Which Tools To Make Chart 1 Look Like Chart 2
Holbox
Mar 29, 2025 · 6 min read
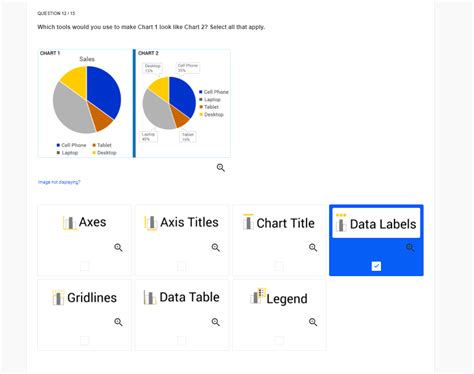
Table of Contents
- Which Tools To Make Chart 1 Look Like Chart 2
- Table of Contents
- Transforming Chart 1 into Chart 2: A Comprehensive Guide to Data Visualization Tools and Techniques
- Understanding the Transformation Goals
- Common Chart Transformation Scenarios & Solutions
- Scenario 1: Improving Clarity and Readability
- Scenario 2: Changing Chart Types for Better Data Representation
- Scenario 3: Enhancing Visual Appeal & Professionalism
- Scenario 4: Adding Interactive Elements
- Scenario 5: Handling Large Datasets
- Choosing the Right Tool: A Comparative Overview
- Beyond the Tools: Best Practices for Chart Design
- Latest Posts
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
Transforming Chart 1 into Chart 2: A Comprehensive Guide to Data Visualization Tools and Techniques
Data visualization is crucial for effectively communicating insights. Often, however, the initial chart generated from your data (Chart 1) might not perfectly represent the story you want to tell. This comprehensive guide dives deep into the tools and techniques you can leverage to transform a less-than-ideal chart (Chart 1) into a compelling and insightful visualization (Chart 2). We'll explore various scenarios and the specific tools best suited for each transformation.
Understanding the Transformation Goals
Before jumping into specific tools, it’s crucial to define what needs changing. Ask yourself:
- What type of chart is Chart 1? (e.g., bar chart, line chart, pie chart, scatter plot)
- What type of chart is Chart 2 (your desired outcome)?
- What aspects of Chart 1 need improvement? (e.g., clarity, aesthetics, data representation, readability)
- What specific message do you want Chart 2 to convey?
Identifying these aspects will guide your choice of tools and techniques.
Common Chart Transformation Scenarios & Solutions
Let's explore some typical scenarios and the tools that can help you achieve your desired visualization:
Scenario 1: Improving Clarity and Readability
Problem: Chart 1 is cluttered, has overlapping labels, or uses inappropriate colors, making it difficult to understand.
Solution: Tools like Tableau, Power BI, Excel, and Google Sheets offer robust features to enhance chart clarity.
- Tableau & Power BI: These offer advanced formatting options, allowing you to adjust font sizes, colors, labels, and legends precisely. They also provide interactive dashboards, making data exploration easier. Their drag-and-drop interfaces make adjustments intuitive, even for beginners.
- Excel & Google Sheets: While less sophisticated than Tableau or Power BI, they still offer decent chart customization options. You can adjust colors, fonts, add data labels, and format axes to improve readability. Consider using conditional formatting to highlight key data points.
Specific Techniques:
- Optimize axis labels and titles: Ensure labels are clear, concise, and appropriately scaled.
- Adjust font sizes and colors: Use legible fonts and a color palette that enhances readability. Avoid clashing colors.
- Reduce clutter: Remove unnecessary elements. If there's too much data, consider using filtering or aggregation techniques.
- Add data labels: This can make it easier to identify specific data points.
- Use clear legends: Ensure the legend is easy to understand and corresponds accurately to the chart elements.
Scenario 2: Changing Chart Types for Better Data Representation
Problem: Chart 1 uses an inappropriate chart type for the data. For example, a pie chart might be used for comparing many categories, hindering understanding.
Solution: This involves recreating the chart in a more suitable format. All the tools mentioned above (Tableau, Power BI, Excel, Google Sheets) allow for switching between different chart types.
Example: If Chart 1 is a pie chart showing the market share of multiple competitors, a bar chart or column chart would be a more effective way to compare the data. A line chart might be better for showcasing trends over time.
Scenario 3: Enhancing Visual Appeal & Professionalism
Problem: Chart 1 looks amateurish or lacks visual appeal.
Solution: Tools like Canva, Adobe Illustrator, and Inkscape can help create visually stunning charts. While they don't handle data manipulation directly, they are excellent for importing charts from other tools and refining their aesthetics.
Specific Techniques:
- Using professional themes and templates: Canva and similar tools offer ready-made templates that improve the chart's overall appearance.
- Adding background images or shapes: Use subtle backgrounds to enhance the visual interest without distracting from the data.
- Customizing colors and fonts: Choose a consistent color palette and fonts to create a cohesive look.
- Adding visual elements (carefully): Icons and other visual elements can be added judiciously to emphasize specific data points. Overdoing this, however, can create clutter.
Scenario 4: Adding Interactive Elements
Problem: Chart 1 is static and doesn't allow for user interaction.
Solution: Interactive dashboards created with Tableau, Power BI, or specialized JavaScript libraries like D3.js are ideal for achieving this.
Specific Techniques:
- Adding tooltips: Show detailed information upon hovering over data points.
- Implementing filtering and drill-down capabilities: Allow users to explore subsets of the data.
- Creating interactive maps: Visualize geographical data dynamically.
- Embedding charts in websites or applications: Make your data accessible to a wider audience.
Scenario 5: Handling Large Datasets
Problem: Chart 1 is overwhelming due to a massive dataset.
Solution: Tools like Tableau, Power BI, and even specialized Python libraries (e.g., matplotlib, seaborn) excel at handling large datasets. Effective aggregation and filtering techniques are essential.
Specific Techniques:
- Data aggregation: Summarize data at a higher level (e.g., showing monthly averages instead of daily data).
- Data filtering: Focus on specific subsets of the data.
- Using appropriate chart types: For example, a heatmap might be more effective than a scatter plot when dealing with extensive datasets.
Choosing the Right Tool: A Comparative Overview
| Tool | Strengths | Weaknesses | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tableau | Powerful data visualization, interactive dashboards, excellent scalability | Relatively expensive, steeper learning curve | Complex datasets, interactive dashboards |
| Power BI | User-friendly interface, robust data connectivity, good integration with Microsoft products | Can be limited in certain advanced visualizations | Business intelligence, reporting, integrating with existing data |
| Excel/Sheets | Widely accessible, easy to use for basic charts | Limited in advanced visualization capabilities, not ideal for large datasets | Simple charts, quick data visualization, basic analysis |
| Canva | Excellent for design, easy to use, many templates | Not designed for data manipulation, limited chart types | Improving the aesthetics of existing charts |
| Adobe Illustrator/Inkscape | Advanced design capabilities, high-quality graphics | Steeper learning curve, not specifically for data visualization | Highly customized and professional-looking charts |
| D3.js | Highly customizable, allows for very complex visualizations | Requires coding skills, steeper learning curve | Highly interactive and custom charts for web developers |
Beyond the Tools: Best Practices for Chart Design
Regardless of the tools you use, adhering to these best practices enhances your charts' effectiveness:
- Clear and Concise Titles and Labels: Always include descriptive titles and labels.
- Appropriate Chart Type: Choose a chart type that best represents your data and message.
- Consistent Color Palette: Use a color scheme that is both aesthetically pleasing and aids comprehension.
- Minimalist Design: Avoid unnecessary clutter. Focus on highlighting key insights.
- Data Accuracy and Integrity: Ensure your data is accurate and appropriately represented.
- Accessibility: Design charts that are accessible to people with disabilities (e.g., using sufficient color contrast).
By understanding your transformation goals, choosing the appropriate tools, and following best practices, you can effectively transform Chart 1 into a compelling and insightful Chart 2 that effectively communicates your data story. Remember to iterate and refine your charts based on feedback and ongoing analysis. The process of data visualization is iterative and often involves several rounds of refinement before achieving the perfect representation.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Two Things Does Fair Chase Emphasize
Apr 01, 2025
-
Productivity Growth Is Also Closely Linked To
Apr 01, 2025
-
When Sugar Is Mixed With Water Equilibrium Is Reached When
Apr 01, 2025
-
Check In Check Out Managing Hotel Operations Vallen
Apr 01, 2025
-
A Company Sold A Machine For 15000 In Cash
Apr 01, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Tools To Make Chart 1 Look Like Chart 2 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
