Which Two Items Are Closely Related To The Reserve Requirement
Holbox
Mar 30, 2025 · 5 min read
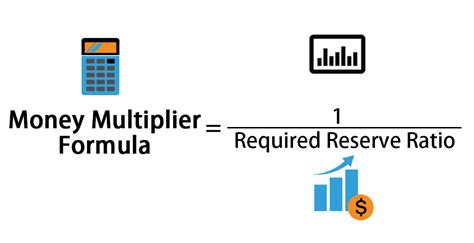
Table of Contents
- Which Two Items Are Closely Related To The Reserve Requirement
- Table of Contents
- Which Two Items Are Closely Related to the Reserve Requirement?
- The Reserve Requirement and the Money Supply: A Delicate Balance
- The Multiplier Effect: Amplifying the Impact
- Impact on Economic Growth and Inflation
- The Reserve Requirement and the Federal Funds Rate: An Intertwined Relationship
- Supply and Demand Dynamics
- Open Market Operations: A Complementary Tool
- The Interplay of Multiple Tools
- Understanding the Nuances: Beyond the Basics
- Conclusion: A Dynamic Interplay
- Latest Posts
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
Which Two Items Are Closely Related to the Reserve Requirement?
The reserve requirement, a cornerstone of monetary policy, dictates the minimum amount of funds banks must hold in reserve against their deposits. While seemingly simple, its implications ripple through the entire financial system, deeply influencing two key elements: the money supply and the federal funds rate. Understanding this intricate relationship is crucial for grasping the mechanics of monetary policy and its impact on the broader economy.
The Reserve Requirement and the Money Supply: A Delicate Balance
The reserve requirement acts as a powerful lever to control the money supply. A lower reserve requirement allows banks to lend out a larger portion of their deposits, thereby increasing the money supply through the process of fractional reserve banking. Conversely, a higher reserve requirement forces banks to hold more reserves, reducing the amount available for lending and consequently shrinking the money supply.
The Multiplier Effect: Amplifying the Impact
The impact of changes in the reserve requirement is not limited to the initial injection or withdrawal of funds. It's amplified through the money multiplier effect. This effect describes how an initial change in reserves leads to a larger change in the overall money supply. For example, if a bank receives an additional $100 in deposits and the reserve requirement is 10%, it can lend out $90. This $90 then becomes a deposit in another bank, which can then lend out 90% of it, and so on. This cascading effect significantly increases the overall money supply.
The formula for calculating the money multiplier is:
Money Multiplier = 1 / Reserve Requirement
Therefore, a 10% reserve requirement results in a money multiplier of 10 (1 / 0.1 = 10), meaning that a $100 increase in reserves could potentially lead to a $1000 increase in the money supply. This highlights the potent influence the reserve requirement holds over the overall money supply.
Impact on Economic Growth and Inflation
Manipulating the reserve requirement is a key tool for central banks to influence economic growth and inflation. Lowering the reserve requirement can stimulate economic growth by increasing the money supply, making credit more readily available and encouraging borrowing and investment. However, it can also lead to inflation if the increased money supply outpaces the growth in goods and services.
Conversely, raising the reserve requirement can curb inflation by reducing the money supply and slowing down economic activity. However, this can also lead to slower economic growth or even a recession if implemented too aggressively. This delicate balancing act is a constant challenge for central banks.
The Reserve Requirement and the Federal Funds Rate: An Intertwined Relationship
The reserve requirement also has a significant indirect impact on the federal funds rate, the target rate at which banks lend reserves to each other overnight. Although not a direct causal link, the reserve requirement influences the supply of reserves in the banking system, which in turn affects the federal funds rate.
Supply and Demand Dynamics
A lower reserve requirement increases the overall supply of reserves in the banking system, putting downward pressure on the federal funds rate. With more reserves available, banks are less likely to compete fiercely for funds, leading to a lower rate. Conversely, a higher reserve requirement reduces the supply of reserves, increasing demand and potentially driving up the federal funds rate. Banks will compete more aggressively for the limited reserves, pushing the rate upwards.
Open Market Operations: A Complementary Tool
It's important to note that the Federal Reserve (or other central banks) primarily uses open market operations to directly target the federal funds rate. These operations involve the buying and selling of government securities to influence the supply of reserves. However, the reserve requirement provides a supplementary mechanism that can either reinforce or counteract the effects of open market operations. For example, if the Fed wants to lower the federal funds rate, it could combine open market purchases with a reduction in the reserve requirement to amplify the downward pressure on rates.
The Interplay of Multiple Tools
It's crucial to understand that the reserve requirement isn't the sole determinant of the federal funds rate. Other factors, such as inflation expectations, economic growth, and global financial conditions, all play a role. The relationship between the reserve requirement and the federal funds rate is indirect and complex, involving the interplay of various market forces and central bank policy decisions.
Understanding the Nuances: Beyond the Basics
While the relationship between the reserve requirement and the money supply and federal funds rate seems straightforward in theory, the practical application is far more nuanced. Several factors complicate this relationship:
-
Excess Reserves: Banks often hold reserves above the legally mandated minimum. These excess reserves act as a buffer against unexpected withdrawals and can influence the effectiveness of changes in the reserve requirement. A high level of excess reserves can lessen the impact of a reduction in the reserve requirement on the money supply.
-
Bank Lending Behavior: The willingness of banks to lend is influenced by various factors beyond the reserve requirement, such as credit risk assessments, economic outlook, and regulatory capital requirements. Even with abundant reserves, banks might be hesitant to lend if they perceive high risks in the market.
-
Global Capital Flows: International capital flows can impact the money supply and the federal funds rate independently of the reserve requirement. Large inflows or outflows of capital can significantly alter the balance of reserves in the banking system.
-
Technological Advancements: The rise of digital banking and fintech innovations has changed the way banks manage their reserves. These technological shifts can influence the relationship between the reserve requirement and its broader impact on the economy.
Conclusion: A Dynamic Interplay
The reserve requirement, while seemingly a simple regulatory tool, plays a pivotal role in shaping the financial landscape. Its close relationship with both the money supply and the federal funds rate underscores its significance in monetary policy. Understanding this intricate interplay is crucial for comprehending how central banks manage economic activity and maintain financial stability. However, it's equally important to remember the complexities and nuances that shape the actual impact of reserve requirement changes, factors that often extend beyond the basic theoretical models. The dynamic interplay between the reserve requirement, the money supply, and the federal funds rate continues to be a subject of ongoing research and debate among economists and policymakers. As the global financial system evolves, so too will the understanding and application of this essential monetary policy tool. Continuous monitoring and analysis of these relationships remain essential for effective economic management.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Hoarding Trichotillomania And Excoriation Are Examples Of
Apr 02, 2025
-
The Orbital Diagram For A Ground State Nitrogen Atom Is
Apr 02, 2025
-
R Larry Todd Discovering Music Third Edition
Apr 02, 2025
-
Which Medical Term Means Pertaining To Horny Creation
Apr 02, 2025
-
Dividend In Arrears On Cumulative Preferred Stock
Apr 02, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Two Items Are Closely Related To The Reserve Requirement . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
