Which Of The Following Disorders Involves The Vertebrae
Holbox
Mar 14, 2025 · 7 min read
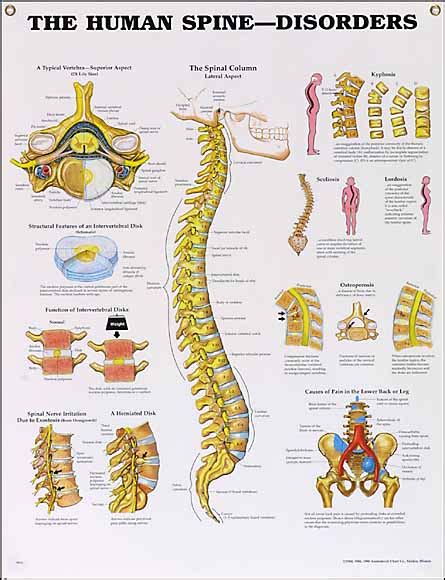
Table of Contents
Which of the Following Disorders Involves the Vertebrae? A Comprehensive Guide to Spinal Conditions
The human vertebral column, or spine, is a complex structure crucial for support, movement, and protection of the spinal cord. A multitude of disorders can affect the vertebrae, leading to a range of symptoms and varying degrees of severity. This article explores several conditions involving the vertebrae, comparing and contrasting their causes, symptoms, and treatments. We'll delve into the specifics of each condition to provide a comprehensive understanding of how these disorders impact the spine.
Understanding the Vertebrae and their Function
Before diving into specific disorders, it's essential to understand the structure and function of the vertebrae. The spine consists of 33 vertebrae, categorized into five regions:
- Cervical (neck): 7 vertebrae (C1-C7)
- Thoracic (upper back): 12 vertebrae (T1-T12)
- Lumbar (lower back): 5 vertebrae (L1-L5)
- Sacrum: 5 fused vertebrae
- Coccyx (tailbone): 4 fused vertebrae
Each vertebra is composed of a body, a vertebral arch, and various processes. Intervertebral discs, made of cartilage, act as cushions between the vertebrae, allowing for flexibility and shock absorption. The spinal cord runs through the vertebral canal, formed by the vertebral arches, protecting delicate nerves.
Disorders Affecting the Vertebrae: A Detailed Overview
Several conditions can affect the vertebrae, impacting their structure, function, and the surrounding tissues. Here are some of the most common:
1. Spondylosis: The Wear and Tear of Aging
Spondylosis, also known as degenerative disc disease, is a common age-related condition affecting the vertebrae. It involves the gradual breakdown of the intervertebral discs, leading to decreased disc height, bone spurs (osteophytes), and narrowing of the spinal canal (spinal stenosis).
Symptoms: Symptoms vary depending on the location and severity of the degeneration. They can include:
- Neck pain: Stiffness, limited range of motion
- Back pain: Localized or radiating pain down the legs (sciatica)
- Numbness or tingling: In the arms or legs
- Muscle weakness: Depending on the nerve compression
Causes: Aging is the primary cause of spondylosis, as the intervertebral discs naturally lose hydration and elasticity over time. Other contributing factors include genetics, repetitive strain injuries, and poor posture.
Treatment: Treatment options range from conservative measures to surgery. Conservative approaches include:
- Pain relievers: Over-the-counter or prescription medications
- Physical therapy: Strengthening and stretching exercises
- Lifestyle modifications: Maintaining a healthy weight, improving posture
Surgery may be necessary in cases of severe nerve compression or instability. Surgical options include:
- Discectomy: Removal of a portion of the damaged disc
- Spinal fusion: Joining vertebrae to stabilize the spine
- Laminectomy: Removal of a portion of the lamina (part of the vertebral arch) to relieve pressure
2. Spondylolysis and Spondylolisthesis: Fractures and Slipping Vertebrae
Spondylolysis refers to a fracture in the pars interarticularis, a small section of bone connecting the facet joints of a vertebra. This fracture typically occurs in the lumbar spine.
Spondylolisthesis is the forward slippage of one vertebra over another. This condition often results from a pre-existing spondylolysis, although it can also be caused by other factors.
Symptoms: Symptoms can range from mild to severe and may include:
- Low back pain: Often worsened by activity
- Stiffness: In the lower back
- Leg pain: Radiating pain down the leg(s) (sciatica)
- Neurological symptoms: Numbness, tingling, muscle weakness
Causes: The primary cause of spondylolysis is a stress fracture, often related to repetitive hyperextension of the spine, common in athletes. Spondylolisthesis can result from spondylolysis, trauma, or degenerative changes.
Treatment: Treatment depends on the severity of the symptoms and the degree of slippage. Conservative management includes:
- Pain relievers: For pain management
- Physical therapy: Strengthening core muscles and improving stability
- Bracing: To support the spine
Surgical intervention may be necessary in severe cases to stabilize the spine and prevent further slippage.
3. Osteoporosis: Weakening of the Bones
Osteoporosis is a systemic skeletal disease characterized by low bone mass and microarchitectural deterioration, leading to increased bone fragility and a consequent increase in fracture risk. While affecting the entire skeleton, osteoporosis significantly weakens the vertebrae, making them susceptible to compression fractures.
Symptoms: Osteoporosis often has no symptoms until a fracture occurs. Compression fractures of the vertebrae can cause:
- Back pain: Sharp, sudden pain
- Loss of height: Gradual decrease in height over time
- Kyphosis (Dowager's hump): Curvature of the spine
Causes: Osteoporosis is caused by an imbalance between bone resorption (breakdown) and bone formation. Risk factors include aging, genetics, hormonal changes (menopause), insufficient calcium and vitamin D intake, and certain medications.
Treatment: Treatment focuses on preventing further bone loss and reducing the risk of fractures. This may include:
- Medications: Bisphosphonates, denosumab, and teriparatide to increase bone density
- Calcium and vitamin D supplements: To maintain adequate levels
- Lifestyle modifications: Weight-bearing exercise, a balanced diet
4. Scoliosis: Curvature of the Spine
Scoliosis is a sideways curvature of the spine. While not directly related to a specific disorder of individual vertebrae, the condition often causes abnormal stresses and forces on the vertebrae, leading to potential long-term complications.
Symptoms: Scoliosis can be asymptomatic in mild cases. Symptoms may include:
- Uneven shoulders: One shoulder higher than the other
- Uneven hips: One hip higher than the other
- Prominent rib cage: One side of the rib cage more prominent than the other
- Back pain: In more severe cases
Causes: In many cases, the cause of scoliosis is unknown (idiopathic scoliosis). Other causes include:
- Congenital scoliosis: Present at birth
- Neuromuscular scoliosis: Associated with neurological or muscular disorders
Treatment: Treatment depends on the severity of the curvature. Mild scoliosis may only require regular monitoring. Moderate to severe scoliosis may require:
- Bracing: To prevent further curvature progression
- Surgery: Spinal fusion to correct the curvature
5. Ankylosing Spondylitis: Inflammatory Arthritis of the Spine
Ankylosing spondylitis (AS) is a chronic inflammatory disease that primarily affects the sacroiliac joints (where the spine connects to the pelvis) and the spine. It causes inflammation and fusion of the vertebrae, leading to stiffness and decreased mobility.
Symptoms: Symptoms typically begin in young adulthood and may include:
- Lower back pain: Stiffness, especially in the morning or after periods of inactivity
- Sacroiliac joint pain: Pain in the lower back and buttocks
- Limited range of motion: Stiffness and decreased flexibility in the spine
- Fatigue: Chronic tiredness
Causes: AS is an autoimmune disease, meaning the body's immune system attacks its own tissues. The exact cause is unknown, but genetic factors play a significant role.
Treatment: Treatment aims to reduce inflammation, manage pain, and improve function. This may involve:
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs): To reduce pain and inflammation
- Physical therapy: To maintain flexibility and mobility
- Biological therapies: Medications that target the immune system
6. Vertebral Compression Fractures: Broken Vertebrae
Vertebral compression fractures are breaks in one or more vertebrae, most commonly caused by osteoporosis. These fractures can occur spontaneously or following a minor trauma.
Symptoms: Symptoms may include:
- Sudden onset of back pain: Severe and localized
- Loss of height: Gradual decrease in height
- Kyphosis: Curvature of the spine
- Neurological symptoms: In cases of severe fractures
Causes: The most common cause is osteoporosis, making bones brittle and prone to fractures. Other causes include trauma, tumors, and infections.
Treatment: Treatment depends on the severity of the fracture and the patient's overall health. This may include:
- Pain relief medication: For pain management
- Bracing: To support the spine
- Vertebroplasty or kyphoplasty: Minimally invasive procedures to stabilize the fractured vertebra
Conclusion: Seeking Professional Help
This overview provides a glimpse into the diverse range of disorders affecting the vertebrae. Each condition has its unique causes, symptoms, and treatment approaches. It's crucial to remember that this information is for educational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. If you experience any symptoms related to spinal problems, it's essential to consult a healthcare professional for accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment. Early diagnosis and intervention can significantly improve outcomes and prevent long-term complications. Don't hesitate to seek medical attention if you suspect any spinal disorder. Your health and well-being are paramount.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Karst Processes And Topography Activity 12 4
Mar 14, 2025
-
Question New York Select All The Reagets
Mar 14, 2025
-
The Media Perform The Signaling Role By
Mar 14, 2025
-
Draw The Major Organic Product For The Reaction
Mar 14, 2025
-
A Solubility Product Constant Lab 17a Answers
Mar 14, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Of The Following Disorders Involves The Vertebrae . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
