Which Statement Is True Regarding Venipuncture Procedures In Mice
Holbox
Mar 28, 2025 · 5 min read
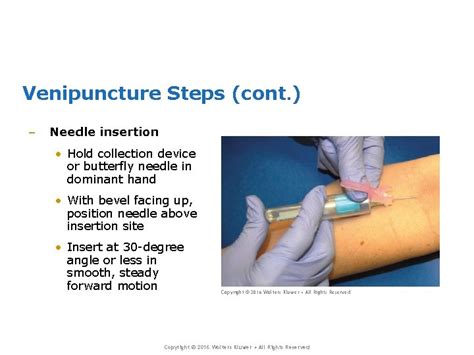
Table of Contents
- Which Statement Is True Regarding Venipuncture Procedures In Mice
- Table of Contents
- Which Statement is True Regarding Venipuncture Procedures in Mice? A Comprehensive Guide
- Understanding the Challenges of Mouse Venipuncture
- Choosing the Right Vein: A Crucial First Step
- 1. Retro-orbital Sinus:
- 2. Saphenous Vein:
- 3. Lateral Tail Vein:
- 4. Cardiac Puncture:
- Essential Equipment and Preparation
- Step-by-Step Guide to Venipuncture in Mice: Focusing on the Lateral Tail Vein
- Minimizing Stress and Pain
- Troubleshooting Common Issues
- Ethical Considerations
- Conclusion: Prioritizing Accuracy and Animal Welfare
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
Which Statement is True Regarding Venipuncture Procedures in Mice? A Comprehensive Guide
Venipuncture in mice, the process of drawing blood from a vein, is a crucial technique in biomedical research. Accuracy and ethical considerations are paramount. This comprehensive guide will explore various aspects of mouse venipuncture, clarifying common misconceptions and highlighting best practices to ensure accurate results while prioritizing animal welfare.
Understanding the Challenges of Mouse Venipuncture
Mice are small, delicate creatures, making venipuncture a technically challenging procedure. Unlike larger animals, their veins are minute and easily damaged. Improper technique can lead to:
- Hematoma formation: Bleeding into surrounding tissue, causing pain and discomfort for the mouse.
- Infection: Introducing bacteria into the puncture site, leading to serious complications.
- Stress and anxiety: The procedure itself can be stressful for the animal, potentially affecting experimental results.
- Inaccurate blood samples: Hemolysis (rupture of red blood cells) or clotting can render the sample unusable.
- Animal death: In extreme cases, improper technique can result in the death of the animal.
Choosing the Right Vein: A Crucial First Step
The success of venipuncture hinges on selecting the appropriate vein. Several veins are commonly targeted, each with its own advantages and disadvantages:
1. Retro-orbital Sinus:
- Advantages: Relatively large blood volume can be obtained.
- Disadvantages: Highly invasive; carries a significant risk of eye injury and severe complications, including death. It's generally discouraged and considered outdated due to the high risk of complications. Many institutions have banned this technique.
2. Saphenous Vein:
- Advantages: Superficial location makes it easier to access; relatively low risk of complications.
- Disadvantages: Smaller blood volume compared to retro-orbital sinus; requires more skill and experience.
3. Lateral Tail Vein:
- Advantages: Easily accessible; relatively low risk of complications; allows for repeated sampling from the same animal.
- Disadvantages: Small blood volume per puncture; requires practice to master; can be stressful for the animal if performed repeatedly.
4. Cardiac Puncture:
- Advantages: Provides a large blood volume; suitable for collecting blood for multiple tests.
- Disadvantages: Highly invasive; requires significant expertise; carries a high risk of complications, including death. Generally reserved for terminal procedures.
Essential Equipment and Preparation
Proper preparation is critical for a successful and humane venipuncture procedure. Here's a checklist of essential equipment:
- Appropriate sized needles: The needle gauge should be chosen based on the selected vein and the anticipated blood volume.
- Syringes: Choose syringes with appropriate volume capacity.
- Heparinized tubes or other anticoagulant-containing collection tubes: Prevent blood clotting.
- 70% isopropyl alcohol: For sterilization of the puncture site.
- Gauze pads: For applying pressure to the puncture site after venipuncture.
- Warm towel or heating pad (optional): To dilate blood vessels and facilitate blood flow.
Step-by-Step Guide to Venipuncture in Mice: Focusing on the Lateral Tail Vein
The lateral tail vein is the preferred site for venipuncture in many research settings due to its relatively accessible location and reduced risk compared to other methods.
1. Preparation:
- Warm the mouse: Gently warm the mouse's tail using a warm towel or heating pad for a few minutes. This helps dilate the blood vessels.
- Restrain the mouse properly: Use appropriate restraint methods to minimize stress and ensure the safety of both the animal and the researcher.
- Sanitize: Clean the puncture site with 70% isopropyl alcohol.
2. Puncture:
- Select the puncture site: Identify a visible blood vessel on the lateral tail vein.
- Insert the needle: Insert the needle at a shallow angle into the vein. A bevel up approach is commonly preferred.
- Aspirate slowly: Gently pull back on the plunger of the syringe to collect blood. Avoid forceful aspiration, which can damage the vein and cause hemolysis.
3. Post-Puncture:
- Remove the needle: Quickly remove the needle and apply gentle pressure to the puncture site with a gauze pad.
- Monitor: Monitor the animal for bleeding or any signs of distress.
- Dispose of needles and other sharps properly: Follow institutional guidelines for waste disposal.
Minimizing Stress and Pain
- Use appropriate analgesics and anesthetics: Consult with your veterinarian or animal care professional to determine the appropriate pain management strategy.
- Minimize handling time: Efficient and practiced techniques minimize stress and discomfort.
- Provide enrichment: Following the procedure, ensure the animals have appropriate housing and enrichment.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
- Difficulty finding a vein: Ensure adequate warming of the tail. If necessary, consult experienced personnel.
- Hematoma formation: Apply gentle, continuous pressure to the puncture site after needle removal.
- Blood clot formation: Ensure the use of appropriate anticoagulants in the collection tubes.
Ethical Considerations
The 3Rs (Replacement, Reduction, Refinement) should always guide experimental design and procedures involving animals.
- Replacement: Consider alternative methods to avoid animal use whenever possible.
- Reduction: Minimize the number of animals used in your experiment.
- Refinement: Employ techniques and procedures that minimize pain and distress. This includes employing proper analgesia, appropriate training for personnel, and adhering to strict aseptic techniques.
Conclusion: Prioritizing Accuracy and Animal Welfare
Choosing the right vein and mastering the technique is paramount for successful mouse venipuncture. While the lateral tail vein is generally preferred for its accessibility and lower risk, it's crucial to prioritize the animal's welfare throughout the entire process. Careful planning, meticulous technique, proper training, and adherence to ethical guidelines are essential for obtaining accurate results while upholding the highest standards of animal care. Remember that the statement "Retro-orbital sinus venipuncture is the most common and easiest method" is false. The lateral tail vein, with proper training and technique, offers a superior alternative with significantly reduced risk to the animal's well-being. Continuous education and refinement of techniques are crucial to improve both the scientific validity of the results and the ethical treatment of laboratory animals.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Statement Is True Regarding Venipuncture Procedures In Mice . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.