To What Does The Term Stroma Refer
Holbox
Apr 01, 2025 · 5 min read
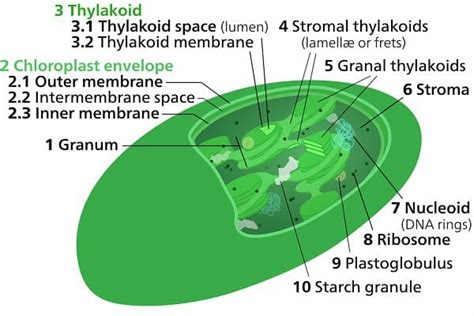
Table of Contents
- To What Does The Term Stroma Refer
- Table of Contents
- To What Does the Term Stroma Refer? A Comprehensive Guide
- Defining Stroma: The Supporting Structure of Life
- Stroma in Plants: The Backbone of Plant Life
- Chloroplast Stroma: The Site of the Calvin Cycle
- Stroma in Animals: A Diverse and Dynamic Landscape
- Stroma in Specific Animal Tissues: A Closer Look
- Stroma and Disease: A Complex Relationship
- Stroma and Regenerative Medicine: Harnessing the Power of Support
- Conclusion: The Unsung Hero of Biological Systems
- Latest Posts
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
To What Does the Term Stroma Refer? A Comprehensive Guide
The term "stroma" might sound like something out of a science fiction novel, but it's a fundamental component of many biological structures. Understanding what stroma is and its diverse roles across different tissues and organs is crucial for comprehending various biological processes, from plant growth to immune responses. This comprehensive guide delves into the multifaceted world of stroma, exploring its definition, functions, composition, and significance across various biological contexts.
Defining Stroma: The Supporting Structure of Life
In its broadest sense, stroma refers to the supportive tissue or framework of an organ or tissue. It's the "background" material, often contrasted with the parenchyma, which represents the functional cells responsible for the organ's or tissue's main activity. Think of it like the scaffolding of a building: the scaffolding (stroma) provides support and structure, while the actual living space and function (parenchyma) reside within.
The composition and function of stroma vary considerably depending on the tissue or organ it supports. This diversity makes a single, universally applicable definition challenging. However, the unifying characteristic is its role in providing structural support, facilitating communication between cells, and contributing to the overall microenvironment in which the functional cells operate.
Stroma in Plants: The Backbone of Plant Life
In plants, the stroma plays a vital role in photosynthesis and overall plant structure. It's specifically found within chloroplasts, the organelles responsible for photosynthesis.
Chloroplast Stroma: The Site of the Calvin Cycle
The chloroplast stroma is a fluid-filled space surrounding the thylakoid membranes. This is where the crucial Calvin cycle, the second stage of photosynthesis, takes place. The Calvin cycle converts carbon dioxide into glucose, the energy source for plant growth. The stroma contains various enzymes and molecules necessary for this process, including:
- Rubisco: The key enzyme responsible for carbon fixation.
- Other enzymes: Many other enzymes involved in carbohydrate synthesis and regulation.
- DNA and ribosomes: Chloroplasts possess their own genetic material (DNA) and protein synthesis machinery (ribosomes), enabling them to synthesize some of their own proteins.
- Starch granules: Excess glucose produced during photosynthesis is stored as starch granules within the stroma.
The structural integrity of the stroma is essential for the proper organization and function of the thylakoid membranes, ensuring efficient light harvesting and energy conversion.
Stroma in Animals: A Diverse and Dynamic Landscape
In animals, the stroma is far more heterogeneous, differing significantly between tissues and organs. It often consists of a complex mixture of:
-
Extracellular Matrix (ECM): A network of proteins and carbohydrates that provide structural support, regulate cell behavior, and guide cell migration. Key components include collagen, elastin, laminin, and various proteoglycans. The ECM's properties vary widely depending on the tissue type, contributing to the distinct characteristics of different organs.
-
Connective Tissue Cells: These cells are responsible for producing and maintaining the ECM. Common types include fibroblasts (in most connective tissues), chondrocytes (in cartilage), and osteocytes (in bone). They play a crucial role in tissue repair and remodeling.
-
Immune Cells: The stroma often houses various immune cells, including lymphocytes, macrophages, and mast cells. These cells play a vital role in immune surveillance and response, protecting the tissue from infection and damage. Their presence and activity within the stroma are crucial for maintaining tissue homeostasis and responding to injury or inflammation.
-
Blood Vessels and Nerves: The stroma also provides a framework for blood vessels and nerves, ensuring adequate oxygen and nutrient supply to the parenchyma and facilitating communication between different parts of the tissue.
Stroma in Specific Animal Tissues: A Closer Look
The nature of the stroma significantly impacts the function of different tissues:
- Connective Tissue: The stroma is the dominant component, providing support and connecting different tissues and organs.
- Muscle Tissue: The stroma supports the muscle fibers, ensuring proper alignment and function.
- Nervous Tissue: The stroma provides structural support for neurons and glial cells.
- Epithelial Tissue: The stroma underlies the epithelium, providing support and regulating its interactions with other tissues.
- Immune Organs (e.g., Lymph Nodes, Spleen): The stroma in these organs provides a specialized microenvironment that supports the development and function of immune cells. It plays a critical role in immune responses.
Stroma and Disease: A Complex Relationship
Changes in the stroma are frequently associated with various diseases. These changes can include:
- Inflammation: Inflammatory responses often lead to significant alterations in the ECM and the recruitment of immune cells to the stroma.
- Fibrosis: Excessive deposition of collagen and other ECM components in the stroma leads to scarring and tissue stiffening. This is a common feature of chronic diseases such as cirrhosis of the liver and pulmonary fibrosis.
- Cancer: The stroma plays a complex role in cancer development and progression. Cancer cells can manipulate the stroma to promote their growth, invasion, and metastasis. The stroma can also contribute to drug resistance and treatment failure.
- Wound Healing: The stroma plays a crucial role in wound healing, facilitating tissue regeneration and repair. Dysregulation of stromal processes can impair wound healing.
Stroma and Regenerative Medicine: Harnessing the Power of Support
The importance of the stroma is increasingly recognized in regenerative medicine. Scientists are investigating ways to manipulate the stroma to promote tissue repair and regeneration. This includes:
- Engineering artificial stromal matrices: Creating biocompatible scaffolds that mimic the natural stroma and provide support for tissue regeneration.
- Delivering therapeutic molecules to the stroma: Targeting the stroma with drugs or growth factors to promote tissue repair or inhibit disease progression.
- Cell-based therapies: Using stromal cells (e.g., mesenchymal stem cells) to regenerate damaged tissues.
Conclusion: The Unsung Hero of Biological Systems
The term "stroma" encompasses a wide range of supportive tissues and frameworks that are essential for the proper function of various biological systems. From the chloroplast stroma facilitating photosynthesis in plants to the complex animal stroma supporting and regulating tissue function, it’s a crucial component of life. Understanding its structure, composition, and role in health and disease is essential for advancing our knowledge in diverse fields such as plant biology, immunology, oncology, and regenerative medicine. Further research into the intricate workings of stroma promises to unlock new therapeutic strategies for treating a wide range of diseases and improving human health. The often-overlooked stroma, truly, is the unsung hero of biological systems.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Select The True Statements About The Citric Acid Cycle
Apr 04, 2025
-
An Example Of A Period Cost Is
Apr 04, 2025
-
Are Fetal Pig Toes Split Or Fused
Apr 04, 2025
-
Chain Ganglia Are Part Of The
Apr 04, 2025
-
Identify A Lateral Projection Of A Vertebra
Apr 04, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about To What Does The Term Stroma Refer . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
