A Production Possibilities Frontier Is Bowed Outward When
Holbox
Mar 15, 2025 · 6 min read
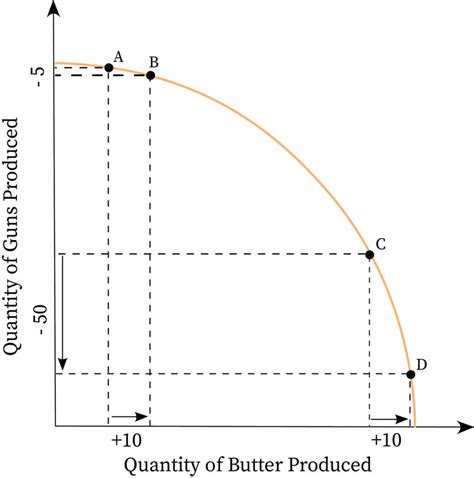
Table of Contents
A Production Possibilities Frontier is Bowed Outward When: Understanding Increasing Opportunity Costs
The production possibilities frontier (PPF), also known as the production possibility curve (PPC), is a fundamental concept in economics illustrating the maximum possible output combinations of two goods or services an economy can produce with its available resources and technology, assuming these resources are fully and efficiently utilized. While often depicted as a straight line, the PPF is more realistically bowed outward, reflecting the crucial economic principle of increasing opportunity costs. This article will delve deep into the reasons behind this outward bow, exploring the underlying factors and their implications.
What is a Production Possibilities Frontier (PPF)?
Before exploring the outward bow, let's solidify our understanding of the PPF itself. Imagine an economy producing only two goods: computers and cars. The PPF represents all the possible combinations of computers and cars that can be produced given the existing resources – labor, capital, land, and entrepreneurship. Each point on the curve represents efficient production, meaning all resources are fully utilized. Any point inside the curve indicates inefficiency, while any point outside the curve is unattainable with the current resources and technology.
A straight-line PPF implies constant opportunity costs – the amount of one good sacrificed to produce an additional unit of another good remains constant. However, this is a simplification. The real-world PPF is usually bowed outward, signifying increasing opportunity costs.
The Bowed-Outward PPF: The Significance of Increasing Opportunity Costs
The outward bow of the PPF is a direct consequence of the law of increasing opportunity costs. This law states that as the production of one good increases, the opportunity cost of producing an additional unit of that good rises. This is because resources are not perfectly adaptable to producing both goods.
Let's illustrate with our computer and car example:
Imagine initially, the economy is producing mostly cars and few computers. Shifting resources from car production to computer production initially involves transferring relatively less productive resources. These resources might be workers or machinery better suited to car production but still capable of contributing somewhat to computer manufacturing. The opportunity cost of producing more computers is relatively low at this stage, represented by a smaller reduction in car production.
However, as we continue to shift resources toward computer production, we start transferring resources that are increasingly specialized in car manufacturing and less efficient in computer production. To produce each additional computer, we have to give up increasingly more car production. This explains the increasing slope of the PPF as we move along the curve towards more computer production. The opportunity cost of producing computers has risen. The same logic applies if we start by producing primarily computers and then shift resources toward car production.
Factors Contributing to the Bowed-Outward PPF
Several factors contribute to the bowed-outward shape of the PPF, all ultimately linking back to the varying resource suitability and efficiency:
1. Resource Specialization:
Resources are not equally adept at producing all goods. Some resources are better suited for one type of production than another. For instance, certain types of labor might be highly skilled in software development (ideal for computer production) but less effective in assembling car parts. Similarly, specialized machinery designed for car manufacturing will be less productive in computer production. This specialization leads to increasing opportunity costs as we shift resources from one good to another.
2. Diminishing Returns:
As we increase the production of one good, using resources increasingly less suited to that production, we may encounter diminishing marginal returns. This means that each additional unit of input (resource) yields successively smaller increases in output. This diminishing productivity directly contributes to the increasing opportunity cost.
3. Different Resource Qualities:
Even within a category of resources, there are inherent quality differences. For example, some workers are more skilled than others, some land is more fertile, and some capital is more technologically advanced. As production of one good increases, we are forced to use lower-quality resources, leading to higher opportunity costs.
4. Technological Differences:
Technological advancements often affect the production of different goods differently. A technological breakthrough in computer manufacturing might significantly increase the output of computers, but have minimal impact on car production. This uneven impact further contributes to the increasing opportunity costs reflected in the bowed-outward PPF.
Implications of the Bowed-Outward PPF
Understanding the bowed-outward shape of the PPF has significant implications for economic decision-making:
-
Efficient Resource Allocation: The PPF highlights the importance of efficient resource allocation. Operating within the curve signifies inefficient use of resources, while points outside the curve are currently unattainable. Policy decisions should aim for efficient production at a point on the PPF.
-
Opportunity Cost Awareness: The increasing opportunity costs implied by the outward bow emphasize the need to carefully consider the trade-offs involved in economic choices. Choosing to produce more of one good necessarily means producing less of another. The magnitude of this trade-off varies depending on the specific production levels.
-
Economic Growth and Technological Advancement: Shifts in the PPF represent economic growth. Improvements in technology, increased resource availability, or enhanced worker skills can expand the PPF, allowing for the production of more of both goods. The outward shift reflects the economy's increased potential.
-
Comparative Advantage and Trade: The PPF also plays a crucial role in understanding the concept of comparative advantage in international trade. Countries specialize in producing goods where they have a lower opportunity cost, allowing for mutually beneficial trade.
Beyond the Simple Two-Good Model
While the two-good model simplifies the analysis, the principles of increasing opportunity costs and the bowed-outward PPF extend to economies producing many goods. The complexity increases, but the fundamental concepts remain valid. The PPF becomes a multi-dimensional surface, but the increasing opportunity costs are still inherent as resources are allocated across multiple production possibilities.
Conclusion: A Realistic Representation of Economic Choices
The bowed-outward production possibilities frontier is not simply a theoretical construct. It provides a far more realistic representation of how economies function compared to a straight-line model. It vividly illustrates the fundamental economic principle of increasing opportunity costs arising from resource specialization, diminishing returns, varying resource qualities, and uneven technological advancements. Understanding this bowed-outward shape is crucial for informed economic decision-making at individual, firm, and national levels, enabling efficient resource allocation, informed trade policies, and a realistic assessment of economic growth prospects. The implications extend to understanding trade-offs, specialization, and the dynamic nature of economic possibilities. By understanding the complexities of the bowed-outward PPF, we gain a more nuanced perspective on the economic choices available to us.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Question Tech 9 Select The Alkene In The Yellow Box
Mar 15, 2025
-
Question Elm Following Iupac Nomeclature Rules
Mar 15, 2025
-
Generosity Is One Of The Six Pillars Of Character
Mar 15, 2025
-
Orlando Company Began Operation In December
Mar 15, 2025
-
Match Each Description To The Corresponding Management Skill
Mar 15, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about A Production Possibilities Frontier Is Bowed Outward When . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
