A Marketing Dashboard Uses Graphical Data
Holbox
Mar 15, 2025 · 7 min read
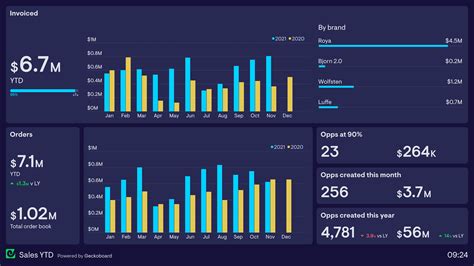
Table of Contents
Marketing Dashboard: Using Graphical Data to Drive Decisions
Marketing is a dynamic field, constantly evolving with new trends and technologies. To stay ahead, marketers need access to real-time data and insightful analytics. This is where a marketing dashboard comes into play. A well-designed dashboard presents crucial marketing data in a visually appealing and easily digestible format, empowering marketers to make informed decisions, optimize campaigns, and ultimately drive business growth. This article dives deep into the world of marketing dashboards, focusing on how graphical data representation unlocks its true potential.
What is a Marketing Dashboard?
A marketing dashboard is a centralized hub that displays key performance indicators (KPIs) and other essential data related to your marketing efforts. Unlike raw data spreadsheets, a dashboard visually summarizes complex information through charts, graphs, and other visual elements. This allows marketers to quickly grasp the performance of various campaigns, identify areas for improvement, and track progress towards marketing objectives. Think of it as your command center for marketing intelligence.
The Power of Graphical Data Representation
The true strength of a marketing dashboard lies in its ability to translate complex data into easily understandable visuals. Raw data in spreadsheets is often overwhelming and difficult to interpret quickly. Graphical representations, however, dramatically improve data comprehension and facilitate faster decision-making. Here's why graphical data is so crucial:
1. Enhanced Data Comprehension:
Charts and graphs offer a concise and intuitive way to understand trends and patterns within your marketing data. Instead of sifting through thousands of rows of numbers, you can instantly see:
- Sales trends over time: Line graphs are perfect for showcasing sales performance month-over-month or year-over-year.
- Campaign performance comparisons: Bar charts effectively compare the performance of different marketing campaigns, highlighting top performers and underachievers.
- Customer demographics: Pie charts provide a clear picture of your audience's age, gender, location, and other demographics.
- Website traffic sources: Donut charts elegantly display the proportion of traffic from different sources like organic search, social media, and paid advertising.
- Conversion rates at different stages of the funnel: Funnels visually represent the customer journey and identify bottlenecks in the conversion process.
2. Faster Decision-Making:
Visualizing data accelerates the decision-making process. Instead of spending hours analyzing spreadsheets, marketers can quickly identify key insights and take appropriate actions. For instance, a sudden drop in website traffic from a specific source can be immediately noticed on a dashboard, enabling prompt investigation and corrective measures.
3. Improved Collaboration and Communication:
Marketing dashboards facilitate better communication and collaboration within marketing teams and across departments. Presenting data visually allows for easier sharing of insights and fostering a common understanding of marketing performance. This shared understanding is crucial for effective team collaboration and alignment on strategic goals.
4. Identifying Key Trends and Patterns:
Graphical representations help to uncover hidden trends and patterns that might be missed in raw data. Visualizations reveal correlations between different data points, leading to a deeper understanding of customer behavior and market dynamics. This deeper understanding is essential for developing more effective marketing strategies.
Key Metrics to Include in Your Marketing Dashboard
The specific metrics you include in your dashboard will depend on your overall marketing objectives and the nature of your business. However, some common and crucial KPIs to consider are:
Website Analytics:
- Website Traffic: Total website visits, unique visitors, and page views. Use line graphs to track traffic over time.
- Bounce Rate: The percentage of visitors who leave your website after viewing only one page. A high bounce rate indicates potential issues with website content or user experience. Use bar charts to compare bounce rates across different pages or campaigns.
- Average Session Duration: The average time visitors spend on your website. Longer session durations generally indicate higher engagement. Use a line graph to track this metric over time.
- Conversion Rate: The percentage of website visitors who complete a desired action, such as making a purchase, filling out a form, or signing up for a newsletter. This is arguably one of the most important metrics. Use bar charts to compare conversion rates across different campaigns or landing pages.
- Top Landing Pages: Identify the pages that attract the most traffic and generate the highest conversion rates. Use a bar chart to rank your landing pages by performance.
Social Media Analytics:
- Follower Growth: Track the number of followers you gain over time across different social media platforms. Use line graphs to show growth trends.
- Engagement Rate: Measure the level of interaction with your social media posts (likes, comments, shares). Use bar charts to compare engagement across different posts or campaigns.
- Reach: The number of unique users who have seen your social media posts. Use bar charts to compare reach across different posts or campaigns.
- Click-Through Rate (CTR): The percentage of users who click on your social media links. Use bar charts to compare CTRs across different posts or campaigns.
Email Marketing Analytics:
- Open Rate: The percentage of recipients who opened your emails. Use bar charts to compare open rates across different campaigns or subject lines.
- Click-Through Rate (CTR): The percentage of recipients who clicked on links within your emails. Use bar charts to compare CTRs across different campaigns or call-to-actions.
- Conversion Rate: The percentage of recipients who completed a desired action after clicking a link in your email. Use bar charts to compare conversion rates across different campaigns or offers.
- Unsubscribe Rate: The percentage of recipients who unsubscribed from your email list. A high unsubscribe rate may indicate issues with email content or frequency. Use line graphs to track this metric over time.
Paid Advertising Analytics:
- Cost Per Click (CPC): The average cost of each click on your paid ads. Use line graphs to track CPC over time.
- Click-Through Rate (CTR): The percentage of users who clicked on your paid ads. Use bar charts to compare CTRs across different ad campaigns or ad creatives.
- Conversion Rate: The percentage of users who completed a desired action after clicking on your paid ads. Use bar charts to compare conversion rates across different campaigns or ad creatives.
- Return on Ad Spend (ROAS): The return you get for every dollar spent on advertising. This is a crucial metric for assessing the effectiveness of your paid campaigns. Use bar charts to compare ROAS across different campaigns.
Choosing the Right Charts and Graphs
The type of chart or graph you use significantly impacts data interpretation. Selecting the appropriate visualization is crucial for effectively communicating your marketing performance.
-
Line Charts: Ideal for showing trends over time. Excellent for tracking website traffic, sales, and social media follower growth.
-
Bar Charts: Effective for comparing different categories or groups. Useful for comparing campaign performance, website bounce rates, and social media engagement.
-
Pie Charts: Show the proportion of different parts of a whole. Useful for displaying customer demographics, website traffic sources, and sales distribution across product categories.
-
Donut Charts: Similar to pie charts but with a hole in the center, allowing for additional text or labels. Often used for displaying website traffic sources or sales distribution.
-
Funnel Charts: Visually represent the customer journey, identifying drop-off points and areas for improvement. Crucial for optimizing conversion rates.
-
Scatter Plots: Illustrate the relationship between two variables. Useful for identifying correlations between marketing efforts and campaign performance.
-
Heatmaps: Show data density using color gradients. Can be used to visualize website click maps, identifying areas of high and low engagement.
Building Your Marketing Dashboard: Tools and Platforms
Numerous tools and platforms are available for building marketing dashboards. The best choice depends on your specific needs, budget, and technical expertise. Some popular options include:
-
Google Data Studio: A free and powerful tool that allows you to connect to various data sources and create custom dashboards.
-
Tableau: A robust data visualization platform, known for its advanced features and interactive capabilities.
-
Power BI: Another powerful platform from Microsoft, offering a wide range of data visualization and analysis capabilities.
-
Marketing Automation Platforms: Many marketing automation platforms (like HubSpot, Marketo, Pardot) include built-in dashboards for tracking marketing performance.
Remember to choose a platform that seamlessly integrates with your existing marketing tools and data sources to streamline data collection and analysis.
Conclusion: Data-Driven Marketing for Success
A well-designed marketing dashboard, leveraging the power of graphical data, is an indispensable tool for modern marketers. By transforming complex data into easily understandable visuals, dashboards empower marketers to make informed decisions, optimize campaigns, and drive business growth. Investing time and resources in creating a comprehensive marketing dashboard is an investment in the success of your marketing efforts. Remember to regularly review and refine your dashboard to ensure it remains aligned with your evolving business objectives and marketing strategies. By embracing data-driven decision-making, you can elevate your marketing performance and achieve significant improvements in your overall business outcomes.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Select The Nmr Spectrum That Corresponds Best To P Anisidine
Mar 15, 2025
-
An Increase In The Quantity Supplied Suggests A
Mar 15, 2025
-
Libreoffice Is An Example Of Which Type Of Software
Mar 15, 2025
-
The Cash Conversion Cycle Is Computed As
Mar 15, 2025
-
What Are Three Ways You Could Use Hootsuite Streams
Mar 15, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about A Marketing Dashboard Uses Graphical Data . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
