A Company's Ledger Or General Ledger Is
Holbox
Mar 31, 2025 · 7 min read
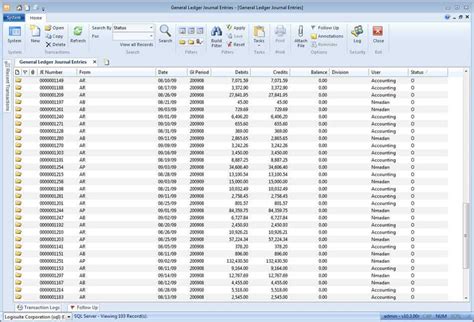
Table of Contents
- A Company's Ledger Or General Ledger Is
- Table of Contents
- A Company's Ledger or General Ledger is the Heart of its Financial Records
- What is a General Ledger?
- Key Components of a General Ledger
- Assets:
- Liabilities:
- Equity:
- Revenue:
- Expenses:
- The Structure of the General Ledger: Debits and Credits
- Maintaining the General Ledger
- The Importance of a Well-Maintained General Ledger
- Troubleshooting Common General Ledger Issues
- Conclusion: The General Ledger – A Critical Business Asset
- Latest Posts
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
A Company's Ledger or General Ledger is the Heart of its Financial Records
A company's ledger, often referred to as a general ledger, is the cornerstone of its financial record-keeping system. It's a comprehensive record of all financial transactions undertaken by the business. Think of it as the central nervous system of a company's finances, providing a complete and detailed picture of its financial health. Understanding the general ledger is crucial for accurate financial reporting, effective decision-making, and overall business success. This in-depth guide will explore the general ledger in detail, examining its purpose, structure, components, and importance.
What is a General Ledger?
The general ledger is a chronological record of all financial transactions impacting a company. Every debit and credit entry is meticulously documented, providing a complete trail of all financial activity. This allows for a clear and accurate representation of the company's financial position at any given time. It's the culmination of all the subsidiary ledgers, combining data from accounts payable, accounts receivable, inventory, and other operational aspects.
The general ledger is essential for several reasons:
- Financial Reporting: It forms the basis for creating financial statements like the balance sheet, income statement, and cash flow statement, which are critical for internal management and external stakeholders (investors, lenders, etc.).
- Auditing: Auditors rely heavily on the general ledger to verify the accuracy and completeness of a company's financial records.
- Compliance: Accurate maintenance of the general ledger ensures compliance with accounting standards and tax regulations.
- Decision-Making: The data contained within provides crucial insights for strategic business decisions, such as budgeting, forecasting, and investment strategies.
- Tracking Financial Performance: It facilitates ongoing monitoring of revenue, expenses, profitability, and overall financial performance.
Key Components of a General Ledger
The general ledger is built upon a system of accounts, each representing a specific aspect of the company's finances. These accounts are organized using a chart of accounts, a structured list that provides a unique code to each account. Common accounts found in a general ledger include:
Assets:
- Cash: Records all cash transactions, including bank deposits, withdrawals, and payments.
- Accounts Receivable: Tracks money owed to the company by customers.
- Inventory: Records the value of goods held for sale.
- Prepaid Expenses: Accounts for expenses paid in advance, such as insurance or rent.
- Property, Plant, and Equipment (PP&E): Represents the value of long-term assets like buildings, machinery, and equipment.
Liabilities:
- Accounts Payable: Tracks money owed to suppliers and vendors.
- Salaries Payable: Records unpaid salaries and wages.
- Loans Payable: Shows the outstanding balance on loans.
- Taxes Payable: Represents unpaid taxes.
Equity:
- Common Stock: Records the value of shares issued to investors.
- Retained Earnings: Shows accumulated profits that haven't been distributed as dividends.
Revenue:
- Sales Revenue: Represents income from the sale of goods or services.
- Service Revenue: Income generated from providing services.
- Interest Revenue: Income earned from interest-bearing accounts.
Expenses:
- Cost of Goods Sold (COGS): Direct costs associated with producing goods sold.
- Salaries Expense: Costs associated with employee salaries and wages.
- Rent Expense: Costs of renting premises.
- Utilities Expense: Costs of electricity, water, and other utilities.
- Marketing Expense: Costs associated with marketing and advertising.
The Structure of the General Ledger: Debits and Credits
The general ledger operates on a double-entry bookkeeping system. This system ensures that every transaction is recorded with both a debit and a credit entry, maintaining the fundamental accounting equation: Assets = Liabilities + Equity.
- Debit: A debit increases the balance of asset, expense, and dividend accounts, while it decreases the balance of liability, equity, and revenue accounts.
- Credit: A credit increases the balance of liability, equity, and revenue accounts, while it decreases the balance of asset, expense, and dividend accounts.
This system ensures that the accounting equation always remains balanced. For every debit entry, there must be a corresponding credit entry of equal value, and vice versa. This double-entry system provides an essential check and balance mechanism, minimizing errors and enhancing the accuracy of financial records.
Maintaining the General Ledger
Manually maintaining a general ledger is a laborious and error-prone process. Modern businesses leverage accounting software to streamline this process. These software solutions automate many tasks, including:
- Automated Journal Entries: Software can automatically post journal entries from source documents like invoices and receipts.
- Real-time Updates: The general ledger is updated in real-time, providing immediate access to the latest financial information.
- Error Detection: Software can identify inconsistencies and potential errors in the ledger.
- Reporting Capabilities: Software generates comprehensive financial reports, simplifying the reporting process.
- Data Security: Software enhances data security, protecting sensitive financial information.
Popular accounting software options include QuickBooks, Xero, and Sage, each offering a range of features tailored to different business needs.
The Importance of a Well-Maintained General Ledger
A well-maintained general ledger is crucial for the success of any business. Its importance extends to several critical areas:
-
Accurate Financial Reporting: A precise general ledger is fundamental to generating accurate and reliable financial statements. These statements are essential for making informed business decisions and communicating the company's financial performance to stakeholders. Inaccurate financial reports can lead to poor decision-making, jeopardizing the company's financial stability.
-
Effective Financial Management: A detailed general ledger provides valuable insights into the company's cash flow, profitability, and financial health. This information empowers management to make strategic decisions related to budgeting, resource allocation, and investment. Real-time monitoring of financial data facilitates proactive identification and mitigation of potential financial risks.
-
Compliance with Regulations: Maintaining an accurate and complete general ledger is essential for complying with various financial regulations, tax laws, and accounting standards. Failure to comply can lead to hefty penalties and legal repercussions. A properly maintained ledger serves as crucial evidence during audits and tax investigations.
-
Improved Decision-Making: The detailed financial information contained within the general ledger offers valuable data-driven insights. This information enables managers to make informed decisions about pricing strategies, cost control measures, expansion plans, and other critical areas impacting the company's profitability and sustainability.
-
Enhanced Investor Confidence: Investors and creditors rely on the accuracy of a company’s financial reports, which are directly derived from the general ledger. A well-maintained ledger, reflecting transparent and accurate financial data, builds trust and confidence among stakeholders, facilitating easier access to funding and investment.
Troubleshooting Common General Ledger Issues
Despite the benefits of accounting software, challenges can still arise. Some common issues include:
-
Data Entry Errors: Human error remains a significant risk. Implementing robust internal controls, such as double-checking entries and using automated data entry features, helps minimize these errors.
-
Reconciliation Discrepancies: Discrepancies between bank statements and the general ledger require thorough investigation and reconciliation. Addressing these inconsistencies promptly is vital for maintaining accurate financial records.
-
Lack of Regular Monitoring: Failure to regularly monitor and review the general ledger can lead to undetected errors and inconsistencies. Regular reviews help to identify potential problems before they escalate.
-
Inconsistent Chart of Accounts: Using a poorly designed or inconsistent chart of accounts can make it difficult to track financial data effectively. A well-structured chart of accounts is crucial for efficient financial reporting.
-
Insufficient Training: Lack of adequate training for accounting personnel can result in errors and inefficient processes. Regular training and ongoing professional development programs are necessary to ensure that accounting staff possesses the necessary skills and knowledge.
Conclusion: The General Ledger – A Critical Business Asset
The general ledger is far more than just a collection of financial records; it’s a vital asset for any business. Its accurate and consistent maintenance is essential for accurate financial reporting, effective financial management, regulatory compliance, and informed decision-making. By understanding the structure, components, and importance of the general ledger, businesses can leverage this powerful tool to improve their financial health and overall success. With the advent of sophisticated accounting software, maintaining a meticulously organized and accurate general ledger is achievable, enabling businesses to focus on their core competencies while ensuring their financial records remain robust and reliable. Investing time and resources in mastering the general ledger is an investment in the future financial stability and growth of any organization.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
As The Aggregate Price Level In An Economy Decreases
Apr 03, 2025
-
Art Labeling Activity Location And Structure Of Lymph Nodes
Apr 03, 2025
-
Incremental Is Incremental Revenues Minus Incremental Costs
Apr 03, 2025
-
What Are The Functions Of The Structure Seen Here
Apr 03, 2025
-
The Temporary Party Organization Only Gets Activated
Apr 03, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about A Company's Ledger Or General Ledger Is . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
