What Ipv4 Address Class Has The Ip Address 221.1 2.3
Holbox
Mar 28, 2025 · 5 min read
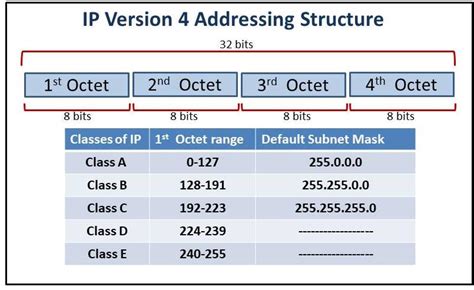
Table of Contents
- What Ipv4 Address Class Has The Ip Address 221.1 2.3
- Table of Contents
- What IPv4 Address Class Has the IP Address 221.1.2.3? A Deep Dive into IP Addressing
- Understanding IPv4 Address Classes
- Class A
- Class B
- Class C
- Class D
- Class E
- Determining the Class of 221.1.2.3
- Implications of a Class C Address
- Classless Inter-Domain Routing (CIDR) and its Impact
- Practical Applications and Considerations
- Conclusion: Beyond the Class System
- Latest Posts
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
What IPv4 Address Class Has the IP Address 221.1.2.3? A Deep Dive into IP Addressing
The internet, the vast network connecting billions of devices globally, relies on a system of unique addresses to identify and communicate between these devices. This system uses Internet Protocol version 4 (IPv4) addresses, a hierarchical structure that categorizes addresses into classes. Understanding these classes is crucial for network administration, troubleshooting, and security. This article will thoroughly explore IP address classes, focusing specifically on determining the class of the IP address 221.1.2.3 and delving into the implications of its class.
Understanding IPv4 Address Classes
IPv4 addresses are 32-bit numbers, typically represented in dotted decimal notation (e.g., 221.1.2.3). Historically, these addresses were divided into five classes: A, B, C, D, and E. Each class has a specific range of addresses and a different default subnet mask, dictating the number of networks and hosts that can be accommodated within that class. While the rigid classful addressing system is largely obsolete due to the introduction of Classless Inter-Domain Routing (CIDR), understanding these classes provides valuable context for understanding network architecture and troubleshooting.
Class A
- Address Range: 1.0.0.0 to 126.255.255.255
- Default Subnet Mask: 255.0.0.0
- Network Bits: 8
- Host Bits: 24
- Number of Networks: 127 (one is reserved for loopback)
- Number of Hosts per Network: 16,777,214
Class A addresses have a large number of available hosts, making them suitable for very large networks. The first octet (the first set of numbers before the first period) identifies the network address, while the remaining three octets identify the host within that network.
Class B
- Address Range: 128.0.0.0 to 191.255.255.255
- Default Subnet Mask: 255.255.0.0
- Network Bits: 16
- Host Bits: 16
- Number of Networks: 16,384
- Number of Hosts per Network: 65,534
Class B addresses offer a medium-sized range of hosts, suitable for medium-sized organizations or networks. The first two octets identify the network, and the last two octets identify the host.
Class C
- Address Range: 192.0.0.0 to 223.255.255.255
- Default Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.0
- Network Bits: 24
- Host Bits: 8
- Number of Networks: 2,097,152
- Number of Hosts per Network: 254
Class C addresses are designed for smaller networks, typically with a limited number of hosts. The first three octets identify the network, and the last octet identifies the host.
Class D
- Address Range: 224.0.0.0 to 239.255.255.255
- Default Subnet Mask: Not applicable
- Use: Multicasting
Class D addresses are not used for individual hosts but for multicast communication. Multicasting allows a single data packet to be sent to multiple recipients simultaneously.
Class E
- Address Range: 240.0.0.0 to 255.255.255.255
- Default Subnet Mask: Not applicable
- Use: Experimental and Reserved
Class E addresses are reserved for experimental purposes and are not generally used in standard network configurations.
Determining the Class of 221.1.2.3
Now, let's determine the class of the IP address 221.1.2.3. By looking at the first octet (221), we can see that it falls within the range of Class C addresses (192.0.0.0 to 223.255.255.255). Therefore, 221.1.2.3 is a Class C IP address.
Implications of a Class C Address
The fact that 221.1.2.3 is a Class C address has several implications:
-
Limited Number of Hosts: Class C networks can only accommodate a maximum of 254 hosts (256 - 2, as the network address and broadcast address are reserved). This means that the network associated with this IP address is relatively small.
-
Subnet Mask: The default subnet mask for a Class C address is 255.255.255.0. This mask defines the network portion and the host portion of the IP address. In this case, the network address would be 221.1.2.0, and the broadcast address would be 221.1.2.255.
-
Network Addressing: Efficient network planning is crucial with Class C addresses due to their limited host capacity. Subnetting, a technique that divides a larger network into smaller subnetworks, is often employed to maximize the utilization of Class C addresses.
-
Modern Networking: While the classification helps understand the historical context, modern network administrators largely use CIDR notation, which allows for more flexible and efficient network address allocation. CIDR replaces the rigid class boundaries with variable-length subnet masks (VLSM), allowing for more precise network planning.
Classless Inter-Domain Routing (CIDR) and its Impact
The original classful addressing scheme proved inefficient and led to the depletion of available IP addresses. CIDR addresses this issue by replacing the fixed subnet masks of the classful system with variable-length subnet masks. CIDR notation represents network addresses and subnet masks using a slash notation, such as 192.168.1.0/24. The number following the slash indicates the number of bits used for the network portion of the address. For example, a /24 represents a Class C network with a subnet mask of 255.255.255.0.
The use of CIDR allows for more efficient allocation of IP addresses. It enables organizations to utilize their IP address space more effectively, reducing wastage and extending the lifespan of available addresses.
Practical Applications and Considerations
Understanding IP address classes, even in the context of the largely superseded classful system, remains important for several reasons:
-
Troubleshooting Network Issues: When troubleshooting network connectivity issues, understanding the class of an IP address can help pinpoint potential problems related to network configuration and addressing. For example, an incorrectly configured subnet mask for a Class C network will result in connectivity problems.
-
Legacy Systems: Many older network systems still operate under the classful addressing scheme. Understanding these classes is essential for maintaining and troubleshooting these systems.
-
Security: Understanding network addressing and subnet masks is crucial for implementing effective network security measures such as firewalls and access control lists. Incorrectly configured subnet masks can create security vulnerabilities.
-
Network Design: While CIDR is the preferred method for modern network design, understanding the limitations and capacities of various IP address classes provides valuable context for network planning and design.
Conclusion: Beyond the Class System
While the IP address 221.1.2.3 falls under the Class C designation in the traditional classification system, it's crucial to remember that this classification is largely historical. Modern networking relies heavily on CIDR notation and VLSM for flexible and efficient IP address management. However, understanding the fundamentals of classful addressing remains essential for comprehending network architecture, troubleshooting issues, and appreciating the evolution of IP addressing. A strong grasp of these concepts provides a solid foundation for navigating the complexities of network administration and security. The move from classful to classless addressing highlights the dynamic nature of internet technology and the continuous adaptation necessary to meet the ever-growing demands of a globally interconnected world.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
The Narrower The Definition Of A Product
Apr 01, 2025
-
Final Goods And Services Refer To
Apr 01, 2025
-
A Decrease In The Interest Rate Will
Apr 01, 2025
-
Which Statements Reflect A Servant Leadership Mindset
Apr 01, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Describes The Plasma Membrane
Apr 01, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Ipv4 Address Class Has The Ip Address 221.1 2.3 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
