Water Is An Example Of What Compound
Holbox
Apr 05, 2025 · 6 min read
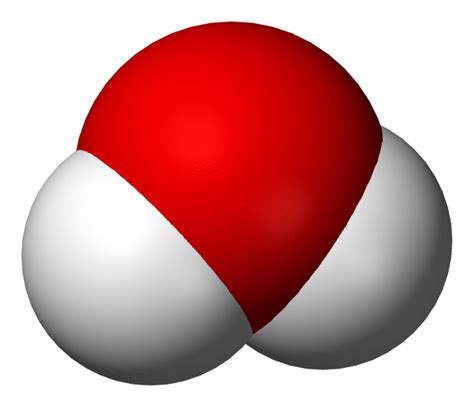
Table of Contents
- Water Is An Example Of What Compound
- Table of Contents
- Water: A Deep Dive into the Most Essential Compound
- Understanding Chemical Compounds
- Water: The Compound H₂O
- Covalent Bonding in Water
- The Unique Properties of Water
- Water's Importance Across Disciplines
- Biology: The Elixir of Life
- Chemistry: A Universal Solvent and Reactant
- Geology: Shaping the Earth's Surface
- Physics: Unique Physical Properties
- Environmental Science: A Precious Resource
- Water: Beyond the Basics
- Latest Posts
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
Water: A Deep Dive into the Most Essential Compound
Water. The very word evokes images of glistening oceans, cascading waterfalls, and the life-sustaining fluid within our own bodies. But beyond its visual appeal and vital role in life, water holds a fascinating scientific story as a quintessential example of a chemical compound. This article will explore the intricacies of water's chemical composition, its unique properties stemming from that composition, and its crucial significance across various fields of science and everyday life.
Understanding Chemical Compounds
Before diving into the specifics of water, let's establish a fundamental understanding of chemical compounds. A chemical compound is a substance formed when two or more chemical elements are chemically bonded together. This bonding involves the sharing or transfer of electrons between atoms, creating a new substance with properties distinctly different from its constituent elements. Unlike mixtures, where components retain their individual properties, compounds have unique properties emerging from the interaction of their bonded elements. The elements are combined in a fixed ratio, represented by its chemical formula. For instance, table salt (sodium chloride, NaCl) is a compound formed by the chemical bonding of sodium (Na) and chlorine (Cl) atoms in a 1:1 ratio.
Water: The Compound H₂O
Water, with its chemical formula H₂O, is a compound formed by the covalent bonding of two hydrogen (H) atoms and one oxygen (O) atom. This seemingly simple molecule harbors remarkable complexity and unique properties that are crucial for life on Earth.
Covalent Bonding in Water
The bonds between the hydrogen and oxygen atoms in water are covalent bonds. In a covalent bond, atoms share electrons to achieve a more stable electron configuration. Oxygen, being more electronegative than hydrogen (meaning it attracts electrons more strongly), pulls the shared electrons closer to itself. This unequal sharing of electrons results in a polar molecule, meaning one side of the molecule carries a slightly negative charge (the oxygen atom) and the other side carries a slightly positive charge (the hydrogen atoms). This polarity is fundamental to many of water's extraordinary properties.
The Unique Properties of Water
Water's unique properties are not simply the sum of its constituent elements' properties; they arise from its specific molecular structure and the interactions between water molecules. These properties are essential for life and shape many aspects of our planet.
1. High Specific Heat Capacity:
Water has an exceptionally high specific heat capacity. This means it takes a significant amount of energy to raise the temperature of water. This property moderates temperature fluctuations, preventing drastic changes that could be detrimental to living organisms. Coastal regions, for example, experience less extreme temperature variations than inland areas due to the moderating effect of the vast bodies of water.
2. High Heat of Vaporization:
Water also possesses a high heat of vaporization, meaning it requires a large amount of energy to convert liquid water into water vapor. This property is crucial for cooling mechanisms in living organisms, such as sweating in humans and transpiration in plants. The evaporation process absorbs a substantial amount of heat, thereby lowering the temperature.
3. Excellent Solvent:
Water's polarity makes it an excellent solvent, meaning it can dissolve many ionic and polar substances. This is because the slightly positive hydrogen atoms in water molecules attract negatively charged ions or parts of molecules, while the slightly negative oxygen atom attracts positively charged ions or parts of molecules. This ability to dissolve a wide range of substances is critical for biological processes, as it allows for the transport of nutrients and other essential molecules within organisms.
4. High Surface Tension:
Water molecules are strongly attracted to each other (cohesion) due to hydrogen bonding. This strong cohesive force results in a high surface tension, allowing water to form droplets and resist external forces. This property is crucial for capillary action, which allows water to move against gravity in plants and other systems.
5. Density Anomaly:
Unlike most substances, water's density is highest at 4°C (39°F). As water cools below this temperature, it becomes less dense, leading to ice floating on water. This unusual property prevents bodies of water from freezing solid from the bottom up, allowing aquatic life to survive even in freezing conditions.
Water's Importance Across Disciplines
The significance of water extends far beyond its simple chemical composition. Its unique properties and abundance on Earth contribute to its crucial role in various fields:
Biology: The Elixir of Life
Water is essential for all known forms of life. It acts as a solvent for biological reactions, a transport medium for nutrients and waste products, a participant in numerous metabolic processes, and a major component of cells and tissues. The properties discussed above, such as its high specific heat capacity and excellent solvent abilities, are directly linked to its life-sustaining role.
Chemistry: A Universal Solvent and Reactant
In chemistry, water serves as a ubiquitous solvent in many reactions. Its ability to dissolve a vast array of substances makes it indispensable in various chemical processes, from laboratory experiments to industrial applications. Furthermore, water itself participates in numerous chemical reactions, acting as both a reactant and a product. Hydrolysis, for instance, involves the breaking down of molecules using water.
Geology: Shaping the Earth's Surface
Water plays a pivotal role in shaping the Earth's geological features through processes like erosion, weathering, and sedimentation. Rivers carve canyons, glaciers sculpt mountains, and rainfall contributes to soil formation. Groundwater systems, aquifers, and even the movement of tectonic plates are all influenced by the presence and movement of water.
Physics: Unique Physical Properties
Water's anomalous density, high surface tension, and high specific heat capacity are subjects of ongoing research in physics. Understanding these properties is critical for applications ranging from fluid dynamics to material science. The behavior of water under different conditions of pressure and temperature is also a significant area of study.
Environmental Science: A Precious Resource
The availability and quality of water are crucial environmental concerns. Water pollution, scarcity, and climate change impacts on water resources are pressing issues demanding scientific attention and sustainable solutions. Understanding the chemistry and behavior of water is crucial for effective environmental management and conservation efforts.
Water: Beyond the Basics
The simple chemical formula H₂O belies the incredible complexity and significance of water. This ubiquitous compound, formed through the covalent bonding of hydrogen and oxygen, possesses exceptional properties that are essential for life and shape our planet. From its role as the universal solvent in biological processes to its influence on geological formations, water's impact is profound and far-reaching. As we continue to explore the intricacies of this remarkable substance, we gain a deeper appreciation for its fundamental role in shaping the world around us and our place within it. Further research into water's behavior under extreme conditions, its role in various ecosystems, and its potential for innovative applications will continue to unveil new facets of this seemingly simple, yet incredibly complex compound. The study of water is an ongoing journey of discovery, with implications that extend to nearly every aspect of scientific inquiry and human life. Understanding the properties of water is not just a scientific endeavor; it is critical for addressing global challenges related to sustainability, resource management, and the preservation of our planet's invaluable ecosystems.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
As An Equity Analyst With An Investment Management Company
Apr 09, 2025
-
They Soon Switched To A Model Based
Apr 09, 2025
-
Is Benzoic Acid Soluble In Hcl
Apr 09, 2025
-
Identify The Outcomes Of Portuguese Exploration Of West Africa
Apr 09, 2025
-
In The Short Run A Monopolistically Competitive Firm
Apr 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Water Is An Example Of What Compound . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.