Which Choices Are Real Numbers Check All That Apply
Holbox
Mar 16, 2025 · 4 min read
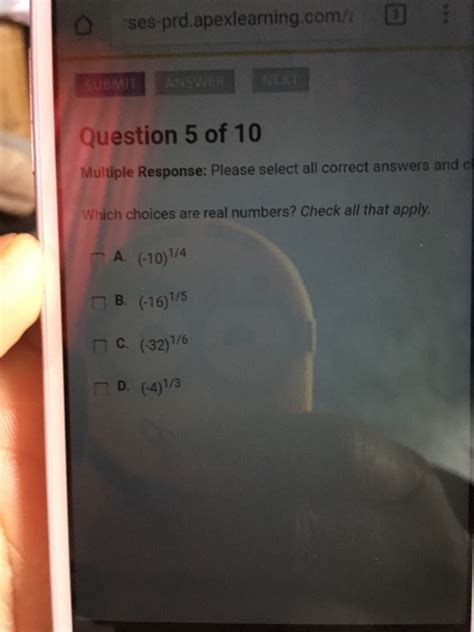
Table of Contents
Which Choices Are Real Numbers? Check All That Apply
Understanding real numbers is fundamental to mathematics and many other fields. This comprehensive guide will delve into the definition of real numbers, explore their different subsets, and provide numerous examples to help you confidently identify which choices represent real numbers. We'll also address common misconceptions and offer practice exercises to solidify your understanding.
What Are Real Numbers?
Real numbers encompass all the numbers that can be plotted on a number line. This expansive category includes both rational and irrational numbers. Let's break down these subsets:
Rational Numbers
Rational numbers are numbers that can be expressed as a fraction p/q, where 'p' and 'q' are integers, and 'q' is not zero. This means they can be represented as a ratio of two whole numbers. Examples include:
- Integers: Whole numbers, including negative whole numbers (e.g., -3, 0, 5).
- Fractions: Numbers expressed as a ratio, like 1/2, -3/4, 7/1 (which simplifies to 7).
- Terminating Decimals: Decimals that end after a finite number of digits, such as 0.75, 2.5, or -1.234.
- Repeating Decimals: Decimals with a pattern of digits that repeats infinitely, like 0.333... (1/3), 0.142857142857... (1/7), or -1.232323...
Irrational Numbers
Irrational numbers cannot be expressed as a fraction of two integers. Their decimal representation goes on forever without repeating. Famous examples include:
- π (Pi): The ratio of a circle's circumference to its diameter, approximately 3.14159...
- e (Euler's number): The base of the natural logarithm, approximately 2.71828...
- √2 (Square root of 2): The number which, when multiplied by itself, equals 2. This has a non-repeating, non-terminating decimal expansion.
- Other Roots: Many square roots, cube roots, and other roots of non-perfect squares/cubes/etc. are irrational.
Identifying Real Numbers: A Step-by-Step Guide
To determine if a number is a real number, follow these steps:
-
Check if it can be plotted on a number line: If yes, it's a real number. If no, it's not a real number. (This eliminates imaginary and complex numbers).
-
Determine if it's rational or irrational: If it can be expressed as a fraction p/q (where q≠0), it's rational. If its decimal representation is non-repeating and non-terminating, it's irrational.
-
Consider special cases: Be mindful of numbers like π and e, which are well-known irrational numbers.
Examples and Practice
Let's test your understanding with some examples:
Which of the following are real numbers? Check all that apply.
- 5: Real Number (Integer, Rational)
- -2/3: Real Number (Rational)
- √-9: Not a real number (Imaginary number - involves the square root of a negative number)
- 0.666...: Real Number (Rational, repeating decimal)
- π/2: Real Number (Irrational, π is irrational)
- √16: Real Number (Rational, equals 4)
- 0.123456789101112...: Real Number (Irrational, non-repeating, non-terminating)
- e<sup>2</sup>: Real Number (Irrational, e is irrational)
- 1/0: Not a real number (Undefined – division by zero is not allowed)
- -√25: Real Number (Rational, equals -5)
- 3.14: Real Number (Rational, terminating decimal, approximation of π)
- i: Not a real number (Imaginary unit, √-1)
- √(-16): Not a Real Number (Imaginary number)
- (√2)<sup>2</sup>: Real Number (Rational, equals 2)
- 0.1010010001...: Real Number (Irrational, non-repeating, non-terminating)
- -5.78: Real Number (Rational, terminating decimal)
- 2<sup>1/3</sup>: Real Number (Irrational; cube root of 2 is not a perfect cube)
- ln(1): Real Number (Rational, equals 0)
- cos(π): Real Number (Rational, equals -1)
- tan(π/2): Not a real number (Undefined – tangent of π/2 is undefined)
Advanced Concepts and Considerations
While the above examples cover many common scenarios, some situations may require deeper understanding:
-
Complex Numbers: These numbers have a real and an imaginary part (e.g., 2 + 3i). Although they include real numbers as a component, they are not themselves considered real numbers.
-
Transcendental Numbers: These irrational numbers are not the roots of any polynomial equation with rational coefficients. π and e are examples of transcendental numbers.
-
Set Theory: Understanding sets (like the set of rational numbers, the set of real numbers) can provide a formal framework for discussing these number systems.
Real-World Applications of Real Numbers
Real numbers are indispensable in various fields:
- Physics: Describing measurements of distance, time, velocity, acceleration, and many other physical quantities.
- Engineering: Designing structures, calculating forces, and modeling systems require extensive use of real numbers.
- Finance: Handling monetary values, interest rates, and financial calculations.
- Computer Science: Representing numerical data, performing calculations, and dealing with approximations.
- Statistics: Analyzing data sets, computing averages, and performing statistical modeling.
Conclusion: Mastering Real Numbers
Identifying real numbers involves understanding the fundamental concepts of rational and irrational numbers and their respective properties. By grasping these concepts and practicing with diverse examples, you'll develop a strong foundation for tackling more complex mathematical and scientific challenges. Remember that while many numbers can be easily identified, it's important to be aware of special cases like π, e, and the potential for irrational roots, ensuring you have a complete picture of the vast world of real numbers. Continual practice and review will solidify your understanding and build confidence in your ability to identify real numbers accurately.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Draw All Resonance Structures For The Nitryl Fluoride Molecule No2f
Mar 16, 2025
-
Property Rights Are Important Because They
Mar 16, 2025
-
Host Range Is Limited By The
Mar 16, 2025
-
Draw The Major Organic Product Formed In The Reaction
Mar 16, 2025
-
Lymph Nodes Do All Of The Following Except
Mar 16, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Choices Are Real Numbers Check All That Apply . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
