A Frequency Table Of Grades Has Five Classes
Holbox
Mar 26, 2025 · 6 min read
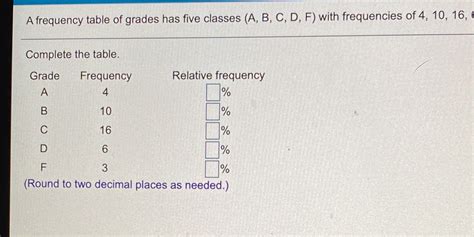
Table of Contents
- A Frequency Table Of Grades Has Five Classes
- Table of Contents
- Understanding and Interpreting Frequency Tables with Five Grade Classes
- What is a Frequency Table?
- Frequency Tables with Five Grade Classes: A Detailed Look
- Choosing Appropriate Class Intervals
- Applications of Frequency Tables with Five Grade Classes
- Beyond Basic Frequency Tables: Advanced Techniques
- Limitations of Frequency Tables
- Best Practices for Creating Effective Frequency Tables
- Conclusion
- Latest Posts
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
Understanding and Interpreting Frequency Tables with Five Grade Classes
A frequency table is a fundamental tool in descriptive statistics, offering a concise summary of data distribution. This article delves into the intricacies of frequency tables, particularly focusing on those with five grade classes. We'll explore how to construct such tables, interpret the results, and understand their significance in data analysis, highlighting practical applications and offering valuable insights for both beginners and experienced data analysts.
What is a Frequency Table?
Before diving into the specifics of five-grade classes, let's establish a clear understanding of frequency tables in general. A frequency table is a way to organize and summarize data by showing the number of times each value or range of values (class intervals) appears in a dataset. It simplifies large datasets, making it easier to identify patterns, trends, and outliers. The table typically includes:
- Classes/Intervals: These are ranges of values that group the data. For example, if analyzing exam scores, classes could be 0-59, 60-69, 70-79, 80-89, and 90-100.
- Frequency: This indicates the number of data points falling within each class.
- Relative Frequency: This represents the proportion or percentage of data points in each class, calculated by dividing the class frequency by the total number of data points.
- Cumulative Frequency: This shows the running total of frequencies up to and including the current class.
Frequency Tables with Five Grade Classes: A Detailed Look
When a frequency table utilizes five grade classes, it suggests a categorization of data into five distinct groups, often representing levels of performance, quality, or other measurable attributes. The classes are usually mutually exclusive and exhaustive, meaning each data point falls into only one class, and all data points are accounted for.
Let's consider an example: imagine a teacher has collected the test scores of 50 students. To create a frequency table with five grade classes, they might choose the following intervals:
| Grade Class | Score Range | Frequency | Relative Frequency | Cumulative Frequency |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 90-100 | 8 | 16% | 8 |
| B | 80-89 | 15 | 30% | 23 |
| C | 70-79 | 18 | 36% | 41 |
| D | 60-69 | 7 | 14% | 48 |
| F | 0-59 | 2 | 4% | 50 |
Interpreting the Table:
This table shows that:
- 8 students scored between 90 and 100 (Grade A).
- 15 students scored between 80 and 89 (Grade B).
- The most frequent grade was C, with 18 students scoring between 70 and 79.
- Only 2 students failed the test (Grade F).
- The cumulative frequency helps visualize the proportion of students achieving a certain grade or better. For example, 41 students achieved a C or better.
Choosing Appropriate Class Intervals
The selection of class intervals is crucial for effective data representation. Poorly chosen intervals can obscure patterns or misrepresent the data. Here's a guide to selecting appropriate class intervals:
- Number of Classes: Five is a common choice, offering a balance between detail and conciseness. However, the optimal number depends on the dataset size and distribution. Too few classes might mask important details; too many might make the table unwieldy.
- Class Width: The width of each class interval should be consistent. Calculate the width by dividing the range of the data (highest value minus lowest value) by the desired number of classes. Round up to a convenient value for easy interpretation.
- Equal Intervals: While not strictly necessary, equal intervals make comparison across classes simpler and more straightforward.
- Consider Data Distribution: If the data is heavily skewed, you might need to adjust the interval widths to better capture the distribution.
Applications of Frequency Tables with Five Grade Classes
Frequency tables with five grade classes find applications in various fields:
- Education: Analyzing student performance on tests or assignments, tracking grade distributions across different courses, and identifying areas needing improvement.
- Quality Control: Assessing the quality of products or services, categorizing defects, and monitoring production processes.
- Market Research: Analyzing customer satisfaction surveys, segmenting customers based on preferences, and understanding product acceptance.
- Healthcare: Analyzing patient outcomes, categorizing disease severity, and tracking treatment effectiveness.
- Human Resources: Evaluating employee performance, categorizing skill levels, and assessing training needs.
Beyond Basic Frequency Tables: Advanced Techniques
While basic frequency tables are valuable, several advanced techniques can enhance their analytical power:
- Relative Frequency Histograms: These visual representations convert the relative frequencies into a bar chart, offering a more intuitive understanding of data distribution. A histogram clearly shows the shape of the distribution, highlighting skewness or other features.
- Cumulative Frequency Polygons (Ogive): These line graphs depict the cumulative frequency, providing a clear visual representation of the cumulative distribution.
- Statistical Measures: Frequency tables are often the foundation for calculating descriptive statistics such as mean, median, mode, and standard deviation. These provide a deeper understanding of the data's central tendency and dispersion.
Limitations of Frequency Tables
While frequency tables are powerful tools, it's important to acknowledge their limitations:
- Loss of Detail: Grouping data into classes inevitably leads to a loss of individual data points' precise values.
- Sensitivity to Class Interval Selection: The choice of class intervals can significantly influence the table's appearance and interpretation. Different choices can reveal different patterns.
- Limited Applicability for Continuous Data: While adaptable, frequency tables are most effective with discrete data or continuous data that can be reasonably grouped into intervals. For extremely large datasets with continuous variables, other techniques like kernel density estimation might be more appropriate.
Best Practices for Creating Effective Frequency Tables
To create effective and informative frequency tables, follow these guidelines:
- Clear and Concise Labeling: Use descriptive labels for classes, frequency, and other columns.
- Appropriate Units: Specify the units of measurement for the data being analyzed.
- Consistent Formatting: Maintain a consistent format throughout the table, ensuring readability.
- Contextualization: Provide context to the data, including the source, sample size, and any relevant background information.
- Visual Aids: Use charts and graphs to supplement the table and improve understanding.
Conclusion
Frequency tables, particularly those with five grade classes, provide a powerful and versatile tool for summarizing and interpreting data. By understanding the principles of constructing and interpreting these tables, and by utilizing advanced techniques and visual aids, data analysts can extract valuable insights from datasets of various sizes and complexities. Remember to choose appropriate class intervals, consider the data's distribution, and always contextualize the findings to ensure accurate and meaningful interpretations. Mastering frequency tables is a fundamental step in becoming a proficient data analyst.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Vail Company Recorded The Following Transactions During November
Mar 29, 2025
-
What Coversheet Is Attached To Help Protect A Secret Document
Mar 29, 2025
-
Elimination Reactions Are Favored Over Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions
Mar 29, 2025
-
One Important Role Of Purchasing Is To
Mar 29, 2025
-
How Should You Arrange Conversion Factors In Dimensional Analysis
Mar 29, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about A Frequency Table Of Grades Has Five Classes . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
