What Function Does The Post Perform In A Computer
Holbox
Mar 12, 2025 · 6 min read
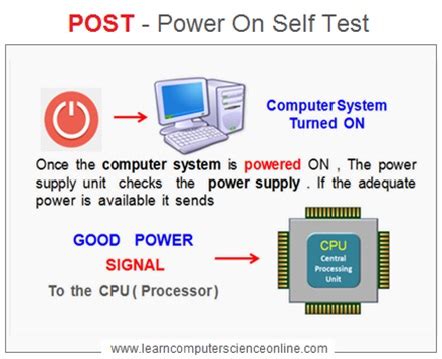
Table of Contents
- What Function Does The Post Perform In A Computer
- Table of Contents
- What Function Does the POST Perform in a Computer?
- The Importance of POST: Ensuring a Smooth Boot
- Stages of the POST Process: A Step-by-Step Breakdown
- 1. Power-On and Initialisation: The Awakening
- 2. BIOS/UEFI Initialization and Self-Test: The Firmware Check
- 3. Memory Test: The RAM Checkup
- 4. Peripheral Device Detection: Identifying the Hardware
- 5. CMOS Setup Check: Checking the BIOS Settings
- 6. Boot Device Selection: Choosing the Path
- POST Error Codes and Troubleshooting: Deciphering the Clues
- The Evolution of POST: From BIOS to UEFI
- Conclusion: The Silent Guardian of Your Computer
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
What Function Does the POST Perform in a Computer?
The Power On Self Test (POST) is a crucial process that occurs every time you turn on your computer. While often unseen and unheard, it's the unsung hero that ensures your system boots correctly and functions as expected. Understanding its function is key to troubleshooting computer problems and appreciating the complex architecture beneath the user interface. This comprehensive guide delves deep into the POST process, exploring its stages, importance, and potential issues.
The Importance of POST: Ensuring a Smooth Boot
The primary function of POST is to perform a series of diagnostic tests to verify that your computer's hardware is functioning correctly before the operating system (OS) loads. Think of it as a pre-flight check for your computer. Without a successful POST, your system won't even attempt to boot into your operating system – you'll be greeted with an error message, a blank screen, or nothing at all.
Key Objectives of POST:
- Hardware Initialization: POST initializes crucial hardware components, such as the CPU, memory (RAM), and storage devices (hard drive or SSD). This involves verifying that these components are present, correctly connected, and respond to commands.
- Memory Test: A significant portion of POST is dedicated to testing the RAM. This involves checking for errors in memory modules and ensuring that the system can access and use the available RAM correctly. Bad RAM can lead to system instability and crashes.
- Peripheral Device Detection: POST identifies and verifies the presence of peripheral devices like keyboards, mice, and graphic cards. It checks their connections and ensures they are functioning properly.
- BIOS/UEFI Check: POST verifies the integrity of the Basic Input/Output System (BIOS) or Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI), the firmware that manages the boot process. A corrupted BIOS can prevent the system from booting altogether.
- Boot Device Selection: Once the hardware checks are complete, POST identifies and selects the boot device – typically a hard drive or SSD containing the operating system. It then passes control to the bootloader on that device.
Stages of the POST Process: A Step-by-Step Breakdown
The POST process is not a monolithic event; it's a sequence of carefully orchestrated steps. While the exact sequence and details can vary depending on the system's BIOS/UEFI, the general stages are consistent across most systems.
1. Power-On and Initialisation: The Awakening
When you press the power button, the power supply unit (PSU) delivers power to the motherboard. The CPU's internal clock starts ticking, initiating the POST process. The CPU then communicates with the BIOS/UEFI chip, stored on a ROM chip on the motherboard. This firmware is the first program to run.
2. BIOS/UEFI Initialization and Self-Test: The Firmware Check
The BIOS/UEFI performs a self-test, checking its own integrity and configuration. This is crucial because any issues with the BIOS/UEFI itself will prevent the system from proceeding further. Errors at this stage often manifest as error codes displayed on the screen.
3. Memory Test: The RAM Checkup
Next, POST conducts a rigorous test of the system's RAM. This involves writing data to the RAM modules and then reading it back to verify accuracy. This process is repeated multiple times, testing different memory locations and patterns. Errors at this stage can result in memory errors, system crashes, or data corruption. The length of this test can vary depending on the amount of RAM and the sophistication of the memory test.
4. Peripheral Device Detection: Identifying the Hardware
After verifying the RAM, POST moves on to detecting and identifying connected peripheral devices. This includes the keyboard, mouse, hard drives, graphic card, and other expansion cards. It checks for the presence of these devices and their compatibility with the system. If a critical device, like a hard drive, is not detected, POST will usually halt and display an error message.
5. CMOS Setup Check: Checking the BIOS Settings
The CMOS (Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor) stores the BIOS settings, such as the boot order, date, and time. POST checks the CMOS settings for validity and consistency. Incorrect settings can prevent the system from booting.
6. Boot Device Selection: Choosing the Path
Finally, having completed the hardware and BIOS checks, POST identifies the boot device based on the BIOS/UEFI boot order settings. This is usually a hard drive or SSD containing the operating system. Once the boot device is selected, POST passes control to the bootloader on that device, initiating the operating system boot process.
POST Error Codes and Troubleshooting: Deciphering the Clues
If the POST process encounters a problem, it often displays error codes on the screen. These error codes provide crucial clues to identify the source of the issue. These codes can vary significantly depending on the motherboard manufacturer. Common error codes may indicate:
- Memory Errors: Errors related to RAM modules, indicating faulty or incompatible RAM.
- CPU Errors: Problems with the CPU itself, including overheating or faulty connections.
- Hard Drive Errors: Issues with the hard drive, such as a failing drive or a connection problem.
- BIOS Errors: Problems with the BIOS or UEFI firmware, often requiring a BIOS update or a replacement motherboard.
Troubleshooting Steps:
- Check Cables and Connections: Ensure all cables are securely connected to the motherboard, power supply, and peripherals.
- Visual Inspection: Look for any signs of damage to the hardware components.
- Reseat RAM Modules: Remove and reinsert the RAM modules to ensure proper contact.
- Test Components Individually: Try booting with only essential components connected to isolate the faulty part.
- Update BIOS/UEFI: If BIOS errors are suspected, updating the firmware might resolve the issue. However, this should be done carefully and only if you understand the process.
- Seek Professional Help: If you're unable to identify and resolve the issue, it's best to seek assistance from a qualified computer technician.
The Evolution of POST: From BIOS to UEFI
The POST process has evolved alongside computer technology. Older systems relied on the BIOS (Basic Input/Output System), a relatively simple firmware. Modern systems increasingly utilize UEFI (Unified Extensible Firmware Interface), a more sophisticated and feature-rich firmware. While the core function of POST remains the same, UEFI offers several advantages:
- Improved Security: UEFI provides enhanced security features, including Secure Boot, which helps protect against malware.
- Larger Disk Support: UEFI supports larger hard drives and SSDs than BIOS.
- GUI Interface: UEFI often provides a more user-friendly graphical interface, making it easier to manage system settings.
- Faster Boot Times: UEFI generally offers faster boot times compared to BIOS.
Despite these advancements, the underlying principles of POST—hardware initialization, diagnostics, and boot device selection—remain fundamental.
Conclusion: The Silent Guardian of Your Computer
The POST process is a critical stage in the boot sequence of any computer. While largely invisible to the average user, it performs a vital function, ensuring that the hardware is functioning correctly before the operating system loads. Understanding the stages of POST, potential errors, and troubleshooting techniques can significantly improve your ability to diagnose and resolve computer problems, ultimately saving time and frustration. From the initial power-on to the final handover to the operating system, POST is the silent guardian, working diligently in the background to keep your computer running smoothly. The next time you power on your computer, remember the intricate dance of the POST, the vital process that makes it all possible.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Function Does The Post Perform In A Computer . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.