin, limiting the effectiveness of treatment. Researchers are actively working to identify mechanisms of drug resistance and develop strategies to overcome them, ensuring the continued usefulness of this valuable anticancer drug.
Conclusion: Doxorubicin's Enduring Legacy in Oncology
Doxorubicin, an anthracycline antitumor antibiotic, remains a crucial component of cancer chemotherapy. Its potent anti-cancer activity, broad-spectrum efficacy, and established clinical use make it a cornerstone of treatment for numerous cancers. However, the significant side effects, particularly cardiotoxicity, necessitate careful monitoring and management. Ongoing research into combination therapies, targeted drug delivery, cardioprotection, and overcoming drug resistance promises to further enhance the therapeutic benefit of doxorubicin while minimizing its risks, ensuring its enduring legacy in the fight against cancer. The multifaceted nature of doxorubicin—its mechanism, applications, side effects, and ongoing research—highlights its continued importance and the ongoing efforts to optimize its use in cancer treatment. Understanding this complex drug is vital for both healthcare professionals and patients navigating the complexities of cancer care.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Select All That Are Functions Of Neurons And Glial Cells
Mar 14, 2025
-
A Medical Record Is An Example Of
Mar 14, 2025
-
Minor Violations May Be Granted Upwards Of Days For Correction
Mar 14, 2025
-
Which One Of The Following Statements Is Correct
Mar 14, 2025
-
Experiment 3 Radioactivity Effect Of Distance And Absorbers
Mar 14, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about An Anthracycline Classified As An Antitumor Antibiotic Is: . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
