What Is The Iupac Name For The Following Compound
Holbox
Mar 10, 2025 · 6 min read
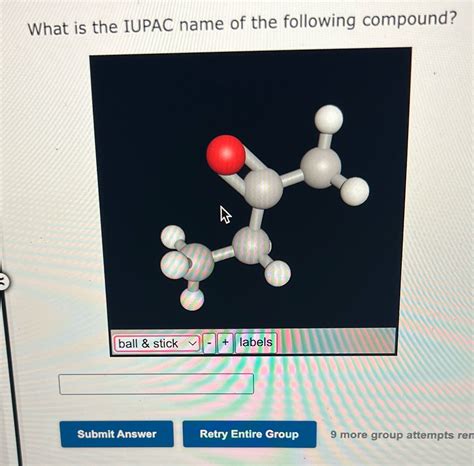
Table of Contents
- What Is The Iupac Name For The Following Compound
- Table of Contents
- Decoding Chemical Structures: A Deep Dive into IUPAC Nomenclature
- Understanding the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC)
- Key Principles of IUPAC Nomenclature
- Naming Alkanes: The Foundation of Organic Nomenclature
- Branching Alkanes: Incorporating Substituents
- Incorporating Functional Groups
- Cyclic Compounds: Navigating Rings
- More Complex Compounds: Putting it All Together
- Inorganic Compounds: A Different Set of Rules
- Conclusion: Mastering the Art of IUPAC Nomenclature
- Latest Posts
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
Decoding Chemical Structures: A Deep Dive into IUPAC Nomenclature
Determining the IUPAC name for a chemical compound might seem daunting at first, but with a systematic approach and understanding of the underlying principles, it becomes a manageable and even fascinating process. This article delves into the intricacies of IUPAC nomenclature, providing a comprehensive guide to naming organic and inorganic compounds, using examples to illustrate the key concepts. We will explore the logic behind the system, clarifying common points of confusion and equipping you with the skills to confidently name a wide range of chemical structures.
Understanding the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC)
The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) is a global organization responsible for developing standardized naming conventions, symbols, and terminology for chemistry. Their nomenclature system, aimed at ensuring unambiguous communication in the scientific community, is crucial for avoiding confusion and misinterpretations in research, industry, and education. The system is based on a set of rules that dictate how to name compounds based on their structural features. These rules are comprehensive and cover a vast range of chemical structures, from simple organic molecules to complex inorganic compounds and polymers.
Key Principles of IUPAC Nomenclature
Several fundamental principles underpin IUPAC nomenclature:
- Parent Chain/Structure: The longest continuous carbon chain or the most complex cyclic structure forms the basis of the name.
- Substituents: Atoms or groups of atoms attached to the parent chain are called substituents. These are named and their positions indicated.
- Numbering: The carbon atoms in the parent chain are numbered to assign the lowest possible numbers to the substituents.
- Alphabetical Order: Substituents are listed in alphabetical order (ignoring prefixes like di- and tri-).
- Functional Groups: Specific groups of atoms (like hydroxyl, carbonyl, carboxyl) are designated by specific suffixes or prefixes that dictate the overall class of the compound (alcohol, ketone, carboxylic acid etc.).
- Isomerism: The nomenclature system accounts for different types of isomerism (structural, geometric, stereoisomerism) to ensure that each isomer has a unique name.
Naming Alkanes: The Foundation of Organic Nomenclature
Alkanes, consisting only of carbon and hydrogen atoms with single bonds, serve as the foundation for naming many other organic compounds. The naming follows a simple pattern:
- 1 Carbon: Methane (CH₄)
- 2 Carbons: Ethane (C₂H₆)
- 3 Carbons: Propane (C₃H₈)
- 4 Carbons: Butane (C₄H₁₀)
- 5 Carbons: Pentane (C₅H₁₂)
- 6 Carbons: Hexane (C₆H₁₄)
- 7 Carbons: Heptane (C₇H₁₆)
- 8 Carbons: Octane (C₈H₁₈)
- 9 Carbons: Nonane (C₉H₂₀)
- 10 Carbons: Decane (C₁₀H₂₂)
For longer chains, the prefixes continue with undecane, dodecane, tridecane, and so on.
Branching Alkanes: Incorporating Substituents
When alkanes have branches (alkyl groups), the naming becomes more complex. Here's a step-by-step approach:
-
Identify the longest continuous carbon chain: This forms the parent alkane.
-
Identify and name the substituents: Methyl (CH₃-), ethyl (CH₃CH₂-), propyl (CH₃CH₂CH₂-), etc.
-
Number the carbon atoms in the parent chain: Start at the end closest to the first substituent. If substituents are equidistant from both ends, number to give the lowest set of numbers overall.
-
List the substituents with their positions: Use numbers to indicate the carbon atom to which each substituent is attached. If there are multiple substituents of the same type, use prefixes like di-, tri-, tetra- etc.
-
Arrange substituents alphabetically: Ignore prefixes like di- and tri- when alphabetizing.
Example: Consider the compound with the structure: CH₃-CH(CH₃)-CH₂-CH₃
-
The longest chain has four carbons, making it a butane.
-
A methyl group (CH₃) is attached to the second carbon.
-
The name is therefore 2-methylbutane.
Incorporating Functional Groups
Functional groups significantly impact the IUPAC name of a compound. They dictate the suffix or prefix used, defining the compound's class. Common functional groups and their associated suffixes/prefixes include:
-
Alcohols (-OH): The suffix "-ol" is added to the parent alkane name. The position of the hydroxyl group is indicated by a number. For example, CH₃CH₂OH is ethanol.
-
Aldehydes (-CHO): The suffix "-al" is added. For example, CH₃CHO is ethanal.
-
Ketones (C=O): The suffix "-one" is added, with a number indicating the carbonyl group's position. CH₃COCH₃ is propan-2-one (commonly known as acetone).
-
Carboxylic Acids (-COOH): The suffix "-oic acid" is used. CH₃COOH is ethanoic acid (commonly known as acetic acid).
-
Amines (-NH₂): The suffix "-amine" is used. CH₃NH₂ is methanamine.
-
Halogen Substituents (F, Cl, Br, I): These are treated as prefixes (fluoro-, chloro-, bromo-, iodo-) and their positions indicated by numbers. For example, CH₃CH₂Cl is chloroethane.
-
Double and Triple Bonds: Suffixes like "-ene" (for double bonds) and "-yne" (for triple bonds) are used, along with numbers indicating the position of the multiple bond. For example, CH₂=CHCH₃ is prop-1-ene.
Cyclic Compounds: Navigating Rings
Cyclic compounds require a different approach to naming:
-
Identify the parent ring: The ring with the most carbon atoms or the most complex structure.
-
Number the ring carbons: Start at a substituent and number consecutively around the ring, giving the lowest possible numbers to the substituents.
-
Name the substituents and their positions: Follow the same rules as for linear alkanes.
-
Combine the name of the ring and the substituents: For example, a cyclohexane ring with a methyl group at position 1 would be named 1-methylcyclohexane.
More Complex Compounds: Putting it All Together
Many compounds contain multiple functional groups and substituents. In these instances, a hierarchical system determines which functional group dictates the principal suffix and how other groups are incorporated as prefixes or secondary suffixes. IUPAC guidelines provide a detailed order of precedence for functional groups.
Inorganic Compounds: A Different Set of Rules
While organic chemistry focuses on carbon-containing compounds, inorganic chemistry encompasses all other substances. The nomenclature of inorganic compounds is also governed by IUPAC, but the rules are different. Key aspects include:
-
Binary Compounds: Composed of two elements. The less electronegative element is named first, followed by the more electronegative element with its ending changed to "-ide." For example, NaCl is sodium chloride.
-
Ternary Compounds: Composed of three or more elements. More complex rules apply, often involving Roman numerals to indicate oxidation states.
Conclusion: Mastering the Art of IUPAC Nomenclature
Mastering IUPAC nomenclature requires practice and a thorough understanding of the principles outlined here. It is a crucial skill for anyone working in chemistry or related fields. This detailed guide has provided a robust foundation for naming a wide range of organic and inorganic compounds. Remember to consult the official IUPAC guidelines for the most comprehensive and up-to-date information. By systematically applying the rules, you can confidently translate chemical structures into their precise and unambiguous IUPAC names and vice versa. The seemingly complex task of naming chemical compounds becomes a clear and logical process with dedicated study and practice. Through consistent application and familiarity with the rules and examples, you can unlock the power of chemical communication, fostering accuracy and clarity in the world of chemistry.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Tall Is 130 Cm In Feet
May 21, 2025
-
How Much Is 83 Kg In Stones
May 21, 2025
-
183 Cm To Inches And Feet
May 21, 2025
-
22 Lbs Is How Many Kg
May 21, 2025
-
122 Cm To Feet And Inches
May 21, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Iupac Name For The Following Compound . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.