Which Of The Following Does Not Belong
Holbox
Apr 01, 2025 · 5 min read
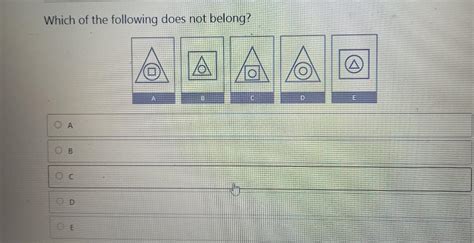
Table of Contents
- Which Of The Following Does Not Belong
- Table of Contents
- Which of the Following Does Not Belong? A Deep Dive into Analogy and Reasoning
- Understanding the Nature of the "Odd One Out"
- Categories of Differences:
- Strategies for Solving "Odd One Out" Puzzles
- 1. Identify Commonalities:
- 2. Look for Differences:
- 3. Consider Relationships:
- 4. Employ Elimination:
- 5. Check Your Answer:
- Examples and Deep Dives
- The Cognitive Benefits of "Odd One Out" Puzzles
- Conclusion: More Than Just a Game
- Latest Posts
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
Which of the Following Does Not Belong? A Deep Dive into Analogy and Reasoning
Finding the odd one out – the element that doesn't belong – is a classic brain teaser that tests our ability to identify patterns, understand relationships, and apply logical reasoning. It's a skill valuable not just for solving puzzles, but also for critical thinking in various aspects of life, from problem-solving at work to making informed decisions in everyday situations. This article explores the nuances of these puzzles, different approaches to solving them, and the cognitive skills they hone.
Understanding the Nature of the "Odd One Out"
The core principle behind "which of the following does not belong" puzzles lies in analogy and difference. We are presented with a set of items seemingly related, yet one stands out due to a key characteristic that distinguishes it from the others. This characteristic can be based on numerous factors:
Categories of Differences:
-
Categorical Differences: This is the most straightforward type. The odd one out simply belongs to a different category. For example:
- Apple, Banana, Orange, Car – The car is the only non-fruit.
-
Attribute Differences: This involves identifying a specific attribute that separates one item from the rest. The attributes could be size, color, shape, function, or any other defining characteristic. For example:
- Red, Blue, Green, Square – Square is the only shape, while the others are colors.
-
Relationship Differences: This is a more complex type where the relationship between items needs to be considered. The odd one out breaks the established pattern or relationship. For example:
- Dog, Cat, Bird, Fish - While all are animals, Fish is the only one that lives primarily in water.
-
Sequential Differences: Sometimes, the items form a sequence or series, and the odd one out disrupts this sequence. For example:
- 2, 4, 6, 8, 11 - The sequence is even numbers; 11 is odd.
Strategies for Solving "Odd One Out" Puzzles
Successfully navigating these puzzles requires a systematic approach:
1. Identify Commonalities:
The first step is to carefully examine all the items and pinpoint their shared attributes. What do they have in common? This helps establish a baseline and highlights the contrasting features of the odd one out. For example, in the set: "Lion, Tiger, Bear, Eagle", the commonality is that they are all mammals except for the Eagle.
2. Look for Differences:
Once commonalities are established, focus on the differences. What makes each item unique? Compare each item individually to the rest of the set, focusing on various aspects like:
- Physical Characteristics: Size, shape, color, texture.
- Functional Characteristics: Purpose, use, role.
- Categorical Characteristics: Type, class, group.
Consider abstract attributes as well. The differences might not be immediately apparent.
3. Consider Relationships:
Beyond individual attributes, consider the relationships between the items. Do they form a sequence, a hierarchy, or a logical group? The odd one out might disrupt this relationship. For example:
- Paris, Rome, London, Tokyo, Apple - The first four are capital cities; Apple is a company.
4. Employ Elimination:
Systematic elimination is a powerful technique. After identifying commonalities and differences, start eliminating items that clearly belong to the group. The remaining item is likely the odd one out.
5. Check Your Answer:
After selecting the odd one out, double-check your reasoning. Does the chosen item truly differ from the rest in a significant way? Can you clearly articulate why it doesn't belong? If not, revisit your analysis.
Examples and Deep Dives
Let's examine several examples and analyze them step-by-step:
Example 1:
- Square, Circle, Triangle, Rectangle, Pentagon
Analysis: All the shapes are polygons except for the Circle which is a curved shape. Therefore, the Circle is the odd one out.
Example 2:
- Dog, Cat, Lion, Tiger, Dolphin
Analysis: All are mammals except the Dolphin, which is a marine mammal. While technically a mammal, the Dolphin’s habitat differentiates it from the others, making it the likely odd one out depending on the intended level of detail.
Example 3:
- Piano, Guitar, Violin, Drums, Trumpet
Analysis: All but the Drums are stringed or wind instruments. Drums are percussion instruments, making it the odd one out.
Example 4:
- January, March, May, July, August
Analysis: This involves a sequential understanding of months. All months listed except August have 31 days. August has 31 days, but the question is intentionally designed to be slightly ambiguous. A deeper consideration may look for other patterns, such as odd-numbered months, making August still arguably the odd one out.
Example 5 (More Complex):
- Obese, Chubby, Plump, Emaciated, Stout
Analysis: This example delves into subtle nuances of language. Obese, chubby, plump, and stout describe varying degrees of being overweight. Emaciated means extremely thin, standing in stark contrast to the rest, making it the odd one out.
Example 6 (Abstract):
- Happy, Sad, Angry, Excited, Tired
Analysis: This involves emotions. While all are emotional states, “Tired” is more a physical state than a purely emotional one, making it the outlier. The distinction can be argued, showing the subjective nature of some puzzles.
The Cognitive Benefits of "Odd One Out" Puzzles
Solving "odd one out" puzzles enhances several cognitive skills:
-
Pattern Recognition: The ability to identify patterns and regularities is crucial for problem-solving and learning. These puzzles directly train this skill.
-
Logical Reasoning: These puzzles necessitate logical deductions and inferences. Identifying the odd one out requires careful reasoning and analysis.
-
Critical Thinking: The process of evaluating information, identifying relationships, and drawing conclusions strengthens critical thinking capabilities.
-
Problem-Solving: These puzzles are miniature problem-solving exercises that improve the ability to tackle more complex problems.
-
Attention to Detail: Successfully solving these puzzles requires careful observation and attention to detail. Overlooking subtle differences can lead to incorrect answers.
Conclusion: More Than Just a Game
"Which of the following does not belong?" puzzles are more than just brain teasers; they are valuable exercises in critical thinking and cognitive development. They help us hone our ability to identify patterns, analyze information, and solve problems effectively. By understanding the different categories of differences and employing systematic strategies, we can improve our skills in logical reasoning and enhance our overall cognitive abilities. So, next time you encounter one of these puzzles, remember the strategies outlined in this article and enjoy the challenge! The satisfaction of solving these puzzles is a testament to the power of logical thinking and attention to detail.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Indicate Which Of The Four Perspectives In The Balanced Scorecard
Apr 04, 2025
-
To Say That Coins Are Token Money Means That
Apr 04, 2025
-
The Shaft Of A Long Bone Is Called
Apr 04, 2025
-
Increasing Marginal Opportunity Cost Implies That
Apr 04, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Is Accurate Concerning Nonverbal Communication
Apr 04, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Of The Following Does Not Belong . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
