Which Image Highlights The Parent Chain
Holbox
Mar 29, 2025 · 5 min read
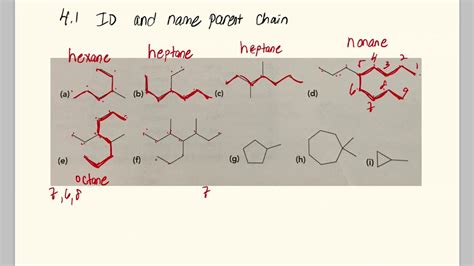
Table of Contents
- Which Image Highlights The Parent Chain
- Table of Contents
- Which Image Highlights the Parent Chain? A Comprehensive Guide to Organic Chemistry
- What is the Parent Chain?
- Identifying the Parent Chain: A Step-by-Step Approach
- 1. Locate the Longest Carbon Chain
- 2. Consider all Possible Orientations
- 3. Handle Branched Chains
- 4. Dealing with Rings (Cyclic Structures)
- 5. Prioritizing Functional Groups
- Examples: Illustrating Parent Chain Identification
- Advanced Scenarios and Considerations
- Practical Tips for Success
- Conclusion: Mastering the Parent Chain
- Latest Posts
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
Which Image Highlights the Parent Chain? A Comprehensive Guide to Organic Chemistry
Understanding the parent chain in organic chemistry is fundamental to correctly naming and understanding the structure of organic molecules. The parent chain is the longest continuous carbon chain within a molecule. Identifying it correctly is crucial for applying IUPAC nomenclature rules. This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of identifying the parent chain, utilizing various examples and illustrating the process with clear visuals (though, as requested, I cannot provide actual images). We’ll explore different scenarios, including branched chains, cyclic structures, and molecules containing multiple functional groups.
What is the Parent Chain?
The parent chain, also known as the principal chain or main chain, forms the basis for the name of an organic compound. It's the longest continuous sequence of carbon atoms within the molecule. This chain doesn't necessarily have to be drawn in a straight line; it can be bent or folded. The key is to find the longest continuous path connecting carbon atoms. Once identified, all other groups or substituents are considered branches or functional groups attached to this primary chain.
Identifying the Parent Chain: A Step-by-Step Approach
Let's break down the process of identifying the parent chain using a systematic approach.
1. Locate the Longest Carbon Chain
This is the most crucial step. Start by carefully examining the molecular structure. Begin at one carbon atom and trace every possible path through connected carbon atoms. Systematically explore every branch and pathway to ensure you've found the absolute longest continuous chain. Don’t get misled by visually shorter, more straightforward paths. The longest chain might appear unexpectedly folded or twisted.
2. Consider all Possible Orientations
Sometimes, the longest chain isn't immediately obvious. The molecule might be drawn in a way that obscures the longest continuous carbon chain. You may need to mentally rotate or rearrange the molecule to identify the longest chain accurately. Practice is key to developing this spatial reasoning skill.
3. Handle Branched Chains
When dealing with branched chains, the longest chain will always incorporate the branch points. The branches themselves are not part of the parent chain; they are substituents attached to it.
4. Dealing with Rings (Cyclic Structures)
When a molecule contains both a ring and an alkyl chain, determine which is longer. The longest structure determines the parent chain. If the ring and chain are of equal length, the ring takes precedence as the parent chain. The ring's name will be the base name, with alkyl substituents identified appropriately.
5. Prioritizing Functional Groups
Functional groups significantly impact the naming of organic compounds. Certain functional groups (like carboxylic acids, ketones, aldehydes) dictate the base name and the parent chain’s selection. If a molecule contains a functional group that defines the parent chain, the longest chain incorporating this group will be selected, even if a longer chain without the functional group exists.
Examples: Illustrating Parent Chain Identification
Let's consider some examples to solidify our understanding. (Note: these descriptions aim to convey the structural information without the use of actual images; imagine the structures as you read.)
Example 1: A Simple Branched Alkane
Consider a molecule with a main chain of six carbons, and a methyl group (CH3) branching off from the third carbon. Even though there are chains of five carbons present, the longest chain is six carbons long and forms the parent chain (hexane). The methyl group is then named as a substituent.
Example 2: A Molecule with a Ring and Alkyl Chain
Imagine a molecule comprising a cyclohexane ring with a butyl chain attached. While the butyl chain is four carbons long, the cyclohexane ring takes precedence as the parent chain due to its ring structure, and the butyl group is a substituent.
Example 3: A Molecule with Competing Chains
Consider a molecule where multiple chains appear equally long. You might encounter a structure with two chains of five carbons each. In such cases, prioritize the chain with the most substituents. If this doesn’t resolve the ambiguity, systematically evaluate all possible chain orientations to confirm the longest continuous chain.
Example 4: A Molecule with a Functional Group
Imagine a molecule with a six-carbon chain and a carboxylic acid (-COOH) functional group attached to the second carbon. Even if another six-carbon chain could be found, the longest chain containing the carboxylic acid group takes precedence. This molecule would be named as a hexanoic acid derivative, with the appropriate substituents noted.
Advanced Scenarios and Considerations
Identifying the parent chain can become more complex in molecules with multiple functional groups or highly branched structures. In such cases, a systematic approach, as described above, coupled with a sound understanding of IUPAC nomenclature rules, is essential. These advanced scenarios often require careful consideration of priority rules based on the types and positions of functional groups present. This involves ranking functional groups according to a hierarchical system which often directs the choice of the parent chain to include the highest priority functional group.
Practical Tips for Success
-
Practice: The more you practice identifying parent chains in various molecules, the better you'll become at recognizing patterns and resolving ambiguities quickly.
-
Systematic Approach: Follow a systematic procedure to avoid overlooking potential parent chains.
-
Visual Aids: While not provided here, drawing and redrawing structures can significantly assist in identifying the longest continuous chain.
-
Nomenclature Rules: A strong understanding of IUPAC nomenclature rules is crucial for selecting the parent chain and naming the molecule accurately. The nomenclature rules dictate the hierarchy of functional groups and their effect on parent chain selection.
Conclusion: Mastering the Parent Chain
Identifying the parent chain is a crucial skill in organic chemistry. The process requires careful observation, systematic exploration of the molecular structure, and a thorough understanding of IUPAC nomenclature rules. By following the steps outlined in this guide and practicing regularly, you will develop the proficiency needed to correctly identify the parent chain in a variety of organic molecules, paving the way for accurate naming and structural understanding. The ability to confidently determine the parent chain is foundational to success in organic chemistry. Remember to prioritize systematic analysis and utilize visual aids to support your identification process, leading to confident and accurate results. Mastering this skill unlocks further understanding of molecular properties and organic chemistry principles.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Locking Out Tagging Out Refers To
Apr 01, 2025
-
When Society Requires That Firms Reduce Pollution There Is
Apr 01, 2025
-
Generally Accepted Accounting Principles Gaap Wants Information To Have
Apr 01, 2025
-
Which Of These Statements Is True
Apr 01, 2025
-
An Increase In Product Price Will Cause
Apr 01, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Image Highlights The Parent Chain . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
