What Is The Medial Border Of The Highlighted Region Called
Holbox
Mar 19, 2025 · 5 min read
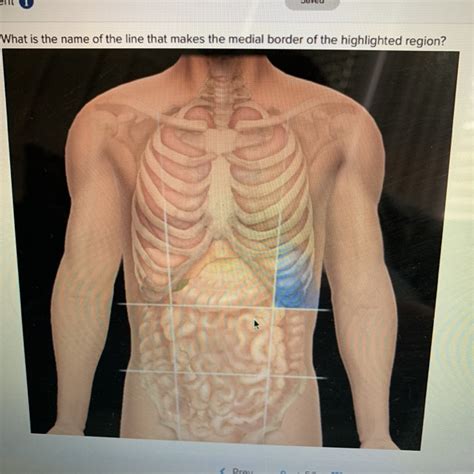
Table of Contents
Decoding the Medial Border: A Deep Dive into Anatomical Terminology and Regional Variations
Understanding anatomical terminology is crucial for effective communication within the medical and scientific community. This article delves into the complexities of identifying the "medial border of the highlighted region," emphasizing the importance of context, specific anatomical structures, and the inherent variability across different body regions. Since "highlighted region" is inherently vague, we'll explore several common scenarios where determining the medial border is critical, providing a comprehensive overview applicable to various anatomical contexts.
The Importance of Context: Why "Highlighted Region" is Insufficient
The term "medial border" is relative. It always depends on the specific anatomical region being examined. To accurately identify a medial border, we need a clear definition of the "highlighted region." Is it a bone, a muscle, an organ, or a section of skin? The answer drastically alters the location and identity of its medial border. Without specifying the highlighted region, any attempt to define its medial border is inherently ambiguous and potentially inaccurate.
Understanding Fundamental Anatomical Directions
Before we explore specific examples, let's review the fundamental directional terms used in anatomy:
- Medial: Towards the midline of the body.
- Lateral: Away from the midline of the body.
- Superior (Cranial): Towards the head.
- Inferior (Caudal): Towards the feet.
- Anterior (Ventral): Towards the front.
- Posterior (Dorsal): Towards the back.
- Proximal: Closer to the point of attachment (e.g., for limbs).
- Distal: Further from the point of attachment (e.g., for limbs).
These directional terms are essential for understanding and interpreting anatomical descriptions, ensuring accurate communication across different contexts. The medial border will always be the edge closest to the body's midline, relative to the structure in question.
Examples: Determining Medial Borders in Various Regions
Let's consider several specific anatomical regions and illustrate how to determine their medial borders:
1. The Medial Border of the Scapula (Shoulder Blade):
The scapula, a flat triangular bone, is located on the posterior aspect of the thorax. Its medial border is the longest border and runs vertically along the vertebral column. This border is relatively straightforward to identify because the scapula's shape and position are relatively consistent across individuals.
2. The Medial Border of the Kidney:
The kidneys are retroperitoneal organs, meaning they lie behind the peritoneum (lining of the abdominal cavity). The medial border of the kidney is concave and faces towards the vertebral column. This border is significant because it contains the hilum, the point where the renal artery and vein, ureter, and lymphatic vessels enter and exit the kidney.
3. The Medial Border of the Thigh Muscle (e.g., Sartorius):
Muscles present more complex considerations. The sartorius, the longest muscle in the human body, runs diagonally across the thigh. Its medial border is more challenging to define precisely since its borders are not sharply demarcated. It's essential to use other anatomical landmarks and relationships to identify it accurately within the context of surrounding muscles.
4. Medial Border of a Lung:
The lungs are cone-shaped organs within the thoracic cavity. The medial border of the lung is the concave surface facing the mediastinum, the central compartment of the thorax containing the heart, great vessels, trachea, and esophagus. This border is crucial for understanding lung anatomy and its relationship to the heart and other mediastinal structures.
5. Medial Border of the Eye:
The medial border of the eye refers to the edge closest to the nose. This is the medial canthus, where the eyelids meet. The medial border of the orbit (bony socket) shares a similar definition.
6. Medial Border of the Tibia (Shinbone):
The tibia is the larger of the two bones in the lower leg. Its medial border forms a prominent, subcutaneous ridge that can easily be palpated. This ridge is essential for surgical approaches and anatomical understanding.
Clinical Significance of Identifying Medial Borders:
Precise identification of medial borders is crucial in numerous clinical settings:
- Surgery: Surgeons rely on accurate anatomical knowledge to plan and execute procedures, avoiding damage to vital structures. Identifying medial borders is critical for precise incisions and the safe manipulation of organs and tissues.
- Imaging Interpretation: Radiologists and other medical professionals interpret medical images (X-rays, CT scans, MRIs) to diagnose and monitor various conditions. Accurate identification of medial borders aids in assessing organ size, position, and any abnormal findings.
- Physical Examination: Physicians use palpation and other physical examination techniques to assess various structures. Knowing the anatomical location of medial borders can help in the detection of abnormalities like masses or inflammation.
Variability and Individual Differences:
It's crucial to acknowledge the significant variability in anatomical structures across individuals. Age, sex, body build, and even past injuries can alter the precise location and shape of different structures. Therefore, defining the medial border must be performed within the context of the individual being examined, using a combination of anatomical landmarks and clinical judgment.
Advanced Anatomical Considerations:
The concept of a medial border becomes increasingly complex when dealing with intricate structures such as the brain, where identifying a clear "border" is less straightforward. In such instances, anatomical planes and sections are used to delineate specific regions and describe their relative positions.
The Importance of High-Quality Anatomical Resources:
Accurate anatomical knowledge is essential, and relying on credible sources is crucial. High-quality anatomy textbooks, reputable online resources, and atlases should always be consulted. It's always advisable to cross-reference multiple sources to ensure the accuracy and consistency of information.
Conclusion:
Determining the medial border of a "highlighted region" requires a precise understanding of the specific region in question. The term "medial" is relative and always depends on the anatomical context. This article provides a framework for understanding how to identify medial borders in various anatomical contexts, highlighting the clinical relevance of this knowledge and the importance of considering individual anatomical variations. Accurate identification of medial borders is crucial for various medical applications, from surgical planning to diagnostic imaging. The continued pursuit of detailed anatomical knowledge is vital for advancing medical practice and patient care. Remember to always consult authoritative anatomical resources to ensure accuracy and consistency in your understanding.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Identify The Correct And Incorrect Statements About The 2022 Electorate
Mar 19, 2025
-
What Color Is The Carbonaria Version Of The Peppered Moths
Mar 19, 2025
-
The Thymus Is The Only Lymphoid Organ That Does Not
Mar 19, 2025
-
Place The Following Hit Songs In Chronological Order
Mar 19, 2025
-
Based On The Table That Displays Expected And Announced
Mar 19, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Medial Border Of The Highlighted Region Called . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
